| nicotinamidase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
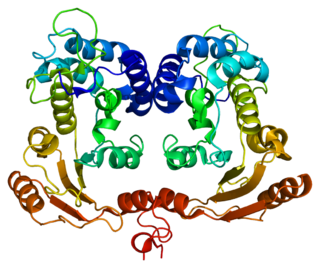
 Nicotinamidase monomer, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.5.1.19 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9033-32-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a nicotinamidase (EC 3.5.1.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- nicotinamide + H2O nicotinate + NH3
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are nicotinamide and H2O, whereas its two products are nicotinate and NH3.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is nicotinamide amidohydrolase. Other names in common use include nicotinamide deaminase, nicotinamide amidase, and YNDase. This enzyme participates in nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism.