
Goniatites is a genus of extinct cephalopods belonging to the family Goniatitidae, included in the superfamily Goniatitaceae. Hibernicoceras and Hypergoniatites are among related genera.
Joseph John Sepkoski Jr. was a University of Chicago paleontologist. Sepkoski studied the fossil record and the diversity of life on Earth. Sepkoski and David Raup contributed to the knowledge of extinction events. They suggested that the extinction of dinosaurs 66 mya was part of a cycle of mass extinctions that may have occurred every 26 million years.

Caturus is an extinct genus of fishes in the family Caturidae. Fossils of this genus range from 200 to 109 mya.

Zaniolepis is a genus of scorpaeniform fish native to the eastern Pacific Ocean. Z. frenata that was a source of food to the Native American inhabitants of San Nicolas Island off the coast of southern California, United States during the Middle Holocene.

Douvilleiceras is a genus of ammonites from the Middle to Late Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found worldwide, in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North and South America.

Dipleura is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida. It was described by Green in 1832, and the type species is Dipleura dekayi. The type locality was in the Hamilton Group in New York.

Nostoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites. The etymology of the name Nostoceras comes from "nostos" meaning return and "ceros" meaning horn, named as such by Alpheus Hyatt because it bends back on itself.

Tarasiiformes is an extinct order of prehistoric ray-finned fish.

Pachydesmoceras is a genus of ammonites belonging to the family Desmoceratidae.

Ampullinopsis is an extinct taxonomic genus of deep-water sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Sorbeoconcha. These sea snails were epifaunal grazers. Sea snails of this genus lived from Paleocene epoch to Miocene epoch.

Glycymeris, common name the bittersweet clams, is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Glycymerididae.

Holopea is an extinct genus of fossil sea snails, Paleozoic gastropod mollusks in the family Holopeidae.

Ludwigia is an extinct genus of ammonites in the family Graphoceratidae, which lived during the Middle Jurassic.
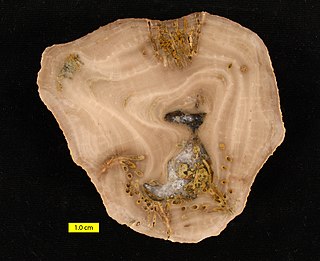
Amplexopora is a genus of bryozoans known in the rock record from the Ordovician to the Permian periods. Species belonging to this genus were stationary epifaunal suspension feeders.

Pterorigonia is an extinct genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Megatrigoniidae. This genus is known in the fossil record from the Jurassic period Tithonian age to the Cretaceous period Maastrichtian age. Species in this genus were facultatively mobile infaunal suspension feeders. The type species of the genus is Pterotrigonia cristata.

Baluchicardia is an extinct genus of fossil saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Carditidae. These clams were facultatively mobile infaunal suspension feeders.

Dufrenoyia is an extinct genus of Cretaceous ammonites included in the family Parahoplitidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous period. The type species of the genus is Ammonites dufrenoyi.

Parkinsonia is a genus of ammonites belonging to the family Parkinsoniidae.

Eotetragonites is an extinct genus of ammonite.

Pygurus is a genus of sea urchins belonging to the family Clypeidae.



















