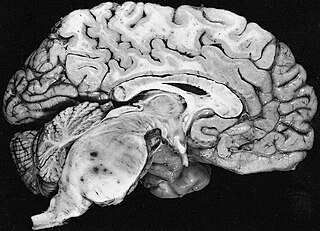
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.

A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. Gliomas comprise about 30 percent of all brain tumors and central nervous system tumours, and 80 percent of all malignant brain tumours.
Spinal tumors are neoplasms located in either the vertebral column or the spinal cord. There are three main types of spinal tumors classified based on their location: extradural and intradural. Extradural tumors are located outside the dura mater lining and are most commonly metastatic. Intradural tumors are located inside the dura mater lining and are further subdivided into intramedullary and extramedullary tumors. Intradural-intramedullary tumors are located within the dura and spinal cord parenchyma, while intradural-extramedullary tumors are located within the dura but outside the spinal cord parenchyma. The most common presenting symptom of spinal tumors is nocturnal back pain. Other common symptoms include muscle weakness, sensory loss, and difficulty walking. Loss of bowel and bladder control may occur during the later stages of the disease.

Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults but are also found in children.

An ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymomas is the fourth ventricle. Rarely, ependymomas can occur in the pelvic cavity.

Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur.

Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness.

Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. After glioblastomas, astrocytomas are the second most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord.

Oligoastrocytomas are a subset of brain tumors that present with an appearance of mixed glial cell origin, astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma. However, the term "Oligoastrocytoma" is now considered obsolete by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network stating "the term should no longer be used as such morphologically ambiguous tumors can be reliably resolved into astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas with molecular testing."

A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak incidence rates are childhood-onset at 5–14 years and adult-onset at 50–74 years. People may present with bitemporal inferior quadrantanopia leading to bitemporal hemianopsia, as the tumor may compress the optic chiasm. It has a point prevalence around two per 1,000,000. Craniopharyngiomas are distinct from Rathke's cleft tumours and intrasellar arachnoid cysts.

A blastoma is a type of cancer, more common in children, that is caused by malignancies in precursor cells, often called blasts. Examples are nephroblastoma, medulloblastoma, and retinoblastoma. The suffix -blastoma is used to imply a tumor of primitive, incompletely differentiated cells, e.g., chondroblastoma is composed of cells resembling the precursor of chondrocytes.

Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a brain tumor that occurs most frequently in children and teenagers. At Boston Children's Hospital, the average age at diagnosis is 12 years.
Neuro-oncology is the study of brain and spinal cord neoplasms, many of which are very dangerous and life-threatening. Among the malignant brain cancers, gliomas of the brainstem and pons, glioblastoma multiforme, and high-grade astrocytoma/oligodendroglioma are among the worst. In these cases, untreated survival usually amounts to only a few months, and survival with current radiation and chemotherapy treatments may extend that time from around a year to a year and a half, possibly two or more, depending on the patient's condition, immune function, treatments used, and the specific type of malignant brain neoplasm. Surgery may in some cases be curative, but, as a general rule, malignant brain cancers tend to regenerate and emerge from remission easily, especially highly malignant cases. In such cases, the goal is to excise as much of the mass and as much of the tumor margin as possible without endangering vital functions or other important cognitive abilities. The Journal of Neuro-Oncology is the longest continuously published journal in the field and serves as a leading reference to those practicing in the area of neuro-oncology.
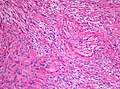
Fibrillary astrocytomas are a group of primary slow-growing brain tumors that typically occur in adults between the ages of 20 and 50.

Anaplastic astrocytoma is a rare WHO grade III type of astrocytoma, which is a type of cancer of the brain. In the United States, the annual incidence rate for anaplastic astrocytoma is 0.44 per 100,000 people.

Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma is a low-grade astrocytic brain tumor (astrocytoma) that arises within the ventricles of the brain. It is most commonly associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). Although it is a low-grade tumor, its location can potentially obstruct the ventricles and lead to hydrocephalus.

Astroblastoma is a rare glial tumor derived from the astroblast, a type of cell that closely resembles spongioblastoma and astrocytes. Astroblastoma cells are most likely found in the supratentorial region of the brain that houses the cerebrum, an area responsible for all voluntary movements in the body. It also occurs significantly in the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe, areas where movement, language creation, memory perception, and environmental surroundings are expressed. These tumors can be present in major brain areas not associated with the main cerebral hemispheres, including the cerebellum, optic nerve, cauda equina, hypothalamus, and brain stem.

Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered (DMG) is a fatal tumour that arises in midline structures of the brain, most commonly the brainstem, thalamus and spinal cord. When located in the pons it is also known as diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG).

Angiocentric glioma (AG) refers to a rare neuroepithelial tumor when the superficial brain malignant cells enclose the brain vessels, commonly found in children and young adults. Initially identified in 2005 by Wang and his team from the University of Texas, AG was classified as Grade I by 2007 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System due to its benign clinical behavior, low proliferation index, and curative properties. AG primarily affects children and young adults at an average initial diagnosis age of 16 years old. Over 85% AG patients experience intractable seizures since childhood, especially partial epilepsy.
Thalamic gliomas are very rare, deep-seated, generally high-grade glial neoplasms that form in the thalamus, representing 1–5% of all pediatric brain tumors. Because of their difficult to reach position, they are a unique and difficult challenge for neuro-oncologists and neurosurgeons.