
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery of Eumillipes persephone, which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures.

Pill millipedes are any members of two living orders of millipedes, often grouped together into a single superorder, Oniscomorpha. The name Oniscomorpha refers to the millipedes' resemblance to certain woodlice (Oniscidea), also called pillbugs or "roly-polies". However, millipedes and woodlice are not closely related ; rather, this is a case of convergent evolution.

Harpaphe haydeniana, commonly known as the yellow-spotted millipede, almond-scented millipede or cyanide millipede, is a species of polydesmidan ("flat-backed") millipede found in the moist forests along the Pacific coast of North America, from Southeast Alaska to California. The dark coloration with contrasting yellow-tipped keels warn of its ability to exude toxic hydrogen cyanide as a defense. Despite the various common names given the species, the coloration pattern, cyanide defense, and associated almond scent occur in other flat-backed millipedes around the world.
Euphoberia is an extinct genus of millipede from the Pennsylvanian epoch of the Late Carboniferous, measuring up to 15 centimetres (5.9 in) in length, that is small in Euphoberiidae which contains species with length about 30 centimetres (12 in). Fossils have been found in Europe and North America.

Glomerida is an order of pill-millipedes found primarily in the Northern Hemisphere. Also known as northern pill millipedes, they superficially resemble pill-bugs or woodlice, and can enroll into a protective ball. They have twelve body segments, 17 to 19 pairs of legs, and males have enlarged rear legs involved in mating. The order includes about 30 genera and at least 280 species, including Glomeris marginata, the common European pill-millipede. The order contains members in Europe, South-east Asia and the Americas from California to Guatemala. Although historically considered closely related with the similar sphaerotheriidans that also enroll, some DNA evidence suggest they may be more closely related to glomeridesmidans, a poorly known order that does not enroll.
Bandeirenica caboverda, locally known in Cape Verde as "mil-pés", is a species of millipedes of the family Odontopygidae. It is endemic to Cape Verde, where it occurs in the islands of Santo Antão and São Vicente. First described in 1987 as Spinotarsus caboverdus, it was placed in the genus Bandeirenica in 2000.

Phallus rubicundus is a species of fungus in the stinkhorn family. First described in 1811, it has a wide distribution in tropical regions. It has the typical stinkhorn structure consisting of a spongy stalk up to 15 cm (5.9 in) tall arising from a gelatinous "egg" up to 3 cm (1.2 in) in diameter. Atop the stalk is a pitted, conical cap that has a foul-smelling, gelatinous, green spore mass spread over it.

Polydesmida is the largest order of millipedes, containing approximately 3,500 species, including all the millipedes reported to produce hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Polydesmids grow and develop through a series of moults, adding segments until they reach a fixed number in the adult stage, which is usually the same for a given sex in a given species, at which point the moulting and the addition of segments and legs stop. This mode of development, known as teloanamorphosis, distinguishes this order from most other orders of millipedes, which usually continue to moult as adults, developing through either euanamorphosis or hemianamorphosis.

Tremella is a genus of fungi in the family Tremellaceae. All Tremella species are parasites of other fungi and most produce anamorphic yeast states. Basidiocarps, when produced, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi". Over 100 species of Tremella are currently recognized worldwide. One species, Tremella fuciformis, is commercially cultivated for food.

Ommatoiulus moreleti, commonly known as the Portuguese millipede, is a herbivorous millipede native to the western Iberian Peninsula where it shares its range with other Ommatoiulus species. From here, it has spread by international commerce to a number of new localities. This species was accidentally introduced into Australia without its natural enemies and has since become an invasive pest. A number of methods have been developed to manage this millipede.

Sphaerotheriida is an order of millipedes in the infraclass Pentazonia, sometimes known as giant pill millipedes. They inhabit Southern Africa, Madagascar, South and Southeast Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Like the Northern Hemisphere pill millipedes of the order Glomerida, these millipedes can roll into a ball when disturbed. When they are rolled-up, most sphaerotheriidans reach a maximum size of a cherry or golf ball, but some species from Madagascar can even reach the size of an orange. When rolled-up, predators are unable to unravel giant pill millipedes since the margins of their second and last dorsal plates fit perfectly into one another, creating a sealed ball. A few giant pill millipede species are able to produce sound, the only millipedes known to do this. This order of millipedes is also unique in that some African species are used for medicinal purposes.

Polyxenida is an order of millipedes readily distinguished by a unique body plan consisting of a soft, non-calcified body ornamented with tufts of bristles – traits that have inspired the common names "bristly millipedes" or "pincushion millipedes". There are at least 86 species in four families worldwide, and are the only living members of the subclass Penicillata.

Archipolypoda is an extinct group of millipedes known from fossils in Europe and North America and containing the earliest known land animals. The Archipolypoda was erected by Scudder (1882) but redefined in 2005 with the description of several new species from Scotland. Distinguishing characteristics include relatively large eyes with densely packed ocelli, and modified leg pairs on the 8th body ring. Some species had prominent spines while others had a flattened appearance.

Chordeumatida is a large order of millipedes containing some 1200 species with a nearly worldwide distribution. Also known as sausage millipedes, they grow and develop through a series of moults, adding segments until they reach a fixed number in the adult stage, which is usually the same for a given sex in a given species, at which point the moulting and the addition of segments and legs stop. This mode of development, known as teloanamorphosis, distinguishes this order from most other orders of millipedes, which usually continue to moult as adults, developing through either euanamorphosis or hemianamorphosis.

Siphoniulus is a poorly known genus of millipede containing only two living species: S. alba from Indonesia, and S. neotropicus from Mexico and Guatemala. An additional two fossil species are known from Cretaceous amber. Siphoniulus species are the only members of the family Siphoniulidae and order Siphoniulida, making Siphoniulida the smallest millipede order. Few specimens are known, and their classification is contentious, although most recent studies place them as basal members of the Helminthomorpha.

Paeromopodidae is a family of large cylindrical millipedes of the order Julida native to the western United States of America. The family contains two genera and ten species and includes the longest millipedes in North America, with individuals reaching up to 16.5 cm (6.5 in) long.
Palaeodesmus tuberculata is an extinct species of millipede known from the lower Devonian period of modern-day Scotland. It was originally described as "Kampecaris tuberculata" by the Reverend Stanley Graham Brade-Birks, but was placed in its own new genus, Palaeodesmus, in 2004. Palaeodesmus has three rows of tubercles or bosses in the shape of round-edged squares or rectangles on the dorsal portion of each body segment. Palaeodesmus is a member of the extinct group Archipolypoda, but its anatomy is too poorly known to place it confidently within any known taxonomic family or order, and so it remains incertae sedis, although possibly related to archidesmidan species such as Archidesmus.
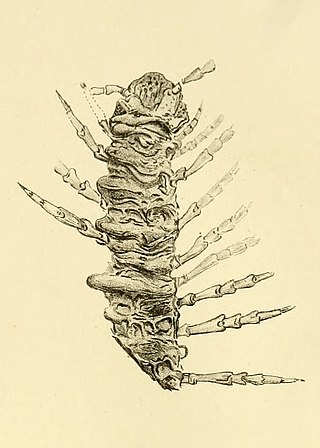
Kampecaris is an extinct genus comprising the Kampecarida, an enigmatic group of millipede-like arthropods, from the Silurian and early Devonian periods of Scotland and England. They are among the oldest known land-dwelling animals. They were small, short-bodied animals with three recognizable sections: an oval head divided along the midline, ten limb-bearing segments forming a cylindrical trunk that tapered slightly towards the front, and a characteristic swollen tail formed by a modified segment that tapers at its rear into an "anal segment". The cuticle forming their exoskeletons was thick, heavily calcified, and composed of two layers.
Nopoiulus kochii is a species of millipede in the genus Nopoiulus. This species is common to Turkey, and has been found living for several years in the intestines of a human.














