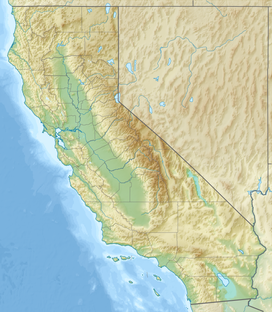
Inyo County is a county in the eastern central part of the U.S. state of California, located between the Sierra Nevada and the state of Nevada. In the 2020 census, the population was 19,016. The county seat is Independence. Inyo County is on the east side of the Sierra Nevada and southeast of Yosemite National Park in Central California. It contains the Owens River Valley; it is flanked to the west by the Sierra Nevada and to the east by the White Mountains and the Inyo Mountains. With an area of 10,192 square miles (26,397 km2), Inyo County is the second-largest county by area in California, after San Bernardino County. Almost one-half of that area is within Death Valley National Park. However, with a population density of 1.8 people per square mile, it also has the second-lowest population density in California, after Alpine County.

The Ansel Adams Wilderness is a wilderness area in the Sierra Nevada of California, United States. The wilderness spans 231,533 acres (93,698 ha); 33.9% of the territory lies in the Inyo National Forest, 65.8% is in the Sierra National Forest, and the remaining 0.3% covers nearly all of Devils Postpile National Monument. Yosemite National Park lies to the north and northwest, while the John Muir Wilderness lies to the south.

The Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest (HTNF) is the principal U.S. National Forest in the U.S. state of Nevada, and has a smaller portion in Eastern California. With an area of 6,289,821 acres (25,454.00 km2), it is the largest U.S. National Forest outside of Alaska.

The John Muir Wilderness is a wilderness area that extends along the crest of the Sierra Nevada of California for 90 miles (140 km), in the Inyo and Sierra National Forests. Established in 1964 by the Wilderness Act and named for naturalist John Muir, it encompasses 652,793 acres (2,641.76 km2). The wilderness lies along the eastern escarpment of the Sierra from near Mammoth Lakes and Devils Postpile National Monument in the north, to Cottonwood Pass near Mount Whitney in the south. The wilderness area also spans the Sierra crest north of Kings Canyon National Park, and extends on the west side of the park down to the Monarch Wilderness.

The Inyo Mountains are a short mountain range east of the Sierra Nevada in eastern California in the United States. The range separates the Owens Valley to the west from Saline Valley to the east, extending for approximately 70 miles (110 km) south-southeast from the southern end of the White Mountains, from which they are separated by Westgard Pass, to the east of Owens Lake.

The Kingston Range, sometimes called the Kingston Mountains, is located in Inyo and San Bernardino counties in the Mojave Desert in eastern California. The range reaches a height of 7,323 feet (2,232 m) above sea level at Kingston Peak.

State Route 190 is a state highway in the U.S. state of California that is split into two parts by the Sierra Nevada. The western portion begins at Tipton at a junction with State Route 99 and heads east towards Porterville before ending at Quaking Aspen in the Sequoia National Forest. The eastern portion begins at US 395 at Olancha, heads east through Death Valley National Park, and ends at State Route 127 at Death Valley Junction. The 43.0-mile (69.2 km) portion over the Sierra Nevada remains unconstructed, and the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) has no plans to build it through the wilderness areas. SR 190 is a National Scenic Byway known as the Death Valley Scenic Byway.

The Resting Spring Range is found in the eastern Mojave Desert of California near the Nevada state line in the United States. The range lies in a generally north–south direction to the west of the Nopah Range and southeast of the Amargosa Range and Greenwater Range.
In 1989 the U.S. Government enacted the Nevada Wilderness Bill, expanding the one existing Wilderness Area (Jarbidge) and creating thirteen new areas. The estimated total of 733,400 acres (296,800 ha) was over eleven times the area that had previously been under wilderness protection.
Emigrant Pass may refer to:

The Eldorado Mountains, also called the El Dorado Mountains, are a north-south trending mountain range in southeast Nevada bordering west of the south-flowing Colorado River; the endorheic Eldorado Valley borders the range to the west, and the range is also on the western border of the Colorado River's Black Canyon of the Colorado, and El Dorado Canyon on the river. The range is 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada; and the Eldorado Mountains connect with the Highland and Newberry mountains.

The Kiavah Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located in the Mojave Desert, Scodie Mountains, and southern Sierra Nevada in Kern County, California, United States. California State Route 178 connects the town of Lake Isabella to State Highway 14 in the east, crossing Walker Pass at the north boundary of the wilderness.

The Sacatar Trail Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located 20 miles (32 km) northwest of Ridgecrest, California USA. It was created in 1994 with the passage of the California Desert Protection Act - Public Law 103-433 - and is managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The wilderness is 51,900 acres (210 km2) in size and protects portions of the southern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range.
The South Sierra Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area in the Southern Sierra Nevada, in eastern California. It is located 65 miles (105 km) northeast of Bakersfield, and is southwest of Owens Lake and Olancha.
The Piper Mountain Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located in the White Mountains 20 miles (32 km) northeast of Big Pine, California in Inyo County, California.

The Chimney Peak Wilderness is a 13,134-acre (53.15 km2) wilderness area located 20 miles (32 km) northwest of Ridgecrest, in southeastern Tulare County, California.
The Mesquite Mountains are a mountain range in eastern San Bernardino County, California, near the border with Nevada. They are north of Interstate 15 in California and southeast of Death Valley.

Peachella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of average size. It lived during the Toyonian stage, 516 to 513 million years ago, in what is today the southwestern United States. It can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by its club-like genal spines.
The protected areas of the Sierra Nevada, a major mountain range located in the U.S. states of California and Nevada, are numerous and highly diverse. Like the mountain range itself, these areas span hundreds of miles along the length of the range, and over 14,000 feet of elevation from the lowest foothills to the summit of Mount Whitney.

Nopah Peak is the highest named mountain in the Nopah Range, a mountain range in Inyo County, California, in the Mojave Desert just west of the state border with Nevada. The peak has an elevation of 6,365 feet and a topographic prominence of 628 ft (191 m). It boasts steep escarpments to both east and west, rising more than 3,000 ft (914 m) in approximately 0.75 miles from the desert floor of Chicago Valley to the west and a drop-off almost as steep to the east.