
Xenophyophorea is a clade of foraminiferans. Xenophyophores are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of 500 to 10,600 metres. They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a test.

Foraminifera are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment, while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths, which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA.

An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3,000 and 6,000 metres. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest, and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins.

The seabed is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
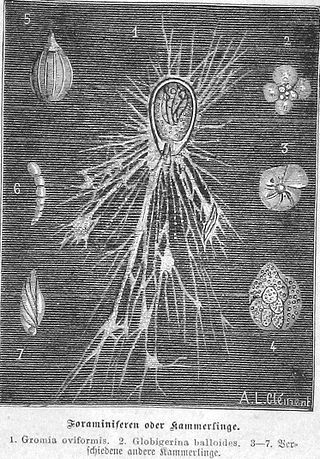
Gromia is a genus of protists, closely related to foraminifera, which inhabit marine and freshwater environments. It is the only genus of the family Gromiidae. Gromia are ameboid, producing filose pseudopodia that extend out from the cell's proteinaceous test through a gap enclosed by the cell's oral capsule. The test, a shell made up of protein that encloses the cytoplasm, is made up of several layers of membrane, which resemble honeycombs in shape – a defining character of this genus.
The Komokiacea are a small group of amoeboid protozoa, considered to be foraminifera, though there have been suggestions that they are a separate group, closely related to foraminifera. Komokiacea are rather large organisms, often exceeding 300 micrometers in maximum dimensions. Along with Xenophyophores they dominate the macro- and megabenthic fauna in the deep sea and are commonly referred to as "giants protists".

Deep-sea exploration is the investigation of physical, chemical, and biological conditions on the ocean waters and sea bed beyond the continental shelf, for scientific or commercial purposes. Deep-sea exploration is an aspect of underwater exploration and is considered a relatively recent human activity compared to the other areas of geophysical research, as the deeper depths of the sea have been investigated only during comparatively recent years. The ocean depths still remain a largely unexplored part of the Earth, and form a relatively undiscovered domain.

Paleodictyon is a trace fossil, usually interpreted to be a burrow, which appears in the geologic marine record beginning in the Precambrian/Early Cambrian and in modern ocean environments. Paleodictyon were first described by Giuseppe Meneghini in 1850. The origin of the trace fossil is enigmatic and numerous candidates have been proposed.
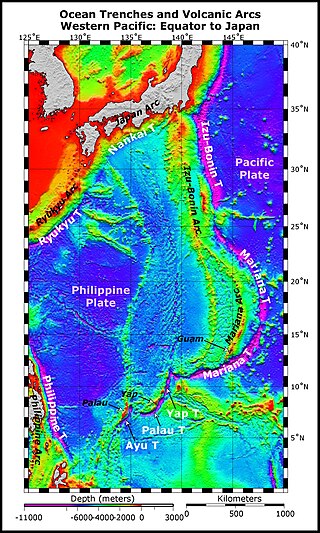
The Izu–Ogasawara Trench, also known as Izu–Bonin Trench, is an oceanic trench in the western Pacific Ocean, consisting of the Izu Trench and the Bonin Trench.

The Porcupine Abyssal Plain (PAP) is located in international waters, adjacent to the Irish continental margin. The PAP lies beyond the Porcupine Bank's deepest point and is southwest of it. It has a muddy seabed, with scattered abyssal hills that covers an area approximately half the size of Europe's landmass. Its depth ranges from 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) to 4,850 m (15,910 ft).

Quinqueloculina is a genus of foraminifera in the family Miliolidae.
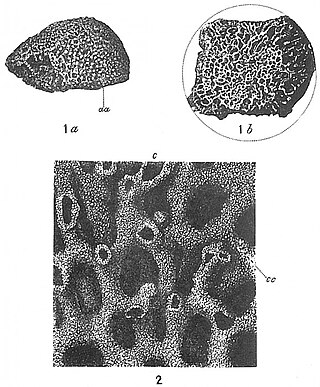
Syringammina is a xenophyophore found off the coast of Scotland, near Rockall. It is one of the largest single-celled organisms known, at up to 20 centimetres (8 in) across. It was first described in 1882 by the oceanographer John Murray, after being discovered on an expedition in the ship Triton which dredged the deep ocean bed off the west coast of Scotland in an effort to find organisms new to science. It was the first xenophyophore to be described and at first its relationship with other organisms was a mystery, but it is now considered to be a member of the Foraminifera.

The Clarion–Clipperton zone (CCZ) or Clarion–Clipperton fracture zone is an environmental management area of the Pacific Ocean, administered by the International Seabed Authority (ISA). It includes the Clarion fracture zone and the Clipperton fracture zone, geological submarine fracture zones. Clarion and Clipperton are two of the five major lineations of the northern Pacific floor, and were discovered by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in 1954. The CCZ is regularly considered for deep-sea mining due to the abundant presence of manganese nodules.
Paleodictyon nodosum is a living creature thought to produce a certain form of burrow nearly identical to Paleodictyon fossils. The modern burrows were found around mid-ocean ridge systems in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Although scientists have collected many of the burrows of Paleodictyon nodosum, they have never seen a live one. What a live specimen would look like is widely debated, with the debate being split into two main sides.

Chondrites is a trace fossil ichnogenus, preserved as small branching burrows of the same diameter that superficially resemble the roots of a plant. The origin of these structures is currently unknown. Chondrites is found in marine sediments from the Cambrian period of the Paleozoic onwards. It is especially common in sediments that were deposited in reduced-oxygen environments.
Stercomata are extracellular pellets of waste material produced by some groups of foraminiferans, including xenophyophoreans and komokiaceans, Gromia, and testate amoebae. The pellets are ovoid (egg-shaped), brownish in color, and on average measure from 10-20 μm in length. Stercomata are composed of small mineral grains and undigested waste products held together by strands of glycosaminoglycans.
Madeira Abyssal Plain, also called Madeira Plain, is an abyssal plain situated at the center and deepest part of the Canary Basin. It is a north-northeast to south-southeast elongated basin that almost parallels the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Its western boundary is marked by a chain of seamounts known as the either Seewarte Seamounts or Atlantis-Great Meteor Seamount Chain. Its eastern boundary is a distinct break of slope that marks the foot of the African Continental Rise. This abyssal plain occupies an area of about 68,000 km2 (26,000 sq mi). Across this basin, slope angles are generally less than 0.01°.

Foraminiferal tests are the tests of Foraminifera.
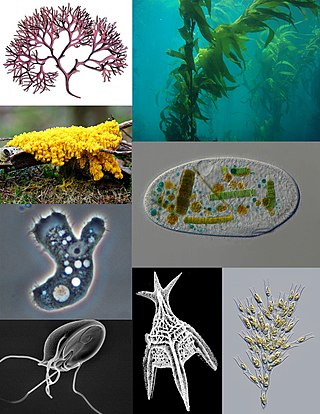
A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor, the last eukaryotic common ancestor, the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like algae, invertebrates and protozoans, the grouping is used for convenience.
















