Related Research Articles

The Globigerinina is a suborder of foraminiferans that are found as marine plankton. They produce hyaline calcareous tests, and are known as fossils from the Jurassic period onwards. The group has included more than 100 genera and over 400 species, of which about 30 species are extant. One of the most important genera is Globigerina; vast areas of the ocean floor are covered with Globigerina ooze, dominated by the shells of planktonic forms.

The Allogromiida is an order of single-chambered, mostly organic-walled foraminiferans, including some that produce agglutinated tests (Lagynacea). Genetic studies indicate that some foraminiferans with agglutinated tests, previously included in the Textulariida or as their own order Astrorhizida, may also belong here. Allogromiids produce relatively simple tests, usually with a single chamber, similar to those of other protists such as Gromia. They are found as both marine and freshwater forms, and are the oldest forms known from the fossil record.

The Fusulinida is an extinct order within the Foraminifera in which the tests are traditionally considered to have been composed of microgranular calcite. Like all forams, they were single-celled organisms. In advanced forms the test wall was differentiated into two or more layers. Loeblich and Tappan, 1988, gives a range from the Lower Silurian to the Upper Permian, with the fusulinid foraminifera going extinct with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. While the latter is true, a more supported projected timespan is from the Mid-Carboniferous period.

The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular.

The Textulariida are an order of foraminifera that produce agglutinated shells or tests. An agglutinated test is one made of foreign particles glued together with an organic or calcareous cement to form an external shell on the outside of the organism. Commonly, the order had been made up of all species of Foraminifera with these types of shells, but genetic studies indicate these organisms do not form an evolutionary group, and several superfamilies in the order have been moved to the order Allogromiida. The remaining forms are sometimes divided into three orders: the Trochamminida and Lituolida, which have organic cement, and the Textulariida sensu stricto, which use a calcareous cement. All three orders or superfamilies are known as fossils from the Cambrian onwards.
The Moravamminacea is a superfamily of foraminifera within Fusulinida that comprises genera in which the proloculus is followed by a coiled or straight second chamber, and in which periods of growth result in partial or incipient septa. Contains three families, Caligellidae, Moravamminidae, and Paratickenellidae, with an overall range from the upper Silurian to the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian).

The Geintizinacea comprises a superfamily of Upper Devonian to Upper Permian uniserial fusulinids, the chamber walls consisting of a dark microgranular inner layer and radially fibrous outer layer. Advanced forms show secondary lateral thickening
The Fusulinidae is a family of fusulinacean foraminifera from the upper Carboniferous to the Upper Permian (Guadalupian), tests of which are fusiform to subcylindrical with walls of two to four layers. Are planispirally coiled throughout or with early whorls at a distinct angle to the later plane of coiling. Septa, flat to well fluted; tunnel, single; chomata variable in development.
Verbeekinidae are a family of large fusulinaceans characterized by subspherical, planispirally coiled tests and a long coiling axis. The wall is composed of a dense outer tectum and inner alveolar keriotheca. They are most prominent in Japan and Southeast Asia.

Globigerinoidea is a superfamily of free-living, calcareous, planktonic foraminiferal protists that have lived in the open ocean since the Eocene. It is part of the suborder Globigerinina.
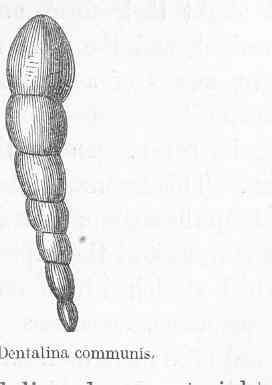
Lagenida is an order of benthic foraminiferal protists in which the tests (shells) are monolamellar, with walls composed of optically and ultra-structurally radiate calcite, with the crystallographic c-axes perpendicular to the surface. Lagenids first appear in the Upper Silurian and continue to the Recent. They are currently divided into two superfamilies, the older Robuloidacea which range from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) and the younger Nodosariacea, ranging from the Permian to Recent.
Nodosariacea is one of two superfamilies making up the foraminiferal order Lagenida. The other being the Robuloidacea. Of these two Nodosariacea is the more advanced, as well as being the younger.
Involutinida is an order of foraminifera included in the Spirillinata found in the fossil record from the early Permian to early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian).

Cibicides is a genus of cosmopolitan benthic foraminifera known from at least as far back as the Paleocene that extends down to the present.
Discorbis is a genus of benthic Foraminifera, that made its first appearance during the Eocene. Its present distribution is cosmopolitan.
Rosalina is a genus of foraminifera included in the rotaliid family Rosalinidae.
Neoconorbina is a genus of recent (Holocene) discorbacean foraminifers related to Rosalina with a low conical trochoidal test, circular in outline. The conical side is the spiral side, on which all three whorls are visible, the final chamber taking up most of the periphery. The umbilical side is flat to concave. exposing only the three to four chambers of the final whorl around an open umbilicus. Chambers on the umbilical side have triangular to platelike umbilical extensions as with other rasalinids. The wall of is calcite, finely and densely perforate on the spiral side, more coarsely perforate on the umbilical side; surface smooth; aperture at the umbilical margin of the chamber, beneath the platelike extension, or folium.
The Hormosinacea is a superfamily of agglutinated foraminifera in the Textulariida, with a range that extends from the Middle Ordovician, that unites seven families characterized by multilocular tests,, in a uniserial arrangement.

Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera.
Alfred R. Loeblich Jr (1914–1994) was an American micropaleontologist. He was married to Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich and the two co-authored a number of important works on the Foraminifera and related organisms.
References
- Loeblich, Alfred R.; Tappan, Helen (1964). Moore, R.C. (ed.). Protista 2: Sarcodina Chiefly "Thecamoebians" and Foraminiferida. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Vol. C (5th ed.). Geological Society of America. ISBN 978-0-8137-3003-5.
- A. Loeblich & H. Tappan,1988. Forminiferal Genera and their Classification. e-book