
The Congridae are the family of conger and garden eels. Congers are valuable and often large food fishes, while garden eels live in colonies, all protruding from the sea floor after the manner of plants in a garden. The family includes over 220 species in 32 genera.
Paraconger is a genus of eels in the family Congridae. It currently contains the following species:

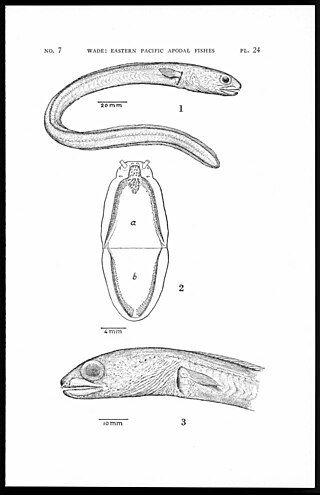
The shorttail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Charles Barkley Wade in 1946, originally under the genus Chiloconger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, the Galapagos Islands, Panama, and Revillagigedo. It dwells at a depth range of 108–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres.
Ariosoma coquettei is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the northern coast of South America, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 75 meters. It can reach a maximum total length of 28.1 centimeters.
The flapnose conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from French Guiana, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 210 metres.
The Californian conger, also known as the ringeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, and Peru. It is known to dwell at a depth of 50 metres. Males reach an average total length of 40 centimetres, but can reach a maximum TL of 60 cm.
The margintail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1867, originally under the genus Echelus. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bahamas, the Gulf of Mexico, Cuba, Venezuela, and Colombia. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 35–75 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting sand and mud in the neritic zone. Males reach an average total length of 35 centimeters, but can reach a maximum TL of 51 cm.
The blackspot conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Conger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira and Azores. It dwells at a depth range of 30–100 meters and burrows into sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 50 centimetres.
The Guinean conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Senegal to Angola, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 25–50 metres, and inhabits benthic sand, which it burrows into backwards. Males can reach a maximum total length of 62.7 centimetres.
The Bullish conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977, originally under the genus Rhechias. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Gulf of Mexico to the Amazon, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 366–475 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 39.5 centimeters.
Bathycongrus polyporus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977, originally under the genus Rhechias. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Straits of Florida and the northern coast of Cuba, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 439–549 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 43 centimeters.
Conger macrocephalus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Philippines, in the western central Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 329 metres.
Conger oligoporus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Hawaii and Guam, in the eastern central and western central Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 2–507 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting crevices of hard substrata. It feeds predominantly on finfish.
Conger philippinus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western central Pacific Ocean.
The manytooth conger, also known as the manytooth conger eel or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bermuda, the Antilles, the western Caribbean, and Brazil. It dwells at a depth range of 3–55 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting rocky regions and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimeters, but more commonly reach a TL of 80 cm.
Gnathophis bathytopos, the blackgut conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Straits of Florida, USA, and the southeastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 180–370 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 35 cm.
Gnathophis bracheatopos, the longeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the United States and the eastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 55–110 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 35 centimeters.
Gnathophis tritos is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Straits of Florida, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 458–567 meters.

The bristletooth conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1989. It is a marine, deep water–dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including northeastern Florida, U.S.A.; the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon River, the Bahamas and the West Indies. It dwells at a depth range of 140–825 metres (459–2,707 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 87.6 centimetres (34.5 in).

Bathymyrinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Congridae, which includes the conger and garden eels. The eels of this subfamily are most diverse in the Indo-Pacific region but are also found in both the Eastern and Western Atlantic Oceans.




