
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of 7 ft —later slightly widened to 7 ft 1⁄4 in —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892.

Tyseley Locomotive Works, formerly the Birmingham Railway Museum, is the engineering arm of steam railtour promoter Vintage Trains based in Birmingham, England. It occupies part of the former Great Western Railway's Tyseley depot, built in 1908 to accommodate expanding operations in the West Midlands, particularly the opening of the North Warwickshire Line as a new main line from Birmingham to Bristol.

George Jackson Churchward was an English railway engineer, and was chief mechanical engineer of the Great Western Railway (GWR) in the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1922.

The Great Western Railway 2900 Class or Saint Class, which was built by the Great Western Railway's Swindon Works, incorporated several series of 2-cylinder passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward and built between 1902 and 1913 with differences in the dimensions. The majority of these were built as 4-6-0 locomotives; but thirteen examples were built as 4-4-2. They proved to be a highly successful class which established the design principles for GWR 2-cylinder classes over the next fifty years, and influenced similar classes on other British railways.

The GWR 5700 Class is a class of 0-6-0PT steam locomotive built by the Great Western Railway (GWR) and British Railways (BR) between 1929 and 1950. With 863 built, they were the most prolific class of the GWR, and one of the most numerous classes of British steam locomotive.

The London and South Western Railway (LSWR) 0298 Class or Beattie Well Tank is a class of British steam locomotive. They are 2-4-0WTs, originally built between 1863 and 1875 for use on passenger services in the suburbs of London, but later used on rural services in South West England. Out of a total production of 85, two locomotives have been preserved, both in operational condition.

The Great Western Railway (GWR) 2800 Class is a class of Churchward-designed 2-8-0 steam locomotive.

The Great Western Railway (GWR) 7200 Class is a class of 2-8-2T steam locomotive. They were the only 2-8-2Ts built and used by a British railway, and the largest tank engines to run on the Great Western Railway.

The LSWR M7 class is a class of 0-4-4T passenger tank locomotive built between 1897 and 1911. The class was designed by Dugald Drummond for use on the intensive London network of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), and performed well in such tasks. Because of their utility, 105 were built and the class went through several modifications over five production batches. For this reason there were detail variations such as frame length. Many of the class were fitted with push-pull operation gear that enabled efficient use on branch line duties without the need to change to the other end of its train at the end of a journey.

GWR 4073 Class 5029 Nunney Castle is a Great Western Railway Castle Class steam locomotive. It was built at the GWR's Swindon Works in 1934, being outshopped on 28 May and taking the name of Nunney Castle near Frome, Somerset. The locomotive was used in many publicity and "life on the railway" type of photographs. During the first day of the evacuation of civilians during World War II, the locomotive hauled trains carrying children being taken from London to the safety of the countryside. Nunney Castle was also used to haul the Royal Train in October 1957 from London Paddington station to Gloucester.

The GWR 4073 Class 5043 Earl of Mount Edgcumbe is a steam locomotive of the GWR 'Castle' Class, built in March 1936. It was originally named Barbury Castle, and was renamed Earl of Mount Edgcumbe in September 1937. It had a double chimney and 4 row superheater fitted in October 1958.

GWR No. 1340 is an 0-4-0ST steam locomotive, built in 1897 by the Avonside Engine Company of Bristol, England.

The South Devon and Tavistock Railway linked Plymouth with Tavistock in Devon; it opened in 1859. It was extended by the Launceston and South Devon Railway to Launceston, in Cornwall in 1865. It was a broad gauge line but from 1876 also carried the standard gauge trains of the London and South Western Railway between Lydford and Plymouth: a third rail was provided, making a mixed gauge. In 1892 the whole line was converted to standard gauge only.
The Didcot, Newbury and Southampton Railway (DN&SR) was a cross-country railway running north–south between Didcot, Newbury and Winchester. Its promoters intended an independent route to Southampton and envisaged heavy traffic from the Midlands and North of England to the port, but they ran out of funds to complete the line to Southampton. The intended heavy through traffic never materialised, and the line was dependent on larger railways—the Great Western Railway and the London and South Western Railway—for support, which was not freely given. The line opened in two stages, in 1882 and 1885.

The network of railways in Plymouth, Devon, England, was developed by companies affiliated to two competing railways, the Great Western Railway and the London and South Western Railway. At their height two main lines and three branch lines served 28 stations in the Plymouth area, but today just six stations remain in use.
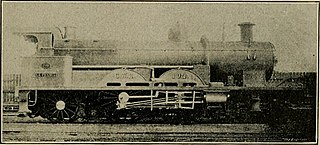
La France, number 102, was a locomotive of the Great Western Railway. It was bought by George Jackson Churchward to evaluate French locomotive practice, and particularly the effect of compounding.

The Turnchapel Branch was a London and South Western Railway (LSWR) single track branch railway line in Devon, England, that ran from Plymouth Friary station to Turnchapel. It crossed the River Plym and opened up the east side of the river to rail connections. The short line opened in 1892 and 1897 (throughout). It closed in 1951 to passengers, and in 1961 completely.
Roye England was a British modeller and museum curator of Australian birth who founded the Pendon Museum.

GWR 2900 "Saint" Class No. 2999 Lady of Legend is a 4-6-0 steam locomotive completed in 2019 to a design by George Jackson Churchward. It was based on the frames and boiler of 4900 "Hall" Class No. 4942 Maindy Hall, and was largely constructed at Didcot Railway Centre in Didcot, Oxfordshire, where it is now based. Described as "building the 78th Saint", the project started in the 1970s to look at building a new 'Saint', since none of the original class-members were preserved.





















