
Toledo is a city and municipality of Spain, the capital of the province of Toledo and the de jure seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha.

Castilla–La Mancha is an autonomous community of Spain. Comprising the provinces of Albacete, Ciudad Real, Cuenca, Guadalajara and Toledo, it was created in 1982. The government headquarters are in Toledo, which is the capital de facto.

Ciudad Real is a municipality of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile–La Mancha, capital of the province of Ciudad Real. It is the 5th most populated municipality in the region.

Talavera de la Reina is a city and municipality of Spain, part of the autonomous community of Castile–La Mancha. Its population of 83,303 makes it the second most populated municipality of the province of Toledo and the fourth largest in the region.

Socuéllamos is a town and municipality of Spain located in the province of Ciudad Real, Castilla–La Mancha. It is famous for its wines. The abandoned town of Torre de Vejezate is located within Socuéllamos municipal term.
Pastrana is a municipality in the province of Guadalajara, Castilla–La Mancha, Spain. As of 1 January 2022, it had a registered population of 850. The municipality spans across a total area of 95.70 km2.

Alcázar de San Juan is a city and municipality of Spain located in the province of Ciudad Real, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. It lies on the plain of La Mancha. From the 13th to the 19th century the history of Alcázar is strongly linked to the Grand Priory of the Order of St. John of Jerusalem. The city became a railway hub in the 19th century.

Almodóvar del Campo is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Ciudad Real, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Featuring a total area of 1.208,25 km2, it is the largest municipality in the region and one of the largest municipalities in Spain. As of 1 January 2020, it had a population of 5,983.

Alcaraz is a municipality of Spain located in the province of Albacete, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 370.53 km2. The locality lies at 953 metres above mean sea level.

Puerto Lápice is a municipality of Spain located in the province of Ciudad Real, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 54.84 km2 and, as of 1 January 2020, it has a registered population of 891.

El Puente del Arzobispo is a municipality of Spain located in the province of Toledo, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 0.98 km2 and, as of 1 January 2020, it has a registered population of 1,225. Together with neighbouring Talavera de la Reina, El Puente del Arzobispo was a producing centre of Maiolica pottery in Early-Modern Spain.

Quintanar de la Orden is a municipality of Spain located in the province of Toledo, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 87.87 km2 and, as of 1 January 2023, the municipality has a registered population of 11,119. It is part of the Mancha Alta de Toledo comarca.

Illescas is a town and municipality of Spain located in the province of Toledo, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 56.75 km2 and, as of 1 January 2020, it has a registered population of 30,229, which makes it the third most populated municipality in the province. It belongs to the traditional comarca of La Sagra.

Uclés is a municipality of Spain located in the province of Cuenca, Castilla–La Mancha. The municipality spans across a total area of 64.61 km2 and, as of 1 January 2020, it has a registered population of 212.
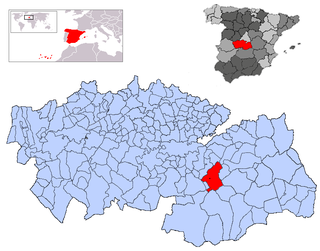
Mora is a town and municipality in Toledo province, in the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha, Spain. The area is most famous for the abandoned ruins of the San Marcos de Yegros monastery of the Order of Santiago, located northeast of the town of Mora about 10 km on the Calle de los Dolores in the village of Paraje de Yegros.
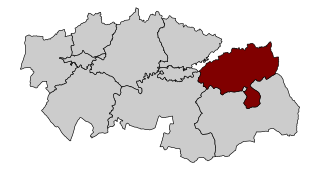
Mesa de Ocaña is a comarca in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, in the province of Toledo. Its capital and administrative center is Ocaña. The comarca is located in the northeast part of the province, and encompasses an area that includes several hundred meters of the Tajo River Valley.

Jean Laurent or, in Spanish, Juan Laurent Minier; sometimes simply J. Laurent was a French photographer who mostly worked in Spain.
Margarita de Mayo Izarra was a Spanish writer, teacher, and journalist.
Fernando Jiménez de Gregorio was a Spanish historian. He served as official cronista of the Province of Toledo.

The Campo de San Juan was the seigneurial lordship of the Order of St. John in the lands of La Mancha. It was the most important possession of the Grand Priory of the langue of Castile and León. It spanned across territory of the current Spanish provinces of Toledo and Ciudad Real. The most important urban centres were Consuegra and Alcázar de San Juan.





















