
Lower Saxony is a German state in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with 47,614 km2 (18,384 sq mi), and fourth-largest in population among the 16 Länder federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers.

Wernigerode is a town in the district of Harz, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until 2007, it was the capital of the district of Wernigerode. Its population was 32,181 in 2020.
Schaumburg is a district (Landkreis) of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Nienburg, Hanover and Hameln-Pyrmont, and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia.

Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont was Queen of the Netherlands and Grand Duchess of Luxembourg as the wife of King-Grand Duke William III. An immensely popular member of the Dutch Royal Family, Queen Emma served as regent for her daughter, Queen Wilhelmina, during the latter's minority from 1890 until 1898.

Ilsenburg is a town in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It is situated under the north foot of the Harz Mountains, at the entrance to the Ilse valley with its little river, the Ilse, a tributary of the Oker, about six 6 miles (9.7

Diez an der Lahn is a town in Germany's Rhein-Lahn district in Rhineland-Palatinate, on the borders of Hesse. Diez is the administrative seat of the municipality of Diez.

The German Emperor was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the abdication of Wilhelm II was announced on 9 November 1918. The Holy Roman Emperor is sometimes also called "German Emperor" when the historical context is clear, as derived from the Holy Roman Empire's official name of "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" from 1512.

The Province of Hanover was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1866 to 1946.

Juliana, Countess of Stolberg-Wernigerode was the mother of William the Silent, the leader of the successful Dutch Revolt against the Spanish in the 16th century.

Stolberg is a town and a former municipality in the district of Mansfeld-Südharz, in the German State of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated in the southern part of the Harz mountains, about 27 kilometres (17 mi) west of Sangerhausen, and 13 km (8.1 mi) northeast of Nordhausen. Since 1 September 2010, it has been part of the municipality of Südharz.
Stapelburg is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.
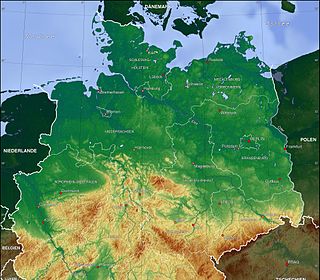
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east.

The County of Wernigerode was a state of the Holy Roman Empire which arose in the Harzgau region of the former Duchy of Saxony, at the northern foot of the Harz mountain range. The comital residence was at Wernigerode, now part of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. The county was ruled by a branch of the House of Stolberg from 1429 until its mediatization to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1806. Nevertheless, the county remained in existence - with one short interruption - until the dissolution of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1918.

This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border.
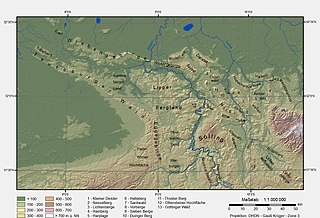
The Lower Saxon Hills are one of the 73 natural regions in Germany defined by the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN). Geographically it covers roughly the same area as the Weser Uplands in its wider sense.
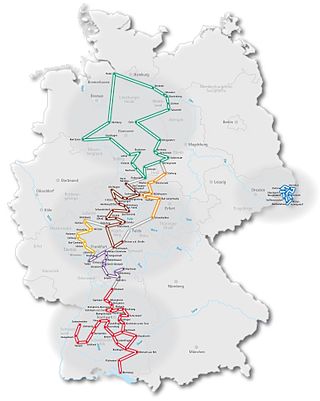
The German Timber-Frame Road is a German tourist route leading from the river Elbe in the north to the Black Forest and Lake Constance in the south. Numerous cities and towns each with examples of the vernacular timber-framed houses traditional to the German states are situated along the road. The total length of the route is nearly 3,000 km (1,864 mi).

Wernigerode Castle is a schloss located in the Harz mountains above the town of Wernigerode in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. The present-day building, finished in the late 19th century, is similar in style to Schloss Neuschwanstein, though its foundations are much older and have been reconstructed several times. Wernigerode Castle was first built at the beginning of the 12th century (1110-1120) as a Romanesque architecture medieval fortress for German emperors to have a secure spot to stop during their hunting trips to the Harz. Few of these medieval walls and foundation remain today. At the end of the 15th century the castle was enlarged in a Gothic architecture style, with large arched windows. During the 16th century, it was rebuilt as a Renaissance fortress. A spiral staircase tower still remains intact today.
The Ahlsburg or Alerdestein was an Imperial castle near Stapelburg in the present-day Harz district, in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.

Countess Walburga of Egmont, Dutch: Walburga Gravin van Egmont, was a countess from the House of Egmond and through marriage Countess of Nassau-Siegen.
















