
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria.

The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many foraminifera and radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, Guttulinopsis vulgaris, a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon.
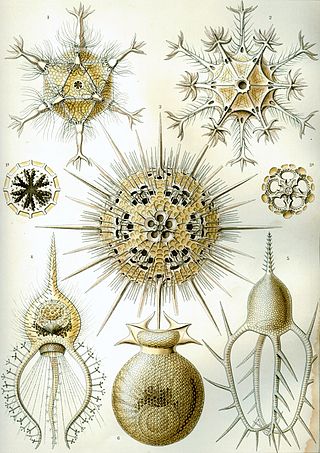
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.

Monadofilosa is a grouping of Cercozoa. These organisms are single-celled amoeboid protists.

Thecofilosea is a class of unicellular testate amoebae belonging to the phylum Cercozoa. They are amoeboflagellates, organisms with flagella and pseudopodia, distinguished from other cercozoa by their scale-lacking test composed of organic material. They are closely related to the Imbricatea, a group of testate amoebae with tests composed of inorganic silica scales.

The spongomonads are a group of flagellated protists in the phylum Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they compose the family Sarcomonadidae and order Sarcomonadida. They were originally placed among the Reticulofilosa, but were later transferred to Monadofilosa. It includes only two genera:

The sarcomonads or class Sarcomonadea are a group of amoeboid biciliate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are characterized by a propensity to move through gliding on their posterior cilium or through filopodia, a lack of scales or external theca, a soft cell surface without obvious cortical filamentous or membranous skeleton, two cilia without scales or hairs, tubular mitochondrial cristae, near-spherical extrusomes, and a microbody attached to the nucleus.
Paracercomonas is a genus of rhizaria.
Proleptomonas is a genus of coprophilic protists, containing the single species Proleptomonas faecicola. It belongs to the phylum Cercozoa, although it was previously considered the only free-living kinetoplastid. It is the only member of family Proleptomonadidae.

Katabia is a genus of soil-dwelling heterotrophic flagellate cercozoans containing the single species Katabia gromovi, and the only member of family Katabiidae.
Eocercomonas is a genus of cercozoa.
Neocercomonas is a protist genus of the order Cercomonadida. It consists of single-celled bacteriophagous organisms that usually live on or nearby terrestrial plants, both above and belowground. Species are biflagellate and may grow up to 60 micrometers long, with a trailing tail-like mass of protoplasm at their posterior end and a pair of roots connecting their posterior flagellum to the cytoskeleton.
The paracercomonads are a group of cercozoan protists. Taxonomically, they comprise the family Paracercomonadidae, order Paracercomonadida and subclass Paracercomonada. Due to their morphological similarities to the cercomonads, members of this family were grouped with Cercomonas and similar taxa from the beginning. However, their similarities are due to convergent evolution.

Ventrifilosa is a highly diverse group of phagotrophic protists that glide through their flagella and emit filose pseudopods from their ventral side for feeding. Because of their mixture of amoeba and flagellate characteristics, they are amoeboflagellates. Members of this group are the Imbricatea, Sarcomonadea and Thecofilosea.
Cryptofilida is an order of small heterotrophic protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are filose amoebae that lack cilia and gliding, and are instead characterized by movement through branching or unbranched granular filopodia that are appressed to the substrate during their feeding.

The glissomonads are a group of bacterivorous gliding flagellated protists that compose the order Glissomonadida, in the amoeboflagellate phylum Cercozoa. They comprise a vast, largely undescribed diversity of soil and freshwater organisms. They are the sister group to cercomonads; the two orders form a solid clade of gliding soil-dwelling flagellates called Pediglissa.
Pediglissa is a subclass of phagotrophic protists that inhabit soil or freshwater habitats. They were defined in 2018 according to phylogenetic analyses that showed a clade containing the orders Cercomonadida and Glissomonadida. They're the sister group of Paracercomonadida.

Viridiraptoridae, previously known as clade X, is a clade of heterotrophic protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They're a family of glissomonads, a group containing a vast, mostly undescribed diversity of soil and freshwater organisms.
The pansomonads, suborder Pansomonadina, are a group of heterotrophic protists that belong to the phylum Cercozoa. Some of them are helioflagellates, with characteristics of heliozoans and amoebo-flagellates.

An amoeboflagellate is any eukaryotic organism capable of behaving as an amoeba and as a flagellate at some point during their life cycle. Amoeboflagellates present both pseudopodia and at least one flagellum, often simultaneously.










