
Pedinellales is a group of single-celled algae found in both marine environments and freshwater.

Lyngbya is a genus of cyanobacteria, unicellular autotrophs that form the basis of the oceanic food chain.
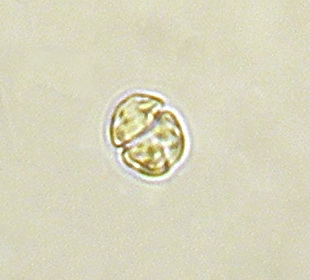
Gymnodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates, a type of marine and freshwater plankton. It is one of the few naked dinoflagellates, or species lacking armor. Since 2000, the species which had been considered to be part of Gymnodinium have been divided into several genera, based on the nature of the apical groove and partial LSU rDNA sequence data. Amphidinium was redefined later. Gymnodinium belong to red dinoflagellates that, in concentration, can cause red tides.

Codium is a genus of seaweed in the Chlorophyta of the order Bryopsidales. Paul Silva was an expert on the genus Codium taxonomy at the University of California at Berkeley. There are about 50 species worldwide.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.

The Trebouxiophyceae are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Their circumscription within the green algae is not well established due to the need for more genetic studies at higher levels within the group.

Bryopsidales is an order of green algae, in the class Ulvophyceae.

Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.

Wittrockiella is a genus of green algae in the family Pithophoraceae. This genus was first described by Nordal Wille in 1909.

Lepilaena is a genus of aquatic and marine flowering plant comprising 6 or more species endemic to coastal and brackish or alkaline inland waters of temperate Australia, Tasmania, and New Zealand.
Pyrenomonas is a genus of cryptomonad.

Ecklonia is a genus of kelp belonging to the family Lessoniaceae.

Oxyrrhis is a genus of dinoflagellates. It includes the species Oxyrrhis marina.
Nemoderma is the only genus in the family Nemodermataceae and order Nemodermatales of the brown algae. The genus contains only a single species, Nemoderma tingitanum.

Ulva intestinalis is a green alga in the family Ulvaceae, known by the common names sea lettuce, gutweed and grass kelp. Until they were reclassified by genetic work completed in the early 2000s, the tubular members of the sea lettuce genus Ulva were placed in the genus Enteromorpha.
Perkinsidae is a family of alveolates in the phylum Perkinsozoa, a sister group to the dinoflagellates.
Ralfsia verrucosa is a species of crustose brown seaweed in the family Ralfsiaceae. It grows intertidally in temperate waters around the world. In South Africa it is part of a mutualistic relationship with a limpet.

Chaetomorpha aerea is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.
Chrysomerophyceae is a monotypic class of photosynthetic heterokont eukaryotes.

Ptilonia willana is a marine red algal species endemic to New Zealand. For a detailed description, see Bonin and Hawkes (1988).














