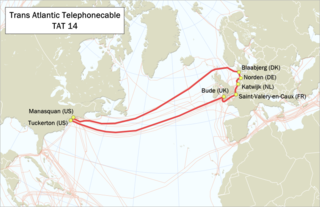
TAT-14 was the 14th consortium transatlantic telecommunications cable system. In operation from 2001 to 2020, it used wavelength division multiplexing. The cable system was built from multiple pairs of fibres—one fibre in each pair was used for data carried in one direction and the other in the opposite direction. Although optical fibre can be used in both directions simultaneously, for reliability it is better not to require splitting equipment at the end of the individual fibre to separate transmit and receive signals—hence a fibre pair is used. TAT-14 used four pairs of fibres—two pairs as active and two as backup. Each fibre in each pair carried 16 wavelengths in one direction, and each wavelength carried up to an STM-256. The fibres were bundled into submarine cables connecting the United States and the European Union in a ring topology.

CANTAT-3 was the third Canadian transatlantic telecommunications cable, in regular operation from 1994 to 2010, carrying 3 x 2.5 Gbit/s between Canada and Europe. It branches to both Iceland and the Faroe Islands. It is out of normal service for international bandwidth and is currently operated by Føroya Tele to service oil platforms in the North Sea.
Telecommunications in Iceland is a diversified market. Iceland has a highly developed telecommunications sector with modern infrastructure. Multiple wholesale and retail providers are operated in a competitive market. As of 2024, Iceland's telecom infrastructure is fully digitised and mostly fibre based, with 93% of households having full-fibre availability. Landlines are based on VoIP technology. Mobile telecoms in Iceland adheres to the GSM standard and 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G services are available, as well as a TETRA network for emergency communications. Iceland is connected by four submarine cables to both Europe and North America. Broadcasting is based on DVB-T2 standard for television and FM for radio. There are a few printed newspapers, although most mass media is consumed online. Postal service is provided under universal obligation by the state-owned Iceland Post, but other private postal companies also operate.

The Øresund or Öresund Bridge is a combined railway and motorway cable-stayed bridge across the Øresund strait between Denmark and Sweden. It is the second longest bridge in Europe with both roadway and railway combined in a single structure, running nearly 8 kilometres from the Swedish coast to the artificial island Peberholm in the middle of the strait. The crossing is completed by the 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) Drogden Tunnel from Peberholm to the Danish island of Amager.

The Royal Norwegian Navy is the branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces responsible for naval operations of Norway, including those of the Norwegian Coast Guard. As of 2008, the Royal Norwegian Navy consists of approximately 3,700 personnel and 70 vessels, including 4 heavy frigates, 6 submarines, 14 patrol boats, 4 minesweepers, 4 minehunters, 1 mine detection vessel, 4 support vessels and 2 training vessels.

The Royal Danish Navy is the sea-based branch of the Danish Armed Forces force. The RDN is mainly responsible for maritime defence and maintaining the sovereignty of Danish territorial waters. Other tasks include surveillance, search and rescue, icebreaking, oil spill recovery and prevention as well as contributions to international tasks and forces.
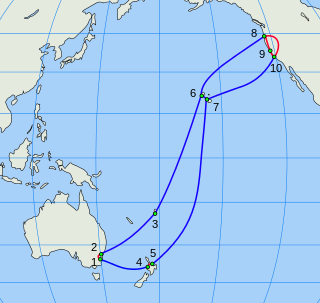
The Southern Cross Cable is a trans-Pacific network of telecommunications cables commissioned in 2000. The network is operated by the Bermuda-registered company Southern Cross Cables Limited. The network has 28,900 km (18,000 mi) of submarine and 1,600 km (990 mi) of terrestrial fiber optic cables, all which operate in a triple-ring configuration. Initially, each cable had a bandwidth capacity of 120 gigabit/s. Southern Cross offers capacity services from 100M/STM-1 to 100 Gbit/s OTU-4, including 1G, 10G and 40G Ethernet Private Line services.
SEA-ME-WE3 or South-East Asia - Middle East - Western Europe 3 is an optical submarine telecommunications cable linking those regions and is the longest in the world. Completed in late 2000, it is led by France Telecom and China Telecom, and is administered by Singtel, a telecommunications operator owned by the Government of Singapore. The Consortium is formed by 92 other investors from the telecom industry. It was commissioned in March 2000.

South East Asia–Middle East–Western Europe 4 is an optical fibre submarine communications cable system that carries telecommunications between Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria and France.

Nickelodeon is a children's channel broadcasting in Denmark, Norway and Finland. It broadcasts programming from the similarly branded channels in the United Kingdom and the United States as well as a few locally produced programmes.
Statnett is a Norwegian state owned enterprise responsible for owning, operating and constructing the stem power grid in Norway. The company has its headquarters in Oslo, Norway.
TenneT is a transmission system operator in the Netherlands and in a large part of Germany.
Nordic electricity market is a common market for electricity in the Nordic countries. It is one of the first free electric-energy markets in Europe and is traded in NASDAQ OMX Commodities Europe and Nord Pool Spot. In 2003, the largest market shares were as follows: Vattenfall 17%, Fortum 14.1%, Statkraft 8.9%, E.on 7.5%, Elsam 5%, Pohjolan Voima 5%. Other producers had 42.5% market share.
Energinet is the Danish national transmission system operator for electricity and natural gas. It is an independent public enterprise owned by the Danish state under the Ministry of Climate and Energy. Energinet has some 1150 employees, and its headquarters are located in Erritsø near Fredericia in Jutland. The gas division is located in Ballerup near Copenhagen.

The DANICE submarine communications cable system transits 2250 km of the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea to connect Iceland and Denmark. It consists of four fibre pairs, capable of carrying in total up to 36.4 Tbit/s of data using 100Gbit/s coherent wavelength technology available in 2013. The cable went into operation in November 2009 and has had no submarine faults. The operator of the cable is Farice. The complementary cable is FARICE-1. DANICE has cable landing points at:
Denmark–Netherlands relations are the bilateral relations between Denmark and the Netherlands. The Netherlands has an embassy in Copenhagen and Denmark has an embassy in The Hague. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO. Princess Beatrix is a Dame of the Order of the Elephant since 29 October 1975. On 31 January 1998, King Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands also received the Order of the Elephant.

Denmark's western electrical grid is part of the Synchronous grid of Continental Europe whereas the eastern part is connected to the Synchronous grid of Northern Europe via Sweden.
COBRAcable is a ±320 kV, 700 MW HVDC submarine power cable pair between Eemshaven, the Netherlands and Endrup near Esbjerg, Denmark. The cable is jointly owned by Energinet.dk and TenneT. Its purpose is to improve the European transmission grid and thus increase the amount of variable wind power in the system while improving supply reliability. Its 700 MW capacity corresponds to an annual transmission capacity of 6.1 TWh.

Viking Link is a 1,400 MW HVDC submarine power cable between the United Kingdom and Denmark, which was completed in 2023. As of 2024, it is the longest land and subsea HVDC interconnector in the world. The project is a cooperation between British National Grid and Danish Energinet.












