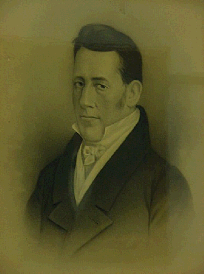
The Democratic-Republican Party was an American political party formed by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison around 1792 to oppose the centralizing policies of the new Federalist Party run by Alexander Hamilton, who was Secretary of the Treasury and chief architect of George Washington's administration. From 1801 to 1825, the new party controlled the presidency and Congress as well as most states during the First Party System. It began in 1791 as one faction in Congress and included many politicians who had been opposed to the new constitution. They called themselves Republicans after their political philosophy, republicanism. They distrusted the Federalist tendency to centralize and loosely interpret the Constitution, believing these policies were signs of monarchism and anti-republican values. The party splintered in 1824, with the faction loyal to Andrew Jackson coalescing into the Jacksonian movement, the faction led by John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay forming the National Republican Party and some other groups going on to form the Anti-Masonic Party. The National Republicans, Anti-Masons, and other opponents of Andrew Jackson later formed themselves into the Whig Party.

The United States presidential election of 1792 was the second quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, November 2 to Wednesday, December 5, 1792. Incumbent President George Washington was elected to a second term by a unanimous vote in the electoral college, while John Adams was re-elected as vice president. Washington was essentially unopposed, but Adams faced a competitive re-election against Governor George Clinton of New York.

The United States presidential election of 1796 was the third quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, November 4 to Wednesday, December 7, 1796. It was the first contested American presidential election, the first presidential election in which political parties played a dominant role, and the only presidential election in which a president and vice president were elected from opposing tickets. Incumbent Vice President John Adams of the Federalist Party defeated former Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson of the Democratic-Republican Party.

The United States presidential election of 1812, the seventh quadrennial American presidential election, was held from Friday, October 30, 1812 to Wednesday, December 2, 1812. Taking place in the shadow of the War of 1812, incumbent Democratic-Republican President James Madison defeated DeWitt Clinton, who drew support from dissident Democratic-Republicans in the North as well as Federalists. It was the first presidential election to be held during a major war involving the United States.

The United States presidential election of 1816 was the eighth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, November 1 to Wednesday, December 4, 1816. In the first election following the end of the War of 1812, Democratic-Republican candidate James Monroe defeated Federalist Rufus King. The election was the last in which the Federalist Party fielded a presidential candidate.

There have been 90 gubernatorial elections in the state of New York since 1777. The next one will be held on November 3, 2022.
New York is a Democratic stronghold and one of the three largest Democratic states alongside California and Illinois.

Daniel Rodney was an American merchant and politician from Lewes in Sussex County, Delaware. He was a member of the Federalist Party, and later the National Republican Party, who served as Governor of Delaware, U. S. Representative from Delaware and U.S. Senator from Delaware.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 18th Congress were held at different dates in each state between July 1, 1822 and August 14, 1823 during James Monroe's second term in office. This was the first election based on the results of the 1820 Census, which added a total of 26 seats to the House. Four states lost one seat each, while nine states gained anywhere between one and eight seats.

John Bell was governor of the U.S. state of New Hampshire for one year. Samuel Bell, a brother, was the Governor of New Hampshire from 1819 to 1823.
Joseph Haslet was an American planter and politician from Cedar Creek Village in Cedar Creek Hundred, Sussex County, Delaware. He was a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, who served twice as Governor of Delaware.
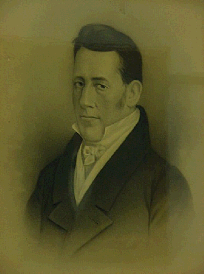
Samuel Paynter was an American merchant and politician from Drawbridge, in Broadkill Hundred, Sussex County, Delaware. He was a member of the Federalist Party, who served in the Delaware General Assembly and as Governor of Delaware.
The 1813 United States Senate election in New York was held on February 2, 1813, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.
The 1824 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from November 1 to 3, 1824, to elect 34 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 19th United States Congress.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1826 occurred on November 7, 1826. Incumbent Democratic governor, John Andrew Shulze, defeated Federalist candidate John Sergeant by a wide margin.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1814 occurred on November 8, 1814. After contemplating retirement, incumