
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
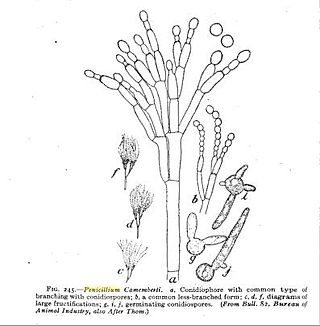
Penicillium camemberti is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is used in the production of Camembert, Brie, Langres, Coulommiers, and Cambozola cheeses, on which colonies of P. camemberti form a hard, white crust. It is responsible for giving these cheeses their distinctive flavors. An allergy to the antibiotic penicillin does not necessarily imply an allergy to cheeses made using P. camemberti.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
Penicillium adametzioides is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium, which was isolated from decayed Grapes in Cheongsoo in Korea.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.
Penicillium bovifimosum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from dry cow manure in Wyoming in the United States.
Penicillium brefeldianum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces Brefeldin A a fungal metabolite.
Penicillium cainii is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil in Korea.
Penicillium catenatum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.
Penicillium cecidicola is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pentacecilide A, pentacecilide B, pentacecilide C.
Penicillium chermesinum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil from Nova Scotia in Canada.Penicillium chermesinum produces plastatin, luteosporin, xanthomegnin, azaphilones, p-terphenyls and costaclavine.
Penicillium cinnamopurpureum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.
Penicillium ochrosalmoneum is an anamorph, ascosporic species in the genus Penicillium which produces citreoviridin.
Penicillium osmophilum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from agricultural soil in Wageningen in the Netherlands
Penicillium paneum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which can spoil cereal grains. Penicillium paneum produces 1-Octen-3-ol and penipanoid A, penipanoid B, penipanoid C, patulin and roquefortine C
Penicillium parvum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil in Papua New Guinea. Penicillium parvum produces ferrichrome siderophores
Penicillium roseopurpureum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces Carviolin.

Penicillium solitum is an anamorphic, mesophilic, salinity-tolerant, and psychrotolerant species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is known to produce various compounds including polygalacturonase, compactin, cyclopenin, cyclopenol, cyclopeptin, dehydrocompactin, dihydrocyclopeptin, palitantin, solistatin, solistatinol, viridicatin, viridicatol.
Penicillium terrenum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. Georegion is New Zealand.
Penicillium viticola is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from grapes in Yamanashi Prefecture in Japan. Penicillium viticola produces calcium malate



