
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.

An oxidizing agent is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent. In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens.
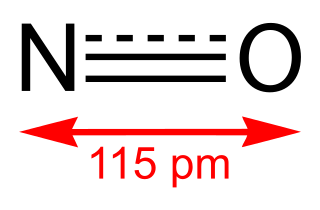
Nitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.

Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula C
2H
4O. It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.

Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.

Periodic acid is the highest oxoacid of iodine, in which the iodine exists in oxidation state +7. Like all periodates it can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula H5IO6 and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula HIO4.
Phosphorus oxoacid is a generic name for any acid whose molecule consists of atoms of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen. There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anions and organic groups are present in stable salts and esters. The most important ones — in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research — are the phosphoric acids, whose esters and salts are the phosphates.

Mesoxalic acid, also called oxomalonic acid or ketomalonic acid, is an organic compound with formula C3H2O5 or HO−(C=O)3−OH.

In chemistry, an amine oxide, also known as an amine N-oxide and N-oxide, is a chemical compound that contains the functional group R3N+−O−, an N/sO coordinate covalent bond with three additional hydrogen and/or hydrocarbon side chains attached to N. Sometimes it is written as R3N→O or, wrongly, as R3N=O.
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

Picolinic acid is an organic compound with the formula C5H4N(CO2H). It is a derivative of pyridine with a carboxylic acid (COOH) substituent at the 2-position. It is an isomer of nicotinic acid and isonicotinic acid, which have the carboxyl side chain at the 3- and 4-position, respectively. It is a white solid that is soluble in water.
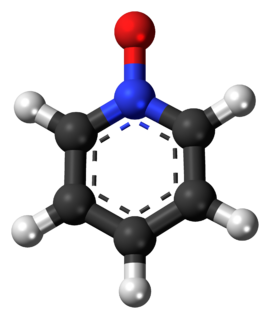
Pyridine-N-oxide is the heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H5NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine. It was originally prepared using peroxyacids as the oxidising agent. The molecule is planar. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. It also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry.

Sodium metaborate is a colorless solid chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with formula NaBO
2. The formula can be written also as Na
2O·B
2O
3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron.

Acetamiprid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C10H11ClN4. It is an odorless neonicotinoid insecticide produced under the trade names Assail, and Chipco by Aventis CropSciences. It is systemic and intended to control sucking insects (Thysanoptera, Hemiptera, mainly aphids) on crops such as leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, pome fruits, grapes, cotton, cole crops, and ornamental plants. It is also a key pesticide in commercial cherry farming due to its effectiveness against the larvae of the cherry fruit fly.

A seleninic acid is an organoselenium compound and an oxoacid with the general formula RSeO2H, where R ≠ H. It is a member of the family of organoselenium oxoacids, which also includes selenenic acids and selenonic acids, which are RSeOH and RSeO3H, respectively. The parent member of this family of compounds is methaneseleninic acid (CH3SeO2H), also known as methylseleninic acid or "MSA".

Nitrolic acids are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NO2)=NOH. They are prepared by the reaction of nitroalkanes with base and nitrite sources:

5-Ethyl-2-methylpyridine is an organic compound with the formula (C2H5)(CH3)C5H3N. One of several isomeric pyridines with this formula, this derivative is of interest because it is efficiently prepared from simple reagents and it is a convenient precursor to nicotinic acid, a form of vitamin B3. 5-Ethyl-2-methylpyridine is a colorless liquid.

Holmium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of holmium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Ho(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

















