Related Research Articles
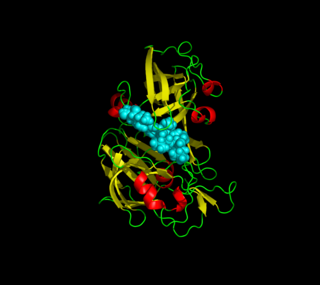
Plasmepsins are a class of at least 10 enzymes produced by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. There are ten different isoforms of these proteins and ten genes coding them respectively in Plasmodium. It has been suggested that the plasmepsin family is smaller in other human Plasmodium species. Expression of Plm I, II, IV, V, IX, X and HAP occurs in the erythrocytic cycle, and expression of Plm VI, VII, VIII, occurs in the exoerythrocytic cycle. Through their haemoglobin-degrading activity, they are an important cause of symptoms in malaria sufferers. Consequently, this family of enzymes is a potential target for antimalarial drugs.

Pepsin A is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aspergillopepsin I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
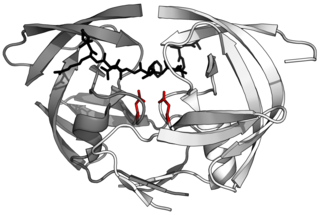
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.

Cathepsin D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSD gene. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a protein dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Cathepsin D is an aspartic endo-protease that is ubiquitously distributed in lysosomes. The main function of cathepsin D is to degrade proteins and activate precursors of bioactive proteins in pre-lysosomal compartments. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase A1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of the CTSD gene is initiated from several sites, including one that is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Homozygous deletion of the CTSD gene leads to early lethality in the postnatal phase. Deficiency of CTSD gene has been reported an underlying cause of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).

Cathepsin E is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTSE gene. The enzyme is also known as slow-moving proteinase, erythrocyte membrane aspartic proteinase, SMP, EMAP, non-pepsin proteinase, cathepsin D-like acid proteinase, cathepsin E-like acid proteinase, cathepsin D-type proteinase) is an enzyme.
Nepenthesin is an aspartic protease of plant origin that has so far been identified in the pitcher secretions of Nepenthes and in the leaves of Drosera peltata. It is similar to pepsin, but differs in that it also cleaves on either side of Asp residues and at Lys┼Arg. While more pH and temperature stable than porcine pepsin A, it is considerably less stable in urea or guanidine hydrochloride. It is the only known protein with such a stability profile.

Aspergilloglutamic peptidase, also called aspergillopepsin II is a proteolytic enzyme. The enzyme was previously thought be an aspartic protease, but it was later shown to be a glutamic protease with a catalytic Glu residue at the active site, and was therefore renamed aspergilloglutamic peptidase.
Rhizopuspepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Endothiapepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mucorpepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhodotorulapepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Acrocylindropepsin (EC 3.4.23.28, Acrocylindrium proteinase, Acrocylindrium acid proteinase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pycnoporopepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Scytalidopepsin A (EC 3.4.23.31, Scytalidium aspartic proteinase A, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase A-2, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase A-I, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase C, Scytalidium lignicolum carboxyl proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum acid proteinase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Phytepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Serralysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Deuterolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human.
References
- ↑ Mains G, Takahashi M, Sodek J, Hofmann T (October 1971). "The specificity of penicillopepsin". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry. 49 (10): 1134–49. doi:10.1139/o71-164. PMID 4946839.
- ↑ Zevaco C, Hermier J, Gripon JC (1973). "[Proteolytic system in Penicillium roqueforti. 2. Purification and properties of acid protease]". Biochimie. 55 (11): 1353–60. doi:10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80543-2. PMID 4790849.
- ↑ Emi S, Myers DV, Iacobucci GA (February 1976). "Purification and properties of the thermostable acid protease of Penicillium duponti". Biochemistry. 15 (4): 842–8. doi:10.1021/bi00649a018. PMID 2287.
- ↑ Hofmann T (1976). Penicillopepsin. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 45. pp. 434–52. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45038-3. PMID 1012008.
- ↑ Hsu IN, Delbaere LT, James MN, Hofmann T (March 1977). "Penicillopepsin from Penicillium janthinellum crystal structure at 2.8 A and sequence homology with porcine pepsin". Nature. 266 (5598): 140–5. doi:10.1038/266140a0. PMID 323722.