
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word cave can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called exogene caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called endogene caves.

Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora, and for fungi, it is funga. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as biota. Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics.

The Kentucky cave shrimp is an eyeless, troglobite shrimp. It lives in caves in Barren County, Edmonson County, Hart County and Warren County, Kentucky. The shrimp's shell has no pigment; the species is nearly transparent and closely resembles its nearest relative, the Alabama cave shrimp.

A biodiversity action plan (BAP) is an internationally recognized program addressing threatened species and habitats and is designed to protect and restore biological systems. The original impetus for these plans derives from the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). As of 2009, 191 countries have ratified the CBD, but only a fraction of these have developed substantive BAP documents.

Pridhamsleigh Cavern is a cave on the outskirts of Ashburton, Devon, England. It is approximately 1.1 kilometres in length with a total depth of just over 50 metres including Prid II.

The Madison Cave isopod, Antrolana lira, is a freshwater, cave-dwelling crustacean species. It is in the family Cirolanidae and it is the only species of its genus Antrolana. This isopod can be found in flooded limestone caves and karst aquifers throughout the Great Appalachian Valley of Virginia and West Virginia. The Madison Cave isopod has been listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 1983 and as a threatened species under the United States Endangered Species Act since 1982. The species was named after the cave in which it was first discovered, Madison Saltpetre Cave. Very little is known about the life history and behavior of the Madison Cave isopod.

Cambarus zophonastes, also known as the Hell Creek Cave Crayfish, is named for its original location of discovery, Hell Creek Cave. It is also found in other similar habitats in Stone County and Marion County, Arkansas. These habitats include springs and caves such as Nesbitt Spring Cave in Stone County. C. zophanastes is critically endangered according to the IUCN. C. zophanastes is also protected by the ESA as an endangered species. Currently conservation efforts focus on monitoring populations, reducing disturbances, and monitoring water quality. More research has to be conducted to better understand and conserve the species.

Niphargus is by far the largest genus of its family, the Niphargidae, and the largest of all freshwater amphipod genera.
Troglocaris anophthalmus is a species of freshwater shrimp in the family Atyidae. It lives in karstic caves in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy and Slovenia. Although morphologically similar across its 500-kilometre (310 mi) range, molecular phylogenetics suggests that there are four or five cryptic lineages with more restricted ranges, although one such lineage does range unusually widely for a troglobite – over 300 kilometres (190 mi).

Troglocaris is a genus of freshwater shrimp in the family Atyidae. These stygobitic, whitish and eyeless shrimp are found in Southern Europe. Although locally very common, the small ranges of the individual species make them highly vulnerable to habitat loss, for example by water extraction. Their underground habitat is often extremely stable; for example, the Vipavska jama cave in Slovenia is home to a population of T. anophthalmus, and its water only varies from 10 °C (50 °F) in the winter to 11 °C (52 °F) in the summer. In some Dinaric caves, notably Vjetrenica, as many as three species may occur together.

The Kretschmarr Cave mold beetle is a small mold beetle.

Chirocephalus diaphanus is a widely distributed European species of fairy shrimp that lives as far north as Great Britain, where it is the only surviving species of fairy shrimp and is protected under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981. It is a translucent animal, about 0.5 in (13 mm) long, with reddened tips to the abdomen and appendages. The body comprises a head, a thorax bearing 11 pairs of appendages, and a seven-segmented abdomen. In males, the antennae are enlarged to form "frontal appendages", while females have an egg pouch at the end of the thorax.
Phylogeny of Malacostraca is the evolutionary relationships of the largest of the six classes of crustaceans, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members display a great diversity of body forms. Although the class Malacostraca is united by a number of well-defined and documented features, which were recognised a century ago by William Thomas Calman in 1904, the phylogenetic relationship of the orders which compose this class is unclear due to the vast diversity present in their morphology. Molecular studies have attempted to infer the phylogeny of this clade, resulting in phylogenies which have a limited amount of morphological support. To resolve a well-supported eumalacostracan phylogeny and obtain a robust tree, it will be necessary to look beyond the most commonly utilized sources of data.
Macromaxillocaris bahamaensis is a species of stenopodidean shrimp, the only species in the family Macromaxillocarididae. It is a troglobite, known only from an anchialine pool in a cave in the Bahamas. It differs from other stenopodideans by the enlargement of its third maxilliped.

The biodiversity of Wales is the wide variety of ecosystems, living organisms, and the genetic makeups found in Wales.
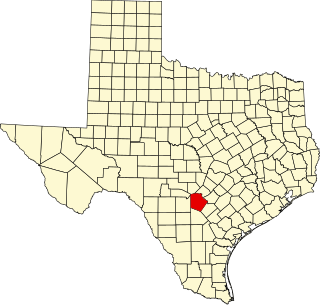
Rhadine infernalis is a species of troglobitic beetle of the family Carabidae. They are endemic to the county of Bexar, Texas. Within this county, R. infernalis has been found in 39 caves. There are 2 named subspecies of R. infernalis: R. infernalis infernalis and R. infernalis ewersi. There is a third possible subspecies that has not been officially described. R. infernalis was classified in 2000 as endangered under the IUCN Endangered Species Act of 1973, along with 8 other karst invertebrates in the same region. It has the widest known range of the endangered karst invertebrates.

Tayshaneta microps, synonym Neoleptoneta microps, is a rare species of spider in the family Leptonetidae known by the common name Government Canyon bat cave spider. It is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known to be found in two caves in Bexar County. It is a troglobite, an animal which spends its entire life in caves. It is one of nine Bexar County troglobites which were listed as endangered species in 2000.

The Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion(Tartarocreagris texana) is a small cave-dwelling arachnid of the family Neobisiidae. The species was originally assigned to the genus Microcreagris, and then reassigned to Austalillocregris before arriving at its current genus, Tartarocreagris. The Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion has a small geographic distribution, known to occur in only two caves in Travis County, Texas. Additionally, it is tentatively identified in two nearby caves in Texas, but more research is necessary to accurately define the range where the species lives. There is little known about the biology, life cycle, and life history of the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion due to a lack of research and study. Because of this, the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion is listed on the IUCN Red List as data deficient. Under the Endangered Species Act, the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion is listed as endangered. Recovery plans for the species focus mostly on preserving the karst ecosystem that the pseudoscorpions live in, especially including lessening human impacts on the environment.
An anchialine system is a landlocked body of water with a subterranean connection to the ocean. Depending on its formation, these systems can exist in one of two primary forms: pools or caves. The primary differentiating characteristics between pools and caves is the availability of light; cave systems are generally aphotic while pools are euphotic. The difference in light availability has a large influence on the biology of a given system. Anchialine systems are a feature of coastal aquifers which are density stratified, with water near the surface being fresh or brackish, and saline water intruding from the coast at depth. Depending on the site, it is sometimes possible to access the deeper saline water directly in the anchialine pool, or sometimes it may be accessible by cave diving.














