Related Research Articles
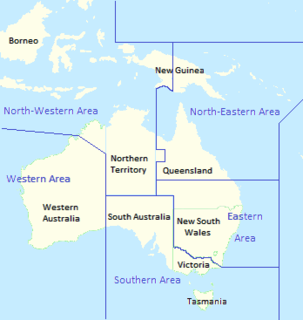
North-Eastern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. For most of its existence it controlled units based in central and northern Queensland as well as Papua New Guinea. It was formed in January 1942 from the eastern part of the former Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Townsville, Queensland, North-Eastern Area Command's responsibilities included air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its territory. Its flying units, equipped with fighters, reconnaissance bombers, dive bombers and transports, took part in the battles of Rabaul, Port Moresby and Milne Bay in 1942, and the landings at Hollandia and Aitape in 1944.

Air Commodore Francis William Fellowes (Frank) Lukis, CBE was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). A veteran of World War I, he first saw combat as a soldier in the Australian Imperial Force at Gallipoli. In 1917, Lukis transferred to the Australian Flying Corps and flew with No. 1 Squadron in the Middle East, where he was twice mentioned in despatches. A member of the Australian Air Corps following the war, he transferred to the fledgling RAAF in 1921, and became the first commanding officer of the newly re-formed No. 3 Squadron at RAAF Station Richmond, New South Wales, in 1925.

Air Vice Marshal George John William Mackinolty, OBE was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Commencing his service in the Australian Flying Corps (AFC) as a mechanic during World War I, he rose to become the RAAF's chief logistics officer for more than twenty years. Mackinolty was born in Victoria and joined the AFC in 1914. He first saw active duty the following year in the Middle East with No. 30 Squadron Royal Flying Corps. In 1916 he was mentioned in despatches and posted to No. 2 Squadron AFC. By the end of the war he had been commissioned a second lieutenant.

RAAF Command was the main operational arm of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. The command was formed in September 1942 and by April 1943 comprised 27 squadrons, including units from the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, as well as Australia. Coming under the operational authority of Allied Air Forces Headquarters in the South West Pacific Area, RAAF Command exercised control of its units through geographically based area commands in Australia and, later, New Guinea, as well as large mobile formations including the Australian First Tactical Air Force. The command reached a strength of 41 squadrons in October 1944. From the time of its establishment, until its disbandment in September 1945, it was led by Air Vice Marshal Bill Bostock.

Eastern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in May 1942, and controlled units located in New South Wales and southern Queensland. Headquartered in Sydney, Eastern Area Command's responsibilities included air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. Its flying units operated fighters, reconnaissance bombers, and dive bombers, and concentrated on convoy escort, maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare. The size of the area was such that the RAAF twice considered splitting it, but nothing came of this.

No. 4 Service Flying Training School was a flying training school of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in February 1941, and commenced flying the following month. Responsible for intermediate and advanced instruction of pilots under the Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS), the school was based at Geraldton, Western Australia, and operated Avro Anson aircraft. Two reserve squadrons were formed in response to the outbreak of war in the Pacific, though they never saw action. Flying activity was reduced towards the end of 1943, and the school was disbanded in May 1945, having graduated over 1,000 pilots. It re-formed as No. 87 Operational Base Unit, which was renamed Care and Maintenance Unit (CMU) Geraldton in May 1946. CMU Geraldton was disbanded in September 1947.

No. 1 Elementary Flying Training School was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) pilot training unit that operated during World War II. It was one of twelve elementary flying training schools employed by the RAAF to provide introductory flight instruction to new pilots as part of Australia's contribution to the Empire Air Training Scheme. The unit was established in November 1939 as No. 2 Flying Training School at Melbourne, Victoria. It was relocated to Parafield, South Australia, in December 1939 and renamed No. 1 EFTS the following month. Training activities relocated to Tamworth, New South Wales, in May 1944; the school was disbanded in December that year.

No. 1 Aircraft Depot (No. 1 AD) was a maintenance unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Formed in July 1921 at RAAF Point Cook, Victoria, it relocated to the nearby RAAF Laverton in March 1926. As well as servicing aircraft and other equipment, in its early years the depot supported survey flights in Australia and the Pacific region. It was also responsible for training maintenance staff.

