The 1998 United States Senate elections were held on November 3 and seen as an even contest between the Republican Party and Democratic Party. While the Democrats had to defend more seats up for election, Republican attacks on the morality of President Bill Clinton failed to connect with voters and anticipated Republican gains did not materialize. The Republicans picked up open seats in Ohio and Kentucky and narrowly defeated Democratic incumbent Carol Moseley Braun (Illinois), but these were cancelled out by the Democrats' gain of an open seat in Indiana and defeats of Republican Senators Al D'Amato and Lauch Faircloth. The balance of the Senate remained unchanged at 55–45 in favor of the Republicans. With Democrats gaining five seats in the House of Representatives, this marked the first time since 1934 that the out-of-presidency party failed to gain congressional seats in a mid-term election, and the first time since 1822 that the party not in control of the White House failed to gain seats in the mid-term election of a President's second term. These are the last senate elections that resulted in no net change in the balance of power.

The 1988 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate in which, in spite of the Republican victory by George H. W. Bush in the presidential election, the Democrats gained a net of one seat in the Senate. Seven seats changed parties, with four incumbents being defeated. The Democratic majority in the Senate increased by one from 54/46 to 55/45.

The 1986 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate in the middle of Ronald Reagan's second presidential term. The Republicans had to defend an unusually large number of freshman Senate incumbents who had been elected on President Ronald Reagan's coattails in 1980. Democrats won a net of eight seats, defeating seven freshman incumbents and regaining control of the Senate for the first time since January 1981. The party not controlling the presidency gained seats, as usually occurs in mid-term elections.

The 1982 United States Senate elections were held on November 2, 1982. They were elections for the United States Senate following Republican gains in 1980. A total of four seats changed hands between parties, and the lone independent, Senator Harry Byrd Jr., retired. Democrats made a net gain of one seat in the elections. A special election in 1983 was then held after the winner of Washington's 1982 election died at the beginning of the term.

The 1976 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate that coincided with Democratic Jimmy Carter's presidential election and the United States Bicentennial celebration. Although almost half of the seats decided in this election changed parties, Carter's narrow victory did not provide coattails for the Democrats, and the balance of the chamber remained the same.

The 1964 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2019, this is the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which would have hypothetically allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, convict and expel certain officials, or invoke cloture without any votes from Republicans. The Senate election coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1956 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. Although the Democrats gained two seats in regular elections, the Republicans gained back two seats in special elections, leaving the party balance of the chamber remained unchanged.

The 1950 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Harry S. Truman's second term as President. As with most 20th-century second-term mid-terms, the party out of the Presidency made significant gains. The Republican opposition made a net gain of five seats, taking advantage of the Democratic administration's declining popularity during the Cold War and the aftermath of the Recession of 1949. The Democrats held a narrow 49 to 47 seat majority after the election. This became the first time since 1932 that the Senate Majority Leader lost his seat and the only instance where the majority leader lost his seat while his party retained the majority.

The United States Senate elections of 1944 coincided with the re-election of Franklin D. Roosevelt to his fourth term as President. The Democrats' large majority remained the same, but they lost one seat to the Republicans in a special election.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 2002 was held on November 5, 2002, and included the races for the governor and lieutenant governor of Pennsylvania. Incumbent Republican Governor Mark Schweiker, who became Governor in 2001 when Tom Ridge resigned to become Homeland Security Advisor, was eligible to run for a full term, but did not do so. Democrat Ed Rendell, the former Mayor of Philadelphia and Chairman of the Democratic National Committee, emerged from a competitive primary to win the general election against Republican Pennsylvania Attorney General Mike Fisher.

Pennsylvania held various elections on November 2, 2010. These include elections for a Senate seat, a gubernatorial race, and many state legislature races.

The Pennsylvania Gubernatorial election of 1990 was held on November 6, 1990. Incumbent Democratic Robert P. Casey easily defeated Republican Barbara Hafer. Governor Casey defeated Ms. Hafer by a margin of 35.29%, and carried 66 out of 67 Pennsylvania counties.
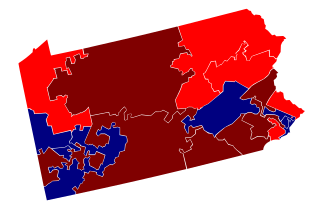
The 2010 congressional elections in Pennsylvania were held on November 2, 2010. Pennsylvania had nineteen seats in the United States House of Representatives. The election was held on the same day as many other PA elections, and the same day as House of Representatives elections in other states. Party primary elections were held May 18, 2010.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1970 was held on November 3. Democrat Milton Shapp challenged incumbent Republican Lieutenant Governor Ray Broderick.

The 1980 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 4, 1980. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Richard Schweiker decided to retire, instead of seeking a third term. Republican nominee Arlen Specter won the open seat, defeating Democratic nominee Peter F. Flaherty.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1817 occurred on November 4, 1817. Incumbent Democratic-Republican governor Simon Snyder was not a candidate for re-election. Simon's preferred successor, State Treasurer William Findlay, was nominated as the Democratic Republican by a caucus of legislative leaders. Conversely, U.S. Representative Joseph Hiester was chosen as a candidate by the Democratic Republican's first popular nominating convention; he additionally gained the endorsement of the declining Federalists.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1808 occurred on November 8, 1808. Incumbent governor Thomas McKean, a former Democratic Republican who had faced impeachment by members of his own party during the prior term, was not a candidate. Democratic-Republican candidate Simon Snyder, former Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives defeated Federalist candidate and former U.S. Senator James Ross to become Governor of Pennsylvania. Snyder, with the aid of a supportive press, campaigned as a "New School Democrat" and attempted to ally himself with James Madison. He painted the former McKean administration as elitist and advocated for popular democracy, governmental intervention in the economy, and infrastructural support for Western Pennsylvania counties.

The 1820-1821 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on three separate dates from December 1820 to December 1821. On December 10, 1821, William Findlay was elected by the Pennsylvania General Assembly to the United States Senate.
The Milton Shapp presidential campaign of 1976 began when then-Governor of Pennsylvania Milton Shapp elected to seek the Democratic Party nomination for President of the United States in the 1976 election. Shapp had won reelection as Governor of Pennsylvania in the 1974 election—the first Pennsylvania Governor to be elected to a second four-year term following an amendment permitting this in 1967—and had hoped to translate his relative popularity in Pennsylvania into the groundwork of a presidential campaign.