Pathology
Microscopy
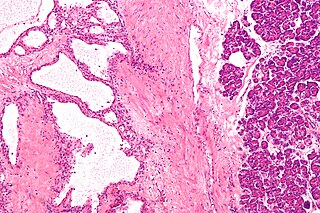
- Mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas
- Mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas
- Mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas
- Mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas
Pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma is a tumour of pancreas. [1] It may be benign or be associated with an invasive carcinoma component. [1]

The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.
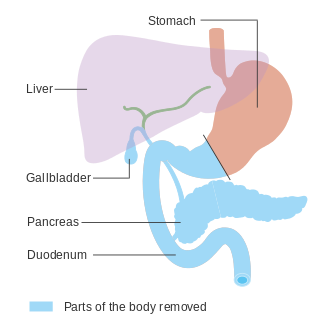
In medicine, a pancreatectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the pancreas. Several types of pancreatectomy exist, including pancreaticoduodenectomy, distal pancreatectomy, segmental pancreatectomy, and total pancreatectomy. In recent years, the TP-IAT has also gained respectable traction within the medical community. These procedures are used in the management of several conditions involving the pancreas, such as benign pancreatic tumors, pancreatic cancer, and pancreatitis.

Cystadenoma is a type of cystic adenoma. When malignant, it is called cystadenocarcinoma.
Pancreatic diseases are diseases that affect the pancreas, an organ in most vertebrates and in humans and other mammals located in the abdomen. The pancreas plays a role in the digestive and endocrine system, producing enzymes which aid the digestion process and the hormone insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. The most common pancreatic disease is pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas which could come in acute or chronic form. Other pancreatic diseases include diabetes mellitus, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, cystic fibrosis, pseudocysts, cysts, congenital malformations, tumors including pancreatic cancer, and hemosuccus pancreaticus.

Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor representing 2% of all salivary tumors. 90% of the time found in the parotid gland, 10% intraorally on buccal mucosa or palate. The disease presents as a slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness in 50% of the cases. Often appears pseudoencapsulated.

Pancreatoblastoma is a rare type of pancreatic cancer. It occurs mainly in childhood and has a relatively good prognosis.

Cystadenocarcinoma is a malignant form of a cystadenoma and is a cancer derived from glandular epithelium, in which cystic accumulations of retained secretions are formed. The neoplastic cells manifest varying degrees of anaplasia and invasiveness, and local extension and metastases occur. Cystadenocarcinomas develop frequently in the ovaries, where pseudomucinous and serous types are recognized. Similar tumor histology has also been reported in the pancreas, although it is a considerably rarer entity representing 1–1.5% of all Pancreatic cancer.

Mucinous cystadenoma is a benign cystic tumor lined by a mucinous epithelium. It is a type of cystic adenoma (cystadenoma).

Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a type of tumor that can occur within the cells of the pancreatic duct. IPMN tumors produce mucus, and this mucus can form pancreatic cysts. Although intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms are benign tumors, they can progress to pancreatic cancer. As such IPMN is viewed as a precancerous condition. Once an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm has been found, the management options include close monitoring and pre-emptive surgery.
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung (MCACL) is a very rare malignant mucus-producing neoplasm arising from the uncontrolled growth of transformed epithelial cells originating in lung tissue.
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of the pancreas. It is usually solitary and found in the body or tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel–Lindau syndrome.

Ovarian serous cystadenoma, also known as serous cystadenoma, is the most common ovarian neoplasm, representing 20% of ovarian neoplasms, and is benign.

A solid pseudopapillary tumour is a low-grade malignant neoplasm of the pancreas of papillary architecture that typically afflicts young women.

Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas, also acinar cell carcinoma, is a rare malignant exocrine tumour of the pancreas. It represents 5% of all exocrine tumours of the pancreas, making it the second most common type of pancreatic cancer. It is abbreviated ACC. It typically has a guarded prognosis.

A pancreatic tumor is an abnormal growth in the pancreas. In adults, almost 90% are pancreatic cancer and a few are benign. Pancreatic tumors are rare in children.

Cystic lesions of the pancreas are a group of pancreatic lesions characterized by a cystic appearance. They can be benign or malignant.

A pancreatic cyst is a fluid filled sac within the pancreas.
A mucinous cystic neoplasm is an abnormal and excessive growth of tissue (neoplasm) that typically has elements of mucin and one or more cysts. By location, they include:
Pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) is a type of cystic lesion that occurs in the pancreas. Amongst individuals undergoing surgical resection of a pancreatic cyst, about 23 percent were mucinous cystic neoplasms. These lesions are benign, though there is a high rate of progression to cancer. As such, surgery should be pursued when feasible. The rate of malignancy present in MCN is about 10 percent. If resection is performed before invasive malignancy develops, prognosis is excellent. The extent of invasion is the single most important prognostic factor in predicting survival.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)