Death Valley National Park is an American national park that straddles the California–Nevada border, east of the Sierra Nevada. The park boundaries include Death Valley, the northern section of Panamint Valley, the southern section of Eureka Valley and most of Saline Valley.

Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the hottest place on Earth during summer.
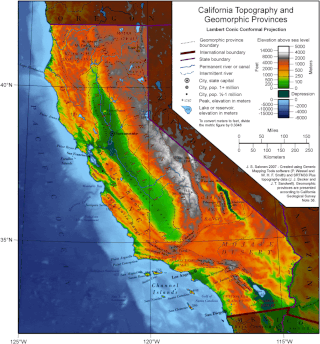
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states.

The Mojave Desert is a desert in the rain shadow of the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and Transverse Ranges in the Southwestern United States. Named for the indigenous Mohave people, it is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada, with small portions extending into Arizona and Utah.

The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, except for the headwaters and several bedrock gorges in the lower reaches.

The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at 11,503 feet (3,506 m) at San Gorgonio Mountain – the tallest peak in Southern California. The San Bernardinos form a significant region of wilderness and are popular for hiking and skiing.

The Amargosa River is an intermittent waterway, 185 miles (298 km) long, in southern Nevada and eastern California in the United States. The Amargosa River is one out of two rivers located in the California portion of the Mojave Desert with perennial flow. It drains a high desert region, the Amargosa Valley in the Amargosa Desert northwest of Las Vegas, into the Mojave Desert, and finally into Death Valley where it disappears into the ground aquifer. Except for a small portion of its route in the Amargosa Canyon in California and a small portion at Beatty, Nevada, the river flows above ground only after a rare rainstorm washes the region. A 26-mile (42 km) stretch of the river between Shoshone and Dumont Dunes is protected as a National Wild and Scenic River. At the south end of Tecopa Valley the Amargosa River Natural Area protects the habitat.

The Panamint Range is a short rugged fault-block mountain range in the northern Mojave Desert, within Death Valley National Park in Inyo County, eastern California. Dr. Darwin French is credited as applying the term Panamint in 1860 during his search for the fabled Gunsight Lode. The orographic identity has been liberally applied for decades to include other ranges.
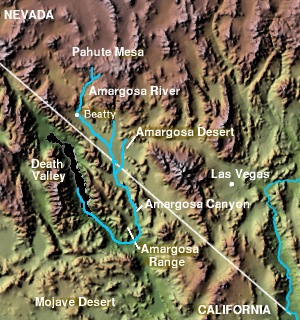
The Amargosa Valley is the valley through which the Amargosa River flows south, in Nye County, southwestern Nevada and Inyo County in the state of California. The south end is alternately called the "Amargosa River Valley'" or the "Tecopa Valley." Its northernmost point is around Beatty, Nevada and southernmost is Tecopa, California, where the Amargosa River enters into the Amargosa Canyon.

The Chuckwalla Mountains are a mountain range in the transition zone between the Colorado Desert—Sonoran Desert and the Mojave Desert, climatically and vegetationally, in Riverside County of southern California.

The Chemehuevi Mountains are a mountain range that are found at the southeast border of San Bernardino County in southeastern California and are adjacent the Colorado River. Located south of Needles, California and northwest of the Whipple Mountains, the mountains are oriented in a north–south direction, and stretch for approximately 15 miles (24 km) in length.
The Clipper Mountains are located in the eastern Mojave Desert and protected within Mojave Trails National Monument, in San Bernardino County, California.
The Palen Mountains are located in the southern Mojave Desert – northern Colorado Desert in eastern Riverside County, California, US. The range lies southeast of the Coxcomb Mountains, and northeast of the Chuckwalla Mountains near Interstate 10. The mountains lie in a southwest-northeasterly direction and are approximately 15 miles long and nine miles wide at their widest point.

The Nopah Range is a mountain range located in Inyo County, California, United States, near the eastern border with Nevada.

Old Woman Mountains Wilderness is a wilderness area in the Old Woman Mountains of the eastern Mojave Desert. It is located south of Essex in San Bernardino County, California.

The Sierra Pelona, also known as the Sierra Pelona Ridge or the Sierra Pelona Mountains, is a mountain ridge in the Transverse Ranges in Southern California. Located in northwest Los Angeles County, the ridge is bordered on the north by the San Andreas fault and lies within and is surrounded by the Angeles National Forest.

The mountains in the McCullough Range lie mostly above the city of Henderson in the U.S. state of Nevada. The range has two distinct areas with the northern portion being primarily volcanic in origin, while the southern part of the range is primarily composed of metamorphic rock.

The Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV) is the river region of the lower Colorado River of the southwestern United States in North America that rises in the Rocky Mountains and has its outlet at the Colorado River Delta in the northern Gulf of California in northwestern Mexico, between the states of Baja California and Sonora. This north–south stretch of the Colorado River forms the border between the U.S. states of California/Arizona and Nevada/Arizona, and between the Mexican states of Baja California/Sonora.

The Eldorado Mountains, also called the El Dorado Mountains, are a north-south trending mountain range in southeast Nevada bordering west of the south-flowing Colorado River; the endorheic Eldorado Valley borders the range to the west, and the range is also on the western border of the Colorado River's Black Canyon of the Colorado, and El Dorado Canyon on the river. The range is 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada; and the Eldorado Mountains connect with the Highland and Newberry mountains.

The Kiavah Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located in the Mojave Desert, Scodie Mountains, and southern Sierra Nevada in Kern County, California, United States. California State Route 178 connects the town of Lake Isabella to State Highway 14 in the east, crossing Walker Pass at the north boundary of the wilderness.