The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.

Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome.

Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.

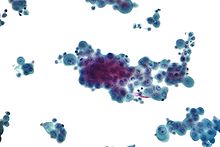
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs. The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding each testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly.

The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura, peritoneum and pericardium.

Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver.
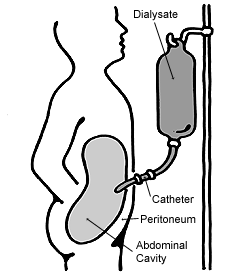
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first two years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease.
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space located between the two layers of the peritoneum—the parietal peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines the abdominal wall, and visceral peritoneum, which surrounds the internal organs. While situated within the abdominal cavity, the term peritoneal cavity specifically refers to the potential space enclosed by these peritoneal membranes. The cavity contains a thin layer of lubricating serous fluid that enables the organs to move smoothly against each other, facilitating the movement and expansion of internal organs during digestion.

Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is a clinical condition caused by cancerous cells that produce abundant mucin or gelatinous ascites. The tumors cause fibrosis of tissues and impede digestion or organ function, and if left untreated, the tumors and mucin they produce will fill the abdominal cavity. This will result in compression of organs and will destroy the function of the colon, small intestine, stomach, or other organs.

Paracentesis is a form of body fluid sampling procedure, generally referring to peritoneocentesis in which the peritoneal cavity is punctured by a needle to sample peritoneal fluid.

Desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor (DSRCT) is an aggressive and rare cancer that primarily occurs as masses in the abdomen. Other areas affected may include the lymph nodes, the lining of the abdomen, diaphragm, spleen, liver, chest wall, skull, spinal cord, large intestine, small intestine, bladder, brain, lungs, testicles, ovaries, and the pelvis. Reported sites of metastatic spread include the liver, lungs, lymph nodes, brain, skull, and bones. It is characterized by the EWS-WT1 fusion protein.

Appendix cancer, also known as appendiceal cancer, is a very rare malignant tumor that forms in the vermiform appendix.

Omental cake is a radiologic sign indicative of an abnormally thickened greater omentum. It refers to infiltration of the normal omental structure by other types of soft-tissue or chronic inflammation resulting in a thickened, or cake-like appearance.
Catumaxomab, sold under the brand name Removab among others, is a rat-mouse hybrid monoclonal antibody which is used to treat malignant ascites, a condition occurring in people with metastasizing cancer. It binds to antigens CD3 and EpCAM. It was developed by Fresenius Biotech and Trion Pharma (Germany).
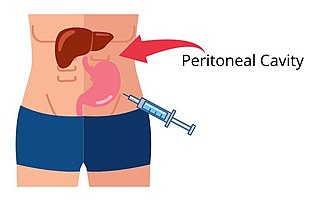
Intraperitoneal injection or IP injection is the injection of a substance into the peritoneum. It is more often applied to non-human animals than to humans. In general, it is preferred when large amounts of blood replacement fluids are needed or when low blood pressure or other problems prevent the use of a suitable blood vessel for intravenous injection.

Erionite is a naturally occurring fibrous mineral that belongs to a group of minerals called zeolites. It usually is found in volcanic ash that has been altered by weathering and ground water. Erionite forms brittle, wool-like fibrous masses in the hollows of rock formations and has an internal molecular structure similar to chabazite. This mineral is likely as toxic as asbestos; however, erionite is not currently regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and there are no occupational exposure limits for erionite fibers. Erionite was first described by A.S. Eakle in 1898, as white woolly fibrous masses in cavities in rhyolite lava near Durkee, Oregon. It was originally thought to be another relatively rare zeolite named offretite, which is very similar to erionite in appearance and chemical composition.

Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is a type of hyperthermia therapy used in combination with surgery in the treatment of advanced abdominal cancers. In this procedure, warmed anti-cancer medications are infused and circulated in the peritoneal cavity (abdomen) for a short period of time. The chemotherapeutic agents generally infused during IPHC are mitomycin-C and cisplatin.

Asbestos-related diseases are disorders of the lung and pleura caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibres. Asbestos-related diseases include non-malignant disorders such as asbestosis, diffuse pleural thickening, pleural plaques, pleural effusion, rounded atelectasis and malignancies such as lung cancer and malignant mesothelioma.
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITOC) is part of a surgical strategy employed in the treatment of various pleural malignancies. The pleura in this situation could be considered to include the surface linings of the chest wall, lungs, mediastinum, and diaphragm. HITOC is the chest counterpart of HIPEC. Traditionally used in the treatment of malignant mesothelioma, a primary malignancy of the pleura, this modality has recently been evaluated in the treatment of secondary pleural malignancies.
Ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are heterogeneous tumors that are derived from the primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonad, which accounts for about 2.6% of all ovarian malignancies. There are four main types of OGCTs, namely dysgerminomas, yolk sac tumor, teratoma, and choriocarcinoma.
This article includes text from the U.S. National Cancer Institute's public domain Dictionary of Cancer Terms.