Northern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in May 1941, and covered the whole of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Townsville, Queensland, Northern Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. In January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, it was divided into North-Western and North-Eastern Area Commands, to counter Japanese threats to northern Australia and Papua, respectively.

Northern Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Established in April 1944, it evolved from No. 9 Operational Group, which had been the RAAF's primary mobile formation in the South West Pacific theatre since September 1942, but had lately become a garrison force in New Guinea. Northern Command was headquartered initially at Milne Bay and then, from August 1944, in Madang. It conducted operations in New Guinea, New Britain, and Bougainville until the end of the war. Re-designated Northern Area in December 1945, it was headquartered in Port Moresby from March 1946 and disbanded in February 1947.

Central Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in March 1940, and covered the central portion of New South Wales. Headquartered at Sydney, Central Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. It was disbanded in August 1941 and control of its units taken over by other RAAF formations. Proposals in 1943–44 to raise a new Central Area Command did not come to fruition.

Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in January 1941, and controlled RAAF units located in Western Australia. Headquartered in Perth, Western Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. Its aircraft conducted anti-submarine operations throughout the war, and attacked targets in the Dutch East Indies during the Borneo campaign in 1945.

Area commands were the major operational and administrative formations of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) between 1940 and 1954. Established in response to the outbreak of World War II, they underpinned the Air Force's geographically based command-and-control system for the duration of the conflict and into the early years of the Cold War, until being superseded by a functional control system made up of Home, Training, and Maintenance Commands.

Southern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in March 1940, and initially controlled units located in Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia and southern New South Wales. Headquartered in Melbourne, Southern Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. From 1942 its operational responsibilities excluded New South Wales.

North-Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Its wartime sphere of operations included the Northern Territory, adjacent portions of Queensland and Western Australia, and the Dutch East Indies. The command was formed in January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, from the western part of Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Darwin, North-Western Area Command was initially responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries.

No. 8 Elementary Flying Training School was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) pilot training unit that operated during World War II. It was one of twelve elementary flying training schools employed by the RAAF to provide introductory flight instruction to new pilots as part of Australia's contribution to the Empire Air Training Scheme. No. 8 EFTS was established in September 1940 at Narrandera, New South Wales. Training ceased in December 1944 and the school was reduced to maintaining base infrastructure and aircraft. It was officially disbanded in June 1945 and renamed Care and Maintenance Unit (CMU) Narrandera. The CMU was disbanded in December 1947.

No. 4 (Maintenance) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was formed in Melbourne in September 1942 as part of a reorganisation of the air force that saw maintenance functions transferred from area commands to dedicated functional groups. In July 1947, No. 4 (Maintenance) Group was renamed Maintenance Group. The area command structure was superseded by a functional command system in October 1953, and Maintenance Group was re-formed as Maintenance Command.

No. 1 (Training) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was formed in Melbourne in August 1941 as part of a reorganisation of the air force, and was disbanded after the war in January 1946.
No. 2 (Training) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was formed in Sydney in August 1941 as part of a reorganisation of the air force, and was disbanded after the war in March 1946.

The Air Board, also known as the Administrative Air Board, or the Air Board of Administration, was the controlling body of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) from 1921 to 1976. It was composed of senior RAAF officers as well as some civilian members, and chaired by the Chief of the Air Staff (CAS). The CAS was the operational head of the Air Force, and the other board members were responsible for specific areas of the service such as personnel, supply, engineering, and finance. Initially based in Melbourne, the board relocated to Canberra in 1961.
References
- Citations
- ↑ Ashworth (2000), pp. 134–135
- 1 2 Ashworth (2000), p. 135
- ↑ "Death of Air Commodore D.E.L. Wilson". The Armidale Express and New England General Advertiser . National Library of Australia. 1 September 1950. p. 8. Retrieved 22 August 2015.
- ↑ Gillison (1962), p. 479
- ↑ Ashworth (2000), p. 286
- ↑ "Order of Battle – Air Force". Department of Veterans' Affairs. Archived from the original on 5 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2015.
- Works consulted
- Ashworth, Norman (2000). How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One – Narrative. Canberra: RAAF Air Power Studies Centre. ISBN 978-0-642-26550-0.
- Gillison, Douglas (1962). Australia in the War of 1939–1945: Series Three (Air) Volume I – Royal Australian Air Force 1939–1942. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 2000369.