Laudonia is an extinct genus of trilobites that lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. There are currently two named species assigned to it.

Mummaspis is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites, with five known species. It lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.

Olenelloides armatus is an extinct, small sized olenelloid redlichiid trilobite arthropod. It lived during the later part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. The most conspicuous feature is the hexagonal head shield that carries 6 ray-like spines..
Elliptocephala is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived from the later part of the Tommotian to the upper Botomian. Elliptocephala can easily be confused with Ellipsocephalus, a trilobite genus of the Ptychopariida order.

Archaeaspis is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites. It lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 521 to 515 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period. The first specimens were first found in Siberia, where they were originally thought to have been endemic. Later, though, more specimen were found in the Inyo Mountains in Southern California. An Ediacarian proarticulatan was given the same name, Archaeaspis Ivantsov, 2001. This is however a junior homonym. The name Archaeaspis Repina in Khomentovskii and Repina, 1965, for the trilobite has priority. The new valid name for the proarticulate is Archaeaspinus Ivantsov, 2007.

Buenellus higginsi is an average size trilobite, which lived during the Lower Cambrian period, in what is now North-West Greenland. It is a prominent member of the Sirius Passet fauna. Buenellus higginsi is the only known species in the genus Buenellus.
Cirquella is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Atdabanian stage, in the former continent Laurentia.

Nevadella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of average size. It lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period.

Elrathia is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite species that lived during the Middle Cambrian of Utah, and possibly British Columbia. E. kingii is one of the most common trilobite fossils in the USA locally found in extremely high concentrations within the Wheeler Formation in the U.S. state of Utah. E. kingii has been considered the most recognizable trilobite. Commercial quarries extract E. kingii in prolific numbers, with just one commercial collector estimating 1.5 million specimens extracted in a 20-year career. 1950 specimens of Elrathia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 3.7% of the community.
...trilobite occupied the exaerobic zone, at the boundary of anoxic and dysoxic bottom waters. E. kingii consistently occur in settings below the oxygen levels required by other contemporaneous epifaunal and infaunal benthic biota and may have derived energy from a food web that existed independently of phototrophic primary productivity. Although other fossil organisms are known to have preferred such environments, E. kingii is the earliest-known inhabitant of them, extending the documented range of the exaerobic ecological strategy into the Cambrian Period.

Fallotaspis is a genus of redlichiid trilobite genus found in Early Cambrian-aged strata of the United States and Morocco.

Phalagnostus is a genus of small trilobites, in the order Agnostida. It lived during the Middle Cambrian, in what are now Canada, China, the Czech Republic, Denmark, England, France, the Russian Federation, Wales, Sweden, and possibly the United States (Vermont). The headshield is almost entirely effaced and wider than the tailshield. The pygidium is also very effaced, but the ovate pygidial axis is well defined and a border furrow is also present.

Peachella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of average size. It lived during the Toyonian stage, 516 to 513 million years ago, in what is today the southwestern United States. It can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by its club-like genal spines.
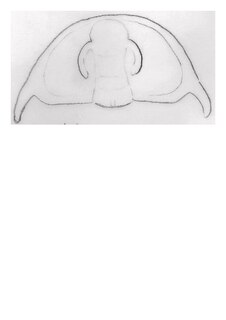
Eopeachella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of probably small size, entire, articulate specimens have not yet been found. It lived during the Toyonian stage, in what is today the South-Western United States. Eopeachella angustispina is the only known species in this genus.

The Biceratopsinae is an extinct subfamily of redlichiid trilobites within the family Biceratopsidae, with species of small to average size. Species belonging to this subfamily lived during the Toyonian stage, 516-513 million years ago, in the former continent of Laurentia, including what are today the South-Western United States and Canada.

Biceratops is an extinct genus of olenelloid redlichiid trilobites, of average size, with the largest specimen 8 centimetres or 3.1 inches long, not including the huge pleural spines of the 3rd segment of the thorax. It lived during the Toyonian stage, in what is today the South-Western United States. Biceratops can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by the absence of genal spines, in combination with effaced features of the raised axial area of the head shield, that is bordering the two horn-like projections that carry the eyes. Biceratops nevadensis is the only known species in this genus.

The Olenelloidea are a superfamily of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They lived during the late Lower Cambrian and species occurred on all paleocontinents.

The Bristoliinae is an extinct subfamily of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of small to average size. Species belonging to this subfamily lived during the Botomian and Toyonian stage (Olenellus-zone), 522-513 million years ago, in the former continent of Laurentia, including what are today Mexico, the Appalachian Mountains and the south-western United States, and Canada.
Lochmanolenellus is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with one small species, L. mexicana. It lived during the Botomian stage (Olenellus-zone), 522–513 million years ago, in the South-West of the former continent of Laurentia, in what are today Mexico, and the South-Western United States.

Bristolia is an extinct genus of trilobite, fossil marine arthropods, with eight or more small to average size species. It is common in and limited to the Lower Cambrian shelf deposits across the southwestern US, which constitutes part of the former paleocontinent of Laurentia.

Fritzolenellus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites, with three known species. It lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. Fritzolenellus occurred in parts of the paleocontinent Laurentia in what are now Northwestern Canada, Northwestern Scotland, and North-Greenland.

















