
The Community of Madrid is one of the seventeen autonomous communities of Spain. It is located in the centre of the Iberian Peninsula, and of the Central Plateau. Its capital and largest municipality is the City of Madrid, which is also the capital of the country. The Community of Madrid is bounded to the south and east by Castilla–La Mancha and to the north and west by Castile and León. It was formally created in 1983, in order to address the particular status of the City of Madrid as the national capital city and in urban hierarchy. Its limits are those of the province of Madrid, which was until then conventionally included in the historical region of New Castile.

Alcalá de Henares is a Spanish city in the Community of Madrid. Straddling the Henares River, it is located 31 kilometres to the northeast of the center of Madrid. As of 2018, it has a population of 193,751, making it the region's third-most populated municipality.
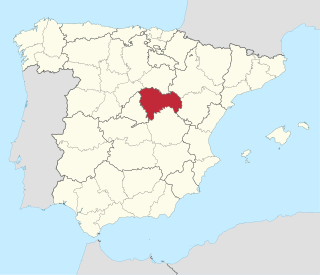
Guadalajara is a province of Spain, belonging to the autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. As of 2019 it had a population of 258,890 people. The population of the province has grown in the last 10 years. It is located in the centre of the Iberian Peninsula.

Aranjuez is a city and municipality of Spain, part of the Community of Madrid.

Soria is a municipality and a Spanish city, located on the Douro river in the east of the autonomous community of Castile and León and capital of the province of Soria. Its population is 38,881, 43.7% of the provincial population. The municipality has a surface area of 271,77 km2, with a density of 144.97 inhabitants/km2. Situated at about 1065 metres above sea level, Soria is the second highest provincial capital in Spain.

Numantia is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray (Soria), Spain.

The Royal Palace of Aranjuez is one of the official residences of the Spanish royal family. It is located in the town of Aranjuez (Madrid), Spain. Established in the 16th century as a royal hunting lodge, the palace was built by order of Philip II. Under his reign it became one of four seasonal seats of the court along Rascafría, El Escorial and the Royal Alcázar of Madrid. The royal estate comprises a set of landscaped and ornate gardens and woodlands that house an extensive botanical collection.

Juan de Herrera was a Spanish architect, mathematician and geometrician.

Ocaña is a municipality of Spain, in the province of Toledo, Castilla–La Mancha.

Cuéllar is a municipality in the Province of Segovia, within the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain.

Chinchón is a town and municipality in the Community of Madrid, Spain. Located 50 km south-east of the city of Madrid, the municipality covers an area of 115.91 km2. As of 2018, it has a population of 5,239. Its historic centre, with a notable main square, was declared a Heritage Site in 1974.

Laguardia is a town and municipality located in the southern province of Álava, in the north of Spain; it belongs to the region of Rioja Alavesa, in the Basque Autonomous Community. It has a population of 1,500; but in the past it had 2,500.

The Diocese of Tarazona is a Latin diocese of the Catholic Church located in north-eastern Spain, in the provinces of Zaragoza, Soria, Navarre and La Rioja, forming part of the autonomous communities of Aragón, Castile-Leon, Navarre and La Rioja. The diocese forms part of the ecclesiastical province of Zaragoza, and is thus suffragan to the Archdiocese of Zaragoza.

Pedro Muñoz is a municipality in the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It is located in the northeast corner of the province of Ciudad Real, on the bank of the Záncara river. It is in the La Mancha region, in the "Mancha Alta" sub-region. It was founded in 1284 by the Archdeacon of Alcaraz, Pero Muñoz, as one of a series of defensible points in the La Mancha plains. The village was abandoned in 1410, due to a severe drought, and re-established in 1525. Since the late 19th century, Pedro Muñoz had been an important economic center in the region.

Sigüenza is a city in the Serranía de Guadalajara comarca, Province of Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha, Spain.

The Carpetani were one of the Celtic peoples inhabiting the Iberian Peninsula prior to the Roman conquest. Their core domain was constituted by the lands between the Tagus and the Anas, in the southern Meseta. Agriculture is thought to have had a greater importance in the Carpetanian economy than other neighboring peoples'.

Camuñas is a municipality located in the province of Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. According to the 2018 census (INE), the municipality had a population of 1,740 inhabitants.

Mascaraque is a municipality located in the province of Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. According to the 2006 census (INE), the municipality had a population of 550 inhabitants.
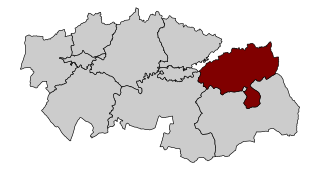
Mesa de Ocaña is a comarca in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, in the province of Toledo. Its capital and administrative center is Ocaña. The comarca is located in the northeast part of the province, and encompasses an area that includes several hundred meters of the Tajo River Valley.

Colmenar de Oreja is a town and municipality of the Las Vegas comarca, in the Community of Madrid, Spain. It was subject to a seven-month siege in 1139.




















