Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communication channel. This allows several users to share a band of frequencies. To permit this without undue interference between the users, CDMA employs spread spectrum technology and a special coding scheme.
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported through a single cable to customers. Since each carrier occupies a different frequency, the channels do not interfere with each other. At the destination end, the carrier signal is demodulated to extract the information bearing modulation signal.
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission and a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, used in applications such as digital television and audio broadcasting, DSL internet access, wireless networks, power line networks, and 4G/5G mobile communications.

In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is an analog of the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal at a much higher frequency.
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflection from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings. When the same signal is received over more than one path, it can create interference and phase shifting of the signal. Destructive interference causes fading; this may cause a radio signal to become too weak in certain areas to be received adequately. For this reason, this effect is also known as multipath interference or multipath distortion.

A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing.

In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel.
In signal processing, a filter bank is an array of bandpass filters that separates the input signal into multiple components, each one carrying a single frequency sub-band of the original signal. One application of a filter bank is a graphic equalizer, which can attenuate the components differently and recombine them into a modified version of the original signal. The process of decomposition performed by the filter bank is called analysis ; the output of analysis is referred to as a subband signal with as many subbands as there are filters in the filter bank. The reconstruction process is called synthesis, meaning reconstitution of a complete signal resulting from the filtering process.

Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users. This allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users.

In mathematics, a wavelet series is a representation of a square-integrable function by a certain orthonormal series generated by a wavelet. This article provides a formal, mathematical definition of an orthonormal wavelet and of the integral wavelet transform.
Multi-carrier code-division multiple access (MC-CDMA) is a multiple access scheme used in OFDM-based telecommunication systems, allowing the system to support multiple users at the same time over same frequency band.
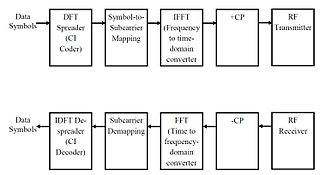
Carrier Interferometry(CI) is a spread spectrum scheme designed to be used in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication system for multiplexing and multiple access, enabling the system to support multiple users at the same time over the same frequency band.
IEEE 802.11a-1999 or 802.11a was an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless local network specifications that defined requirements for an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system. It was originally designed to support wireless communication in the unlicensed national information infrastructure (U-NII) bands as regulated in the United States by the Code of Federal Regulations, Title 47, Section 15.407.
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended throughput to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s. This specification under the marketing name of Wi-Fi has been implemented all over the world. The 802.11g protocol is now Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard, and Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2012 standard.

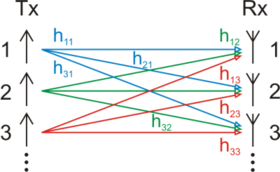
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO, is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11ac, HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification.
Binary offset carrier modulation was developed by John Betz in order to allow interoperability of satellite navigation systems. It is currently used in the US GPS system, Indian IRNSS system and in Galileo and is a square sub-carrier modulation, where a signal is multiplied by a rectangular sub-carrier of frequency equal to or greater than the chip rate. Following this sub-carrier multiplication, the spectrum of the signal is divided into two parts, therefore BOC modulation is also known as a split-spectrum modulation. Their major advantages are, that one can shape the spectrum to allow inter-system-compatibility and better theoretically achievable tracking capabilities, due to higher frequencies if downmixed to the complex baseband. On the other hand, a huge variety of different implementations or instantiations was setup, making it difficult to get the whole picture. Early publications dealing with that topic usually do not include matched filters for pulse shaping as well as the concept of complex Gaussian noise - which is very often not treated correctly - to yield a mathematically consistent baseband description, that although complicated looking, models the physics correctly. I.e. if these standards are not treated correctly, theoretical results are not reliable. This is independent of the media and the peer-review and the person, who published it.
Multiple-input, multiple-output orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) is the dominant air interface for 4G and 5G broadband wireless communications. It combines multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) technology, which multiplies capacity by transmitting different signals over multiple antennas, and orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), which divides a radio channel into a large number of closely spaced subchannels to provide more reliable communications at high speeds. Research conducted during the mid-1990s showed that while MIMO can be used with other popular air interfaces such as time-division multiple access (TDMA) and code-division multiple access (CDMA), the combination of MIMO and OFDM is most practical at higher data rates.
Carrier frequency offset (CFO) is one of many non-ideal conditions that may affect in baseband receiver design. In designing a baseband receiver, we should notice not only the degradation invoked by non-ideal channel and noise, we should also regard RF and analog parts as the main consideration. Those non-idealities include sampling clock offset, IQ imbalance, power amplifier, phase noise and carrier frequency offset nonlinearity.
IQ imbalance is a performance-limiting issue in the design of a class of radio receivers known as direct conversion receivers. These translate the received radio frequency signal directly from the carrier frequency to baseband using a single mixing stage.

Vadym Slyusar – Soviet and Ukrainian scientist, Professor, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Honored Scientist and Technician of Ukraine, founder of tensor-matrix theory of digital antenna arrays (DAAs), N-OFDM and other theories in fields of radar systems, smart antennas for wireless communications and digital beamforming.