
The Chatham Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 km (430 nmi) east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about 10 islands within an approximate 60 km (30 nmi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island (Rangiauria). They include New Zealand's easternmost point, the Forty-Fours. Some of the islands, formerly cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.

The Pyramid is a small island south of Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. The site has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports the only known breeding colony of Chatham albatrosses, with 4575 pairs recorded in 2001.

Tiwai Point lies at the entrance to Bluff Harbour on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. A spit which extends from the western end of the Awarua Plain, it lies between Awarua Bay to the north and Foveaux Strait to the south. It is known for the Tiwai Point Aluminium Smelter, one of the largest industrial facilities in New Zealand. In July 2020 Rio Tinto announced plans to close the aluminium smelter in August 2021.

Little Barrier Island, or Hauturu in Māori, lies off the northeastern coast of New Zealand's North Island. Located 80 kilometres (50 mi) to the north of Auckland, the island is separated from the mainland to the west by Jellicoe Channel, and from the larger Great Barrier Island to the east by Cradock Channel. The two aptly named islands shelter the Hauraki Gulf from many of the storms of the Pacific Ocean.

The Otago shag,, together with the Foveaux shag formerly known as the Stewart Island shag and in its dark phase as the bronze shag, is a species of shag now found only in coastal Otago, New Zealand.

The Campbell Islands are a group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. They lie about 600 km south of Stewart Island. The islands have a total area of 113.31 km2 (43.75 sq mi), consisting of one big island, Campbell Island, and several small islets, notably Dent Island, Isle de Jeanette Marie, Folly Island, Jacquemart Island, and Monowai Island. Ecologically, they are part of the Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion. The islands are one of five subantarctic island groups collectively designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
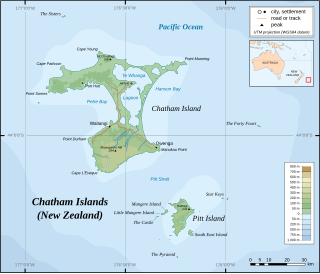
Mangere Island is part of the Chatham Islands archipelago, located about 800 kilometres (500 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island and has an area of 113 hectares. The island lies off the west coast of Pitt Island, 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of the main settlement in the Chathams, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

Hokorereoro, Rangatira, or South East Island is the third largest island in the Chatham Islands archipelago, and covers an area of 218 hectares. It lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island off the south-east coast of Pitt Island, 55 kilometres (34 mi) south-east of the main settlement, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

The Sisters / Rangitatahi is a group of three islands located 16 kilometres (10 mi) north of Cape Pattison, Chatham Island. They are the northernmost members of the Chatham Archipelago, located 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island.

Hanson Bay is a large bay which comprises almost the entire east coast of Chatham Island, the largest island in New Zealand's Chatham Islands archipelago. It is 35 kilometres (22 mi) in extent, stretching from Okawa Point in the island's northeast to Manukau Point in the southeast. The bay may formerly have been used as a resting ground by southern right whales and dolphins.

The Pitt shag, also known as the Pitt Island shag or Featherstone's shag is a species of bird in the family Phalacrocoracidae. It is endemic to Pitt Island. Its natural habitats are open seas and rocky shores. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Chatham shag, also known as the Chatham Island shag, is a species of bird in the cormorant and shag family, Phalacrocoracidae. It is endemic to the Chatham Islands of New Zealand. For a long time the species was placed in the genus Phalacrocorax; today it is mostly placed with the other blue-eyed shags of New Zealand and Antarctica in the genus Leucocarbo. Its closest relative is the Otago shag of South Island.

Rakiriri, also known as Goat Island and officially Goat Island/Rakiriri is the second largest island in Otago Harbour, in the South Island of New Zealand. It is located between Port Chalmers and Portobello, to the northeast of Dunedin's city centre.

The Mararoa River is one of the braided rivers of the Southland Region of the South Island of New Zealand.
The Tuku Nature Reserve is a nature reserve on Chatham Island, New Zealand, in the Tuku-a-tamatea (Tuku) River Valley in the south-west of the island. The 1238 hectares of land, largely covered with dense native forest, are owned by the New Zealand government and is managed by its Department of Conservation.

Centre Island is a small island in Lake Te Anau in the Southland Region of New Zealand. About 600 m long by 300 m wide, it has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports a breeding colony of bronze shags.

Matarakau Point is a headland on the north coast, and 13 km from the easternmost point, of the main Chatham Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies of the critically endangered Chatham and endangered Pitt shags.

Rabbit Island is a rocky islet lying off Tarawhenua Point on the north-west coast of Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. About 300 m long by 200 m across, its highest point is 44 m above sea level. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports breeding colonies of the critically endangered Chatham and endangered Pitt shags.

Flowerpot Bay, also spelt Flower Pot Bay, is a small bay, some 250 m across, on the north coast of Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands group of New Zealand. With a jetty at its western end, it is the main point of access by sea to the island.


















