Proteasome activator complex subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSME1 gene. [5] [6]
Proteasome activator complex subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSME1 gene. [5] [6]
The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. The immunoproteasome contains an alternate regulator, referred to as the 11S regulator or PA28, that replaces the 19S regulator. Three subunits (alpha, beta and gamma) of the 11S regulator have been identified. This gene encodes the alpha subunit of the 11S regulator, one of the two 11S subunits that is induced by gamma-interferon. Three alpha and three beta subunits combine to form a heterohexameric ring. Two transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified. [6]
PSME1 has been shown to interact with:

Proteasome subunit beta type-1 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB1 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-1, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides.
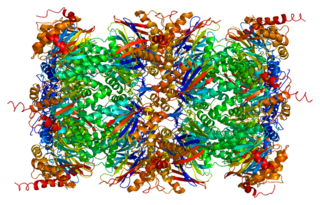
Proteasome subunit beta type-4 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB4 gene.

Proteasome subunit beta type-10 as known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-2i is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB10 gene.
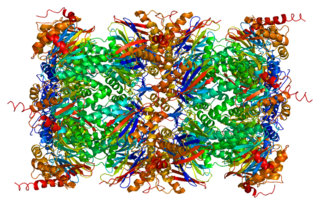
Proteasome subunit beta type-2 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB2 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-2, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides.

Proteasome subunit beta type-3, also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB3 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contribute to the complete assembly of the 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-2, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. The eukaryotic proteasome recognizes degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes.

Proteasome subunit beta type-8 as known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-5i is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB8 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-5, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. This protein contains "Chymotrypsin-like" activity and is capable of cleaving after large hydrophobic residues of peptide. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. The constitutive subunit beta1, beta2, and beta 5 can be replaced by their inducible counterparts beta1i, 2i, and 5i when cells are under the treatment of interferon-γ. The resulting proteasome complex becomes the so-called immunoproteasome. An essential function of the modified proteasome complex, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of numerous MHC class-I restricted T cell epitopes.

Proteasome subunit beta type-9 as known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-1i is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB9 gene.

26S protease regulatory subunit 7, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC2 gene This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex. Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Proteasome subunit alpha type-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMA6 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex.

Proteasome subunit alpha type-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMA1 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex.
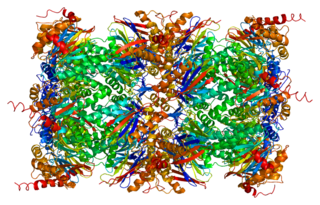
Proteasome subunit beta type-5 as known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB5 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-5, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. This protein contains "chymotrypsin-like" activity and is capable of cleaving after large hydrophobic residues of peptide. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides.

26S protease regulatory subunit 4, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC1 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex. Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Proteasome activator complex subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSME3 gene.
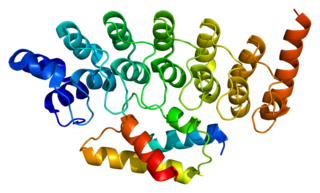
26S protease regulatory subunit 6B, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC4 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Proteasome activator complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSME2 gene.

Proteasome inhibitor PI31 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMF1 gene.
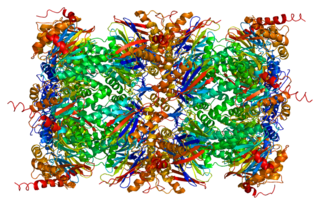
Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 also known as 20S proteasome subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMA5 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex.
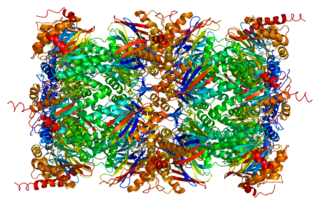
Proteasome subunit beta type-7 as known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB7 gene.

26S protease regulatory subunit S10B, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC6 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

Proteasomal ubiquitin receptor ADRM1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADRM1 gene. Recent evidences on proteasome complex structure confirmed that the protein encoded by gene ADRM1, also known in yeast as 26S Proteasome regulatory subunit Rpn13, is a subunit of 19S proteasome complex.