
The narwhal, is a species of toothed whale, and the only member of the genus Monodon. Its closest living relative is the beluga whale, and cases of interbreeding between the two species has been recorded. It is sexually dimorphic, as adult males are larger than females and have a long single tusk that can be up to 3 m (9.8 ft). The narwhal has a mottled pigmentation, with blackish-brown markings over a white background. Instead of a dorsal fin, the narwhal possesses a shallow dorsal ridge which is thought to facilitate movement under the ice, or reduce surface area, and so heat loss. An adult narwhal is typically 3.0 to 5.5 m in length and 800 to 1,600 kg in weight. Carl Linnaeus scientifically described the species in his 1758 work Systema Naturae.

The humpback whale is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual and is the only species in the genus Megaptera. Adults range in length from 14–17 m (46–56 ft) and weigh up to 40 metric tons. The humpback has a distinctive body shape, with long pectoral fins and tubercles on its head. It is known for breaching and other distinctive surface behaviors, making it popular with whale watchers. Males produce a complex song typically lasting 4 to 33 minutes.

The tiger shark is a species of ground shark, and the only extant member of the genus Galeocerdo and family Galeocerdonidae. It is a large macropredator, with females capable of attaining a length of over 5 m. Populations are found in many tropical and temperate waters, especially around central Pacific islands. Its name derives from the dark stripes down its body, which resemble a tiger's pattern, but fade as the shark matures.

Risso's dolphin is a dolphin, the only species of the genus Grampus. Some of the closest related species to these dolphins include: pilot whales, pygmy killer whales, melon-headed whales, and false killer whales.

The common dolphin is the most abundant cetacean in the world, with a global population of about six million. Despite this fact and its vernacular name, the common dolphin is not thought of as the archetypal dolphin, with that distinction belonging to the bottlenose dolphin due to its popular appearances in aquaria and the media. However, the common dolphin is often depicted in Ancient Greek and Roman art and culture, most notably in a mural painted by the Greek Minoan civilization.

The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin is one of three species of bottlenose dolphin in the genus Tursiops. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it receives in captivity in marine parks and dolphinariums, and in movies and television programs. Spending their entire life in water, common bottlenose dolphins inhabit temperate and tropical oceans throughout the world, absent only from polar waters. While formerly known simply as the bottlenose dolphin, this term is now applied to the genus Tursiops as a whole. As considerable genetic variation has been described within this species, even between neighboring populations, many experts think additional species may be recognized.

The snailfishes or sea snails are a family of marine ray-finned fishes. These fishes make up the Liparidae, which is classified within the order Scorpaeniformes.
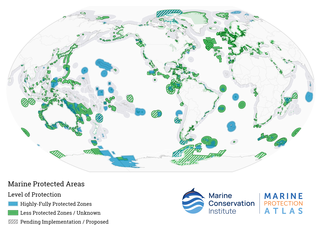
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are protected areas of the world's seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting marine life. In some situations, MPAs also provide revenue for countries, potentially equal to the income that they would have if they were to grant companies permissions to fish. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown.

Carcinus maenas is a common littoral crab. It is known by different names around the world. In the British Isles, it is generally referred to as the shore crab, or green shore crab. In North America and South Africa, it bears the name European green crab.

Onychopoda are a specialised order of branchiopod crustaceans, belonging to the superorder Cladocera.

The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approx. 70.8% of Earth. In English, the term ocean also refers to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided. The following names describe five different areas of the ocean: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, thus the ocean is essential to life on Earth. The ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle by acting as a huge heat reservoir.

The Burrunan dolphin is a proposed species of bottlenose dolphin found in parts of Victoria, Australia first described in 2011. Its exact taxonomy is debated: numerous studies support it as being a separate species within the genus Tursiops and occupying a basal position within the genus, with limited phylogenetic studies using different methodologies indicate that it is a subspecies of the Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin. The Burrunan dolphin is not currently recognized as a species by the Society for Marine Mammalogy or American Society of Mammalogists, which cites problematic methodology in the original study proposing species status and recommends further research.

There are many effects of climate change on oceans. One of the main ones is an increase in ocean temperatures. More frequent marine heatwaves are linked to this. The rising temperature contributes to a rise in sea levels due to melting ice sheets. Other effects on oceans include sea ice decline, reducing pH values and oxygen levels, as well as increased ocean stratification. All this can lead to changes of ocean currents, for example a weakening of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC). The main root cause of these changes are the emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities, mainly burning of fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide and methane are examples of greenhouse gases. The additional greenhouse effect leads to ocean warming because the ocean takes up most of the additional heat in the climate system. The ocean also absorbs some of the extra carbon dioxide that is in the atmosphere. This causes the pH value of the seawater to drop. Scientists estimate that the ocean absorbs about 25% of all human-caused CO2 emissions.

Blue carbon is a concept within climate change mitigation that refers to "biologically driven carbon fluxes and storage in marine systems that are amenable to management". Most commonly, it refers to the role that tidal marshes, mangroves and seagrasses can play in carbon sequestration. These ecosystems can play an important role for climate change mitigation and ecosystem-based adaptation. However, when blue carbon ecosystems are degraded or lost, they release carbon back to the atmosphere, thereby adding to greenhouse gas emissions.

Sididae is a family of ctenopods in the order Diplostraca. There are about 6 genera and at least 20 described species in Sididae. Some Sididae are non-native species.

Penilia is a genus of ctenopods in the family Sididae. There is one described species in Penilia, P. avirostris.

Holopedium gibberum is a species of water flea in the family Holopediidae, known for its gelatinous mantle. It is found in Europe, as well as throughout the Great Lakes Basin of North America.

Sida crystallina is a species of ctenopod in the family Sididae. It is found in Europe.

The lipid pump sequesters carbon from the ocean's surface to deeper waters via lipids associated with overwintering vertically migratory zooplankton. Lipids are a class of hydrocarbon rich, nitrogen and phosphorus deficient compounds essential for cellular structures. This lipid carbon enters the deep ocean as carbon dioxide produced by respiration of lipid reserves and as organic matter from the mortality of zooplankton.

Human activities affect marine life and marine habitats through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.




















