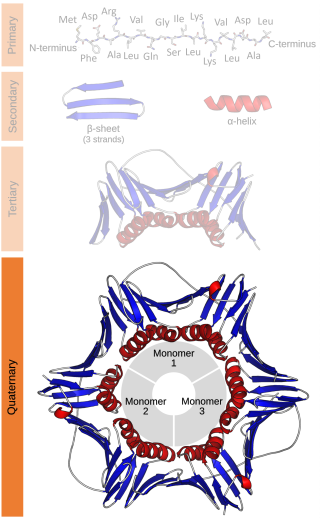
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains. Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors.

Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol or polyphenol and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts.

In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers. The name is composed of Greek elements oligo-, "a few" and -mer, "parts". An adjective form is oligomeric.

Gnetum gnemon is a gymnosperm species of Gnetum, its native area spans from Mizoram and Assam in India down south through Malay Peninsula, Malay Archipelago and the Philippines in southeast Asia to the western Pacific islands. Common names include gnetum, joint fir, two leaf, melinjo, belinjo, bago, and tulip.
Tin (50Sn) is the element with the greatest number of stable isotopes. This is probably related to the fact that 50 is a "magic number" of protons. In addition, twenty-nine unstable tin isotopes are known, including tin-100 (100Sn) and tin-132 (132Sn), which are both "doubly magic". The longest-lived tin radioisotope is tin-126 (126Sn), with a half-life of 230,000 years. The other 28 radioisotopes have half-lives of less than a year.

Pentacene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of five linearly-fused benzene rings. This highly conjugated compound is an organic semiconductor. The compound generates excitons upon absorption of ultra-violet (UV) or visible light; this makes it very sensitive to oxidation. For this reason, this compound, which is a purple powder, slowly degrades upon exposure to air and light.

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.

α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
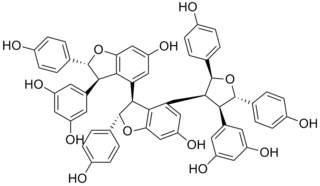
Kobophenol A is a stilbenoid. It is a tetramer of resveratrol. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu, from Caragana sinica and from Carex folliculata seeds.

A tetramer (tetra-, "four" + -mer, "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called tetramery. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula Ti(OCH3)4, which is tetrameric in solid state and has the molecular formula Ti4(OCH3)16. An example from organic chemistry is kobophenol A, a substance that is formed by combining four molecules of resveratrol.

Caragana sinica is a species belonging to the genus Caragana.
Vitis chunganensis is a species of climbing vine in the grape family native to China. In Chinese it is called dong nan pu tao, or Southeast grape.

Pallidol is a resveratrol dimer. It can be found in red wine, in Cissus pallida or in Parthenocissus laetevirens.

Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae like Shorea ovalis. It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.

Miyabenol C is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol trimer. It is found in Vitis vinifera (grape), in Foeniculi fructus, in Caragana sinica.

Quadrangularin A is an oligostilbene found in Cissus quadrangularis and in Parthenocissus laetevirens. It is a resveratrol dimer.

Isorhapontigenin is a tetrahydroxylated stilbenoid with a methoxy group. It is an isomer of rhapontigenin and an analog of resveratrol. It is found in the Chinese herb Gnetum cleistostachyum, in Gnetum parvifolium and in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.
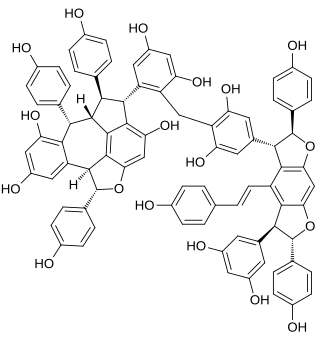
Chunganenol is a resveratrol hexamer found in Vitis chunganensis.
A Phosphide chloride is a mixed anion compound containing both phosphide (P3−) and chloride (Cl−) ions.

















