IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies Wireless Specialty Networks (WSN) standards. The working group was formerly known as Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks, and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.
In telecommunications and computer networks, a channel access method or multiple access method allows more than two terminals connected to the same transmission medium to transmit over it and to share its capacity. Examples of shared physical media are wireless networks, bus networks, ring networks and point-to-point links operating in half-duplex mode.
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer.
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.
IEEE 802.15.4 is a technical standard that defines the operation of a low-rate wireless personal area network (LR-WPAN). It specifies the physical layer and media access control for LR-WPANs, and is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group, which defined the standard in 2003. It is the basis for the Zigbee, ISA100.11a, WirelessHART, MiWi, 6LoWPAN, Thread, Matter and SNAP specifications, each of which further extends the standard by developing the upper layers, which are not defined in IEEE 802.15.4. In particular, 6LoWPAN defines a binding for the IPv6 version of the Internet Protocol (IP) over WPANs, and is itself used by upper layers such as Thread.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.
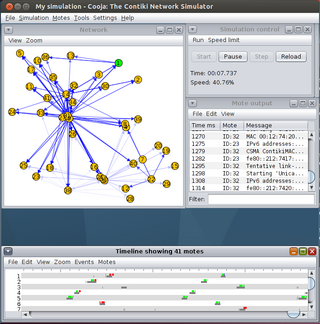
Contiki is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Contiki is used for systems for street lighting, sound monitoring for smart cities, radiation monitoring and alarms. It is open-source software released under the BSD-3-Clause license.

The Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) is an IP routing protocol optimized for mobile ad hoc networks, which can also be used on other wireless ad hoc networks. OLSR is a proactive link-state routing protocol, which uses hello and topology control (TC) messages to discover and then disseminate link state information throughout the mobile ad hoc network. Individual nodes use this topology information to compute next hop destinations for all nodes in the network using shortest hop forwarding paths.
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental conditions such as temperature, sound, pollution levels, humidity and wind.
Clock synchronization is a topic in computer science and engineering that aims to coordinate otherwise independent clocks. Even when initially set accurately, real clocks will differ after some amount of time due to clock drift, caused by clocks counting time at slightly different rates. There are several problems that occur as a result of clock rate differences and several solutions, some being more acceptable than others in certain contexts.
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers or wireless access points. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes. The determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.
Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance for Wireless (MACAW) is a slotted medium access control (MAC) protocol widely used in ad hoc networks. Furthermore, it is the foundation of many other MAC protocols used in wireless sensor networks (WSN). The IEEE 802.11 RTS/CTS mechanism is adopted from this protocol. It uses RTS-CTS-DS-DATA-ACK frame sequence for transferring data, sometimes preceded by an RTS-RRTS frame sequence, in view to provide solution to the hidden node problem. Although protocols based on MACAW, such as S-MAC, use carrier sense in addition to the RTS/CTS mechanism, MACAW does not make use of carrier sense.

Mobile Slotted Aloha (MS-Aloha) is a wireless network protocol proposed for applications such as vehicle networks.

PowWow is a wireless sensor network (WSN) mote developed by the Cairn team of IRISA/INRIA. The platform is currently based on IEEE 802.15.4 standard radio transceiver and on an MSP430 microprocessor. Unlike other available mote systems, PowWow offers specific features for a very-high energy efficiency:
A mobile wireless sensor network (MWSN) can simply be defined as a wireless sensor network (WSN) in which the sensor nodes are mobile. MWSNs are a smaller, emerging field of research in contrast to their well-established predecessor. MWSNs are much more versatile than static sensor networks as they can be deployed in any scenario and cope with rapid topology changes. However, many of their applications are similar, such as environment monitoring or surveillance. Commonly, the nodes consist of a radio transceiver and a microcontroller powered by a battery, as well as some kind of sensor for detecting light, heat, humidity, temperature, etc.
Sensor Media Access Control(S-MAC) is a network protocol for sensor networks. Sensor networks consist of tiny, wirelessly communicating computers, which are deployed in large numbers in an area to network independently and as long as monitor their surroundings in group work with sensors, to their energy reserves are depleted. A special form of ad hoc network, they make entirely different demands on a network protocol and therefore require network protocols specially build for them (SMAC). Sensor Media Access Control specifies in detail how the nodes of a sensor network exchange data, controls the Media Access Control (MAC) to access the shared communication medium of the network, regulates the structure of the network topology, and provides a method for synchronizing.
Zebra Media Access Control (Z-MAC) is a network protocol for wireless sensor networks. It controls how a Media Access Control (MAC) accesses a common communication medium of a network.
Time Slotted Channel Hopping or Time Synchronized Channel Hopping (TSCH) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks.









