| Rotaliida Temporal range: Middle Triassic - present, | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ammonia beccarii (Rotaliidae) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Sar |
| Clade: | Rhizaria |
| Phylum: | Retaria |
| Subphylum: | Foraminifera |
| Class: | Globothalamea |
| Subclass: | Rotaliana |
| Order: | Rotaliida Lankester, 1885 |
| Suborders and superfamilies | |
See text | |
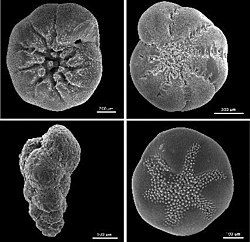
The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular.
Contents
In form, rotaliid tests are typically enrolled, but may be reduced to biserial or uniserial, or may be encrusting with proliferated chambers. Chambers may be simple or subdivided by secondary partitions; the surface is smooth, papillate, costate, striate, or cancellate; the aperture is simple or with an internal toothplate, entosolenian tube, or hemicylindrical structure; it may have an internal canal or stolen systems.
Rotaliids are primarily oceanic benthos, although some are common in shallower estuarine waters. They also include many important fossils, such as the nummulitids.