
The Chatham Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 km (430 nmi) east of New Zealand's South Island, administered as part of New Zealand, and consisting of about 10 islands within an approximate 60 km (30 nmi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island (Rangiauria). They include New Zealand's easternmost point, the Forty-Fours. Some of the islands, formerly cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.

The Moriori are the first settlers of the Chatham Islands. Moriori are Polynesian settlers who came from the New Zealand mainland around 1500 CE. which was close to the time of the shift from the archaic to the classical period of Polynesian Māori culture on the mainland. Oral tradition records migration to the Chathams in the 16th century. The settlers' culture diverged from mainland Māori, and they developed a distinct Moriori language mythology, artistic expression and way of life. Currently there are around 700 people who identify as Moriori, most of whom no longer live on the Chatham Islands. During the late 19th century some prominent anthropologists proposed that Moriori were pre-Māori settlers of mainland New Zealand, and possibly Melanesian in origin.

Chatham Island is the largest island of the Chatham Islands group, in the south Pacific Ocean off the eastern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It is said to be "halfway between the equator and the pole, and right on the International Date Line", although that point is 173 miles WSW of the island's westernmost point. The island is called Rekohu in Moriori, and Wharekauri in Māori.

The Pyramid (Moriori: Tcharako; Māori: Te Tara Koi Koia; officially The Pyramid (Tarakoikoia)) is a small island south of Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. The site has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports the only known breeding colony of Chatham albatrosses, with 4575 pairs recorded in 2001.

Pitt Island is the second largest island in the Chatham Archipelago, New Zealand. It is called Rangiauria in Māori and Rangiaotea in Moriori.

Moturoa / Rabbit Island is a small island that lies across the southernmost part of Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere, on the northern coast of New Zealand's South Island. The long narrow island runs east–west for 8 kilometres (5 mi), and covers 15 km2 (5.8 sq mi).
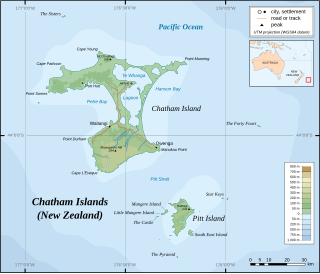
Mangere Island is part of the Chatham Islands archipelago, located about 800 kilometres (500 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island and has an area of 113 hectares. The island lies off the west coast of Pitt Island, 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of the main settlement in the Chathams, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

Hokorereoro, Rangatira, or South East Island is the third largest island in the Chatham Islands archipelago, and covers an area of 218 hectares. It lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island off the south-east coast of Pitt Island, 55 kilometres (34 mi) south-east of the main settlement, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

The Sisters is a group of three main islands located 16 kilometres (10 mi) north of Cape Pattison, Chatham Island. They are the northernmost members of the Chatham Archipelago, located 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island.

The Star Keys are group of five rocky islets in the Chatham Archipelago, about 12 kilometres (7 mi) east of Pitt Island. The archipelago is part of New Zealand, whose South Island lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) to the west.

Little Mangere is a small island of the Chatham Archipelago, just off the western end of Mangere Island, about 4 km west of Pitt Island and 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of the town of Waitangi on Chatham Island. The island is called Tapuaenuku in Moriori and Māori, and was formerly called The Fort. The archipelago is part of New Zealand and is located about 800 kilometres (500 mi) to the east of the South Island.

Petre Bay is a large bay which comprises about half of the west coast of Chatham Island, the largest island in New Zealand's Chatham Islands archipelago. It is some 20 kilometres (12 mi) in extent, and contains the far smaller Waitangi Bay, where the island group's largest settlement, Waitangi is located.
Pitt Strait is a channel, 25 kilometres (16 mi) wide, separating Chatham Island and Pitt Island, the two largest islands in New Zealand's Chatham Islands.

Cape Fournier is a headland on Chatham Island, in New Zealand's Chatham Islands group. It is the southeasternmost point in the island, and is the closest point on the island to the second largest of the Chatham Islands, Pitt Island, which lies 20 kilometres to the south-southeast across Pitt Strait.
Te Roto is a small settlement on Chatham Island, in New Zealand's Chatham Islands group. It is located close to the northern end of Petre Bay, 12 kilometres north of Waitangi. A small lake of the same name is located nearby.
The Tuku Nature Reserve is a nature reserve on Chatham Island, New Zealand, in the Tuku-a-tamatea (Tuku) River Valley in the south-west of the island. The 1238 hectares of land, largely covered with dense native forest, are owned by the New Zealand government and is managed by its Department of Conservation.
The Nairn River, also known as the Mangatukurewa Creek is a river in the Chatham Islands of New Zealand. Located in the southwest of Chatham Island, it runs north to reach the coast close to the southern end of Petre Bay. The main settlement of the Chatham Islands, Waitangi, stands close to the mouth of the Nairn River.

Okawa Point lies at the north-eastern end of Hanson Bay near the easternmost point of the main Chatham Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies of the critically endangered Chatham and endangered Pitt shags.

Matarakau Point is a headland on the north coast, and 13 km from the easternmost point, of the main Chatham Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies of the critically endangered Chatham and endangered Pitt shags.

Rabbit Island is a rocky islet lying off Tarawhenua Point on the north-west coast of Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. About 300 m long by 200 m across, its highest point is 44 m above sea level. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies of the critically endangered Chatham and endangered Pitt shags.











