
Juncaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the rush family. It consists of 8 genera and about 464 known species of slow-growing, rhizomatous, herbaceous monocotyledonous plants that may superficially resemble grasses and sedges. They often grow on infertile soils in a wide range of moisture conditions. The best-known and largest genus is Juncus. Most of the Juncus species grow exclusively in wetland habitats. A few rushes, such as Juncus bufonius are annuals, but most are perennials.

Juncus is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants, commonly known as rushes. It is the largest genus in the family Juncaceae, containing around 300 species.

Luzula is a genus of flowering plants in the rush family Juncaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with species occurring throughout the world, especially in temperate regions, the Arctic, and higher elevation areas in the tropics. Plants of the genus are known commonly as wood-rush, wood rush, or woodrush. Possible origins of the genus name include the Italian lucciola or the Latin luzulae or luxulae, from lux ("light"), inspired by the way the plants sparkle when wet with dew. Another etymology sometimes given is that it does derive from lucciola but that this meant a mid-summer field, or from the Latin luculus, meaning a small place; the same source also states that this name was applied by Luigi Anguillara in 1561.

Damasonium is a genus of six species of flowering plants in the family Alismataceae, commonly known as starfruit and by the older name thrumwort. The genus has a subcosmopolitan but very patchy distribution.

Rostkovia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Juncaceae. It was described in 1809.

Juncus acutus, the spiny rush, sharp rush or sharp-pointed rush, is a flowering plant in the monocot family Juncaceae. It is native to the Americas, Northern and Southern Africa, Western and Southern Europe and West Asia, and is found in a variety of wet habitats, such as bogs, fens, meadows, and salt marshes, and along the edges of ponds and lakes.
Ernst Heinrich Friedrich Meyer was a German botanist and botanical historian. Born in Hanover, he lectured in Göttingen and in 1826 became a professor of botany at the University of Königsberg, as well as Director of the Botanical Garden. His botanical specialty was the Juncaceae, or family of rushes. His major work was the four-volume Geschichte der Botanik. His history covered ancient authorities such as Aristotle and Theophrastus, explored the beginnings of modern botany in the context of 15th- and 16th-century intellectual practice, and offered a wealth of biographical data on early modern botanists. Julius von Sachs pronounced him “no great botanist” but admitted that he “possessed a clever and cultivated intellect.”

Franz Georg Philipp Buchenau was a German botanist and phytogeographer who was a native of Kassel. He specialized in flora of northwestern Germany.

Entorrhizomycetes is the sole class in the phylum Entorrhizomycota within the Fungi subkingdom Dikarya along with Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. It contains three genera and is a small group of teliosporic root parasites that form galls on plants in the Juncaceae (rush) and Cyperaceae (sedge) families. Prior to 2015 this phylum was placed under the subdivision Ustilaginomycotina. A 2015 study did a "comprehensive five-gene analyses" of Entorrhiza and concluded that the former class Entorrhizomycetes is possibly either a close sister group to the rest of Dikarya or Basidiomycota.

Luzula hawaiiensis, commonly known as Hawai'i wood-rush, Wood rush or the Hawaii Wood Rush, is a species of perennial plant in Juncaceae family that is endemic to Hawaii. L hawaiiensis lives in rocky areas, slopes, cliffs, ridges, grasslands, shrub lands and etc. This species can grow to a height of 71.12 centimeters tall. This species is Vulnerable.
Luzula wahlenbergii, commonly known as Wahlenberg's woodrush or reindeer wood-rush, is a perennial species of plant in the genus Luzula of the (rush) family Juncaceae.

Limnocharis is a genus of plants in the family Alismataceae, native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies and South America) but naturalized in China, India, and Southeast Asia as well. Two species are recognized as of May 2014:

Distichia is a genus of plants in the family Juncaceae described as a genus in 1843.
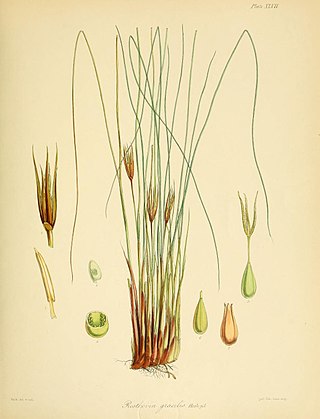
Marsippospermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Juncaceae described in 1809.

Oxychloe is a genus of flowering plants in the family Juncaceae. It was described as a genus in 1860.

Marsippospermum gracile, common name alpine rush, is a flowering plant species in the rush family Juncaceae which is native to New Zealand.

Oreojuncus is a small genus of flowering plants in the rush family Juncaceae, found in the eastern United States, eastern Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroes, most of Europe, northern Russia, western Siberia and the Altai. Their chromosome number is 2n=30 (x=15), whereas Juncus, from which they were split, has x=20.
Juncus filicaulis, the thread rush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Juncaceae. It is native to southeastern Australia, and it has been introduced to New Zealand. A perennial reaching 45 cm (18 in), it forms dense tufts.
















