History
Earlier known as Sun ONE Web Proxy server, the Sun Java System Web Proxy Server 4.0 is a major rewrite of the older 3.x version of Sun's Proxy server, formerly known as Netscape Proxy Server.
The Netscape Proxy Server version 3.x was essentially a coupling between the Netscape browser client, responsible for talking to remote servers, and the Netscape web server 4.x, which in turn handled the duty of talking to a client. Support for multithreading was absent, and the Proxy server operated in multi-process mode where each request was handled by a dedicated process.
Sun Java System Web Proxy server 4.0 resulted from a major rewrite of Netscape Proxy Server in 2003–2004, when Sun decided to reinvest in Proxy technology. Switching to Sun web server 6.1's core architecture brought in support for multi-threading while still allowing users to configure the server for multiple processes when so desired. A brand new http client, admin and installer GUI, and localization were the other major changes involved. 4.0 retained other significant features of 3.x such as the ftp client, gopher client, connect client, batch updates, and so on.
After acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation in 2010, Sun Java System Web Proxy Server 4.0 was rebranded as Oracle iPlanet Web Proxy Server 4.0.

Java applets are small applications written in the Java programming language, or another programming language that compiles to Java bytecode, and delivered to users in the form of Java bytecode, applets were deprecated by Java 9 in 2017.

Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages.
Netscape Communications Corporation was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California, and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was once dominant but lost to Internet Explorer and other competitors in the first browser war, with its market share falling from more than 90 percent in the mid-1990s to less than one percent in 2006. An early Netscape employee, Brendan Eich, created the JavaScript programming language, the most widely used language for client-side scripting of web pages. A founding engineer of Netscape, Lou Montulli, created HTTP cookies. The company also developed SSL which was used for securing online communications before its successor TLS took over.

Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California, on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center.

StarOffice is a discontinued proprietary office suite. Its source code continues today in derived open-source office suites Collabora Online and LibreOffice. StarOffice supported the OpenOffice.org XML file format, as well as the OpenDocument standard, and could generate PDF and Flash formats. It included templates, a macro recorder, and a software development kit (SDK).
In computing, a directory service or name service maps the names of network resources to their respective network addresses. It is a shared information infrastructure for locating, managing, administering and organizing everyday items and network resources, which can include volumes, folders, files, printers, users, groups, devices, telephone numbers and other objects. A directory service is a critical component of a network operating system. A directory server or name server is a server which provides such a service. Each resource on the network is considered an object by the directory server. Information about a particular resource is stored as a collection of attributes associated with that resource or object.

iPlanet was a product brand that was used jointly by Sun Microsystems and Netscape Communications Corporation when delivering software and services as part of a non-exclusive cross marketing deal that was also known as "A Sun|Netscape Alliance".

GlassFish is an open-source Jakarta EE platform application server project started by Sun Microsystems, then sponsored by Oracle Corporation, and now living at the Eclipse Foundation and supported by OmniFish, Fujitsu and Payara. The supported version under Oracle was called Oracle GlassFish Server. GlassFish is free software and was initially dual-licensed under two free software licences: the Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) and the GNU General Public License (GPL) with the Classpath exception. After having been transferred to Eclipse, GlassFish remained dual-licensed, but the CDDL license was replaced by the Eclipse Public License (EPL).
Sun Java System was a brand used by Sun Microsystems to market computer software. The Sun Java System brand superseded the Sun ONE brand in September 2003. There are two major suites under this brand, the Sun Java Enterprise System suite of infrastructure software, and the Sun Java Desktop System graphical user environment.
Oracle Communications Messaging Server is Oracle's messaging (email) server software. The software was obtained by Oracle as part of the company's acquisition of Sun in 2010.

Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms from embedded devices and mobile phones to enterprise servers and supercomputers. Java applets, which are less common than standalone Java applications, were commonly run in secure, sandboxed environments to provide many features of native applications through being embedded in HTML pages.

Network Security Services (NSS) is a collection of cryptographic computer libraries designed to support cross-platform development of security-enabled client and server applications with optional support for hardware TLS/SSL acceleration on the server side and hardware smart cards on the client side. NSS provides a complete open-source implementation of cryptographic libraries supporting Transport Layer Security (TLS) / Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and S/MIME. NSS releases prior to version 3.14 are tri-licensed under the Mozilla Public License 1.1, the GNU General Public License, and the GNU Lesser General Public License. Since release 3.14, NSS releases are licensed under GPL-compatible Mozilla Public License 2.0.
The Sun Java System Directory Server is a discontinued LDAP directory server and DSML server written in C and originally developed by Sun Microsystems. The Java System Directory Server is a component of the Java Enterprise System. Earlier iterations of Sun Java System Directory Server were known as Sun ONE Directory Server, iPlanet Directory Server, and, before that, Netscape Directory Server.
NetDynamics Application Server was an early Java-based integrated software platform. The product was developed by NetDynamics, a Silicon Valley start-up company founded in 1995 by Zack Rinat and Ofer Ben-Shachar. Unlike other early application server competitors, NetDynamics chose Java as the development language for the platform.
Oracle Secure Global Desktop (SGD) software provides secure access to both published applications and published desktops running on Microsoft Windows, Unix, mainframe and IBM i systems via a variety of clients ranging from fat PCs to thin clients such as Sun Rays.
Tarantella was a line of products developed by a branch of the company Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) since 1993. In 2001, SCO was renamed Tarantella, Inc. as it retained only the division that produced Tarantella. On July 13, 2005, Tarantella, Inc. was purchased by Sun Microsystems for US$25M. Tarantella exists now as a division of Oracle Corporation.
Oracle iPlanet Web Server (OiWS) is a web server designed for medium and large business applications. Previous versions were marketed as Netscape Enterprise Server, iPlanet Web Server, Sun ONE Web Server, and Sun Java System Web Server.
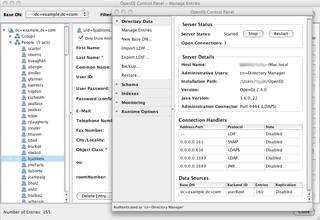
OpenDJ is a directory server which implements a wide range of Lightweight Directory Access Protocol and related standards, including full compliance with LDAPv3 but also support for Directory Service Markup Language (DSMLv2). Written in Java, OpenDJ offers multi-master replication, access control, and many extensions.
An Internet operating system, or Internet OS, is any type of operating system designed to run all of its applications and services through an Internet client, generally a web browser. The advantages of such an OS would be that it would run on a thin client, allowing cheaper, more easily manageable computer systems; it would require all applications to be designed on cross-platform, open standards; and would not tie a user's applications, documents, and preferences to a single computer, but rather place them in the Internet cloud. The Internet OS has also been promoted as the perfect type of platform for software as a service.
Kiva Software was the leading provider and pioneer of internet application server software. Kiva Software released the industry's first application server in January 1996, offering companies a robust platform on which to develop and deploy transaction-oriented business applications on the Web. Kiva's customers included Bank of America, E-Trade, Travelocity, Internet Shopping Network, Hong Kong Telecom and Pacific Bell Internet.









