
The Altai Mountains, also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia and Eastern Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E.

The Sayan Mountains are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of Tsardom of Russia, the mountain range served as the border between Mongolian and Russian cultures and cultural influences.

The Tuvans or Tyvans are a Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Siberia who live in Russia (Tuva), Mongolia, and China. They speak Tuvan, a Siberian Turkic language. In Mongolia they are regarded as one of the Uriankhai people groups.
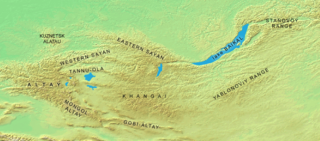
The Tannu-Ola mountains is a mountain range in southern Siberia, in the Tuva Republic of Russia. It extends in an east–west direction and curves along the Mongolian border. Its highest peak reaches 3,061 m (10,043 ft). The Tannu-ola mountains are mentioned in the 13th-century text The Secret History of the Mongols under the name "Tanglu mountains" (唐麓), and also in the JāmiʿAl-tawārīkh of Rashid-al-Din Hamadani (1247–1318) under the name "Toungat mountains" (تنغات). By the Qing dynasty the name has been changed to Tangnu (唐努) mountains, from which the modern name is derived. All names are probably rooted in the old Turkic word taŋ - "wonder, awe, wondrous."

Leymus is a genus of plants in the grass family Poaceae (Gramineae). It is widespread across Europe, Asia, and the Americas.

Boloria is a brush-footed butterfly (Nymphalidae) genus. Clossiana is usually included with it nowadays, though some authors still consider it distinct and it seems to warrant recognition as a subgenus at least.

Uvs Lake Basin is an endorheic basin located on the territorial border of Mongolia and Tuva, a republic of the Russian Federation. The basin is part of the Central Asian Internal Drainage Basin and is named after Uvs Lake, a large saline lake situated in the western part of its drainage basin, and is one of the last remnants of the mammoth steppes. Uvs Lake is a shallow lake with an area of 3,350 km2 (1,290 sq mi). Its entire basin, which includes several smaller lakes, is 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi).

Oeneis is a butterfly genus of the Satyrinae. All but one of its members are Arctic, sub-Arctic or high-altitude alpine in distribution. Some of the members of the genus are among the butterflies that can get along in the harshest climates of any butterflies. Four species in Europe, more are found in Arctic Russia, Siberia, Mongolia, Arctic North America and the Rocky Mountains. Curiously, there are no observations from Greenland. The development of most species takes two years.
South Central Siberia is a geographical region north of the point where Russia, China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia come together.

Oeneis jutta, the Jutta Arctic or Baltic grayling, is a species of butterfly in the subfamily Satyrinae with a Circumboreal distribution. It occurs in bogs and tundra in the north of Europe, the Baltic states, the Urals, Siberia, northern Kazakhstan, the Russian Far East, northern Mongolia, northeastern China, North Korea, and northern North America. Larvae feed on Carex and Eriophorum, possibly also Glyceria, Molinia, and Juncus. Ledum palustre is the preferred nectar plant of the adult butterflies. The species has one generation every one or two years, depending on the location.

Colias nastes, the Labrador sulphur, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. In Europe, it is found in the north of Norway and Sweden and on rare occasions in northern Finland. It is also found in North America, specifically in Alaska, Canada, and the Rocky Mountains, Washington, Montana and on Greenland. In Asia, it is found in the Altai Mountains, the border regions of Russia, China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, the Sayan Mountains, the north of Siberia, and in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug.
Oeneis elwesi is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found south of the Altai and Sayan Mountains and Mongolia.

Oeneis tarpeja is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found from the Caucasus and Volga region across Kazakhstan and southern Siberia to the Amur region and Mongolia. In Ukraine this species became extirpated in the mid-twentieth century. The habitat consists of steppe-clad plains and foothills.

Acossus terebra is a species of moth of the family Cossidae. It is found in Eurasia, including Israel, Turkey, northern Spain, central and southern Europe, southern Sweden, Finland, the Baltic region, Ukraine, the central part of European Russia, the Caucasus, southern Siberia to southern Yakutia, the southern part of the Russian Far East, Korea, Heilongjiang, Jilin and inner Mongolia.

Oeneis urda is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It was described by Eduard Friedrich Eversmann in 1847. It is found from Russia to northern Mongolia, north-eastern China and Korea. The habitat consists of steppe-clad slopes.
The Altai-Sayan region is an area of Inner Asia proximate to the Altai Mountains and the Sayan Mountains, near to where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan come together. This region is one of the world centers of temperate plant diversity. Its biological, landscape, historical, cultural and religious diversity is unique. 3,726 species of vascular plants are registered in the region including 700 threatened or rare species, 317 of which are endemic; fauna consists of 680 species, 6% of which are endemic. Its ecosystem is comparatively unchanged since the last ice age, and it is the host of endangered species that include the saiga, nerpa, and snow leopard. It is the focus of ongoing international and regional environmental conservation initiatives.

Oeneis bore, the white-veined Arctic or Arctic grayling, is a butterfly, a species of Satyrinae that occurs in North America and Asia.

The Sayan montane conifer forests ecoregion covers the mid-elevation levels of the Sayan Mountains, the high mountain range between the taiga of Siberia, Russia to the north, and the steppes of Mongolia to the south. The slopes of the mountains at the mid-altitudes are covered by Temperate coniferous forest. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, with a cold semi-arid climate. It covers 35,741,835 km2 (13,800,000 sq mi).

The South Siberian Mountains are one of the largest mountain systems of the Russian Federation. The total area of the system of mountain ranges is more than 1.5 million km². The South Siberian Mountains are located in the Siberian and Far Eastern Federal Districts of Russia, as well as partly in Mongolia. The territory of the mountain system is one of the Great Russian Regions.

















