
The Mycosphaerellaceae are a family of sac fungi. They affect many common plants, such as eucalyptus, the myrtle family, and the Proteaceae. They have a widespread distribution.
Teratosphaeria is a genus of fungi in the family Teratosphaeriaceae; according to the 2007 Outline of Ascomycota, it was placed in the Phaeosphaeriaceae, but the placement within this family was uncertain. It was confirmed in 2020, within Teratosphaeriaceae by Wijayawardene et al. 2020.

Herpotrichiellaceae is a family of ascomycetous fungi within the order Chaetothyriales and within the class Eurotiomycetes. It contains 16 genera and about 270 species. The type genus of the family, Herpotrichiella, is now synonymous with Capronia.

Ramularia is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Its species, which are anamorphs of the genus Mycosphaerella, are plant pathogens. Economically important host species include Narcissus, sugar beet, and barley.
'Distocercospora livistonae' was a fungus in the family Mycosphaerellaceae, it was then moved in 2017 to genus Exosporium as Exosporium livistonicola.
Distocercospora is a genus of plant-pathogenic fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1988 with Distocercospora pachyderma as the type species in 1988.
Stenella is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. The widespread genus contained about 155 species in 2008.
Phaeoramularia is a genus of fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. It was circumscribed in 1960.
Myrmecridium is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. It was circumscribed in 2007 and is distinguished from similar fungi by having entirely hyaline (translucent) vegetative hyphae and widely scattered, pimple-shaped denticles on the long hyaline rachis. The generic name derives from a combination of the Ancient Greek word "myrmekia", meaning "wart", and the suffix "-ridium" from "Chloridium".

Teratosphaeriaceae is a family of fungi in the order Mycosphaerellales.
Stigmina is a genus of fungal plant pathogens in the family Mycosphaerellaceae.

The Didymellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. They have a world-wide distribution.

Asperisporium is a genus of ascomycete fungi whose members are plant pathogens.
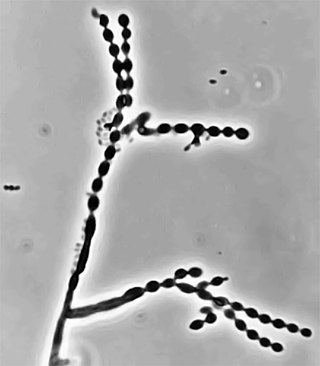
Cladophialophora is a genus of fungi in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It has 35 species. The genus contains black yeast-like fungi, some of which are species of important medical significance. Cladophialophora bantiana causes the rare brain disease cerebral phaeohyphomycosis. Cladophialophora carrionii is a common cause of chromoblastomycosis in semi-arid climates. Some of the species are endophytes–associating with plants. For example, Cladophialophora yegresii is a cactus endophyte, which is sometimes introduced into humans via cactus spines.

Cordieritidaceae is a family of fungi in the order Cyttariales. Species in this family are saprobes or lichenicolous.

Passalora is a genus of fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. It has about 250 species.
Mycovellosiella is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mycosphaerellaceae.

Thedgonia is a genus of fungi in the family Drepanopezizaceae of the order Helotiales. They have been recorded in most places in Europe including Great Britain.

Coniothyriaceae is a family of ascomycetous marine based fungi within the order of Pleosporales in the subclass Pleosporomycetidae and within the class Dothideomycetes. They are pathogenic or they can be saprobic on dead branches. They are generally a anamorphic species.










