The United States presidential election of 1816 was the eighth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, November 1 to Wednesday, December 4, 1816. In the first election following the end of the War of 1812, Democratic-Republican candidate James Monroe defeated Federalist Rufus King. The election was the last in which the Federalist Party fielded a presidential candidate.

The United States presidential election of 1896 was the 28th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1896. Former Governor William McKinley, the Republican candidate, defeated Democrat William Jennings Bryan. The 1896 campaign, which took place during an economic depression known as the Panic of 1893, was a realigning election that ended the old Third Party System and began the Fourth Party System.

The United States presidential election of 1908 was the 31st quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1908. Secretary of War and Republican Party nominee William Howard Taft defeated three-time Democratic nominee William Jennings Bryan.
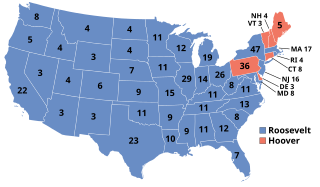
The United States presidential election of 1932 was the thirty-seventh quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. Incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the Governor of New York. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans.

The United States presidential election of 1936 was the thirty-eighth quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Governor Alf Landon of Kansas. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular and electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System.

The 1964 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2019, this is the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which would have hypothetically allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, convict and expel certain officials, or invoke cloture without any votes from Republicans. The Senate election coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 2006 South Carolina gubernatorial election took place on November 7, 2006. Incumbent Republican Governor Mark Sanford won re-election against Democratic State Senator Tommy Moore, becoming only the third Republican governor in South Carolina to win a second term. Sanford started the campaign with a double-digit edge over Moore and he maintained that lead to election day. During the course of the campaign, Sanford's approval rating averaged in the mid fifties. In Sanford's re-election victory, he also garnered 22% of the African American vote, which was considered very high for a Republican statewide candidate.
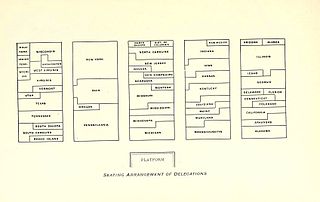
The 1896 Democratic National Convention, held at the Chicago Coliseum from July 7 to July 11, was the scene of William Jennings Bryan's nomination as the Democratic presidential candidate for the 1896 U.S. presidential election.

Claude Matthews was the 23rd governor of the U.S. state of Indiana from 1893 to 1897. A farmer, he was nominated to prevent the loss of voters to the Populist Party. The Panic of 1893 occurred just before he took office, leading to severe economic problems during his term. Republicans took the Indiana General Assembly in the 1894 mid-term election and repudiated many of the Democrats' laws, leading to violence in the assembly. A popular party figure when he left office, he was a nominee to run for president at the 1896 Democratic National Convention, but lost his bid for the nomination to William Jennings Bryan.

The 1870 South Carolina gubernatorial election was held on October 10, 1870 to select the governor of the state of South Carolina. Governor Robert Kingston Scott easily won reelection based entirely on the strength of the black vote in the state. The election was significant because it proved to the white conservatives of the state that political harmony between the white and black races was impossible and only through a straightout Democratic attempt would they be able to regain control of state government.
The following offices were up for election in the United States Commonwealth of Virginia in the November 2009 general election:

The 2010 Illinois gubernatorial election took place on November 2, 2010. Incumbent Democratic Governor Pat Quinn sought and was elected to a full term in office. Quinn was elected as the Democratic nominee, the Illinois Green Party nominee was attorney and 2006 nominee Rich Whitney, the Republican nominee was State Senator Bill Brady, the Libertarian Party nominee was Lex Green, and Scott Lee Cohen ran as an independent. Governor Quinn won election to a full term in a very close race, beating Senator Brady by only about 32,000 votes, despite Brady winning in 98 of 102 Illinois counties.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1982 was held on November 2, 1982 between incumbent Republican Dick Thornburgh and Democratic U.S. Congressman Allen E. Ertel.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial of 1860 was held on October 9, almost one month before Presidential election. Andrew Curtin of the newly formed Republican Party won the governor's mansion over Democrat Henry Donnel Foster.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1820 occurred on November 7, 1820. Incumbent Democratic-Republican governor William Findlay sought re-election but was defeated U.S. Representative Joseph Hiester. Findlay entered the race with significantly reduced popularity. He had been renounced in the press as an opponent of democracy due to his nomination during the 1817 campaign by a group of party insiders. He additionally faced allegations of corruption over the misappropriation of funds during his tenure as State Treasurer, although all charges were dismissed during impeachment proceedings before the State Legislature. For this campaign, Findlay was chosen for a slot on the ballot at a popular convention of Democratic Republicans; Hesiter was selected at a separate convention of Federalists and "Old School Democrats". The sour state of the economy was a key factor in the defeat of the incumbent, as Pennsylvania was reeling from the effects of the Panic of 1819.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1811 occurred on November 5, 1811. Incumbent Democratic-Republican governor Simon Snyder won re-election over Federalist candidate William Tilghman, the Chief Justice of the Pennsylvania Supreme Court, by a wide margin. Two of the major policy goals on which Snyder campaigned were increasing spending for infrastructural upgrades and authorizing the transfer of governmental operations from Lancaster to Harrisburg.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1805 occurred on November 5, 1805. Incumbent governor Thomas McKean won a contentious election over the endorsed Democratic-Republican candidate, Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives Simon Snyder.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Wisconsin took place on November 8, 1988. All 50 states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. Wisconsin voters chose 11 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The Iowa elections, 2018 were held in the U.S. state of Iowa on November 6, 2018. A closed primary election was held on June 5, 2018. All of Iowa's executive officers were up for election as well as all four of Iowa's seats in the United States House of Representatives, 25 (half) of the seats in the Iowa Senate, and all 100 seats in the Iowa House of Representatives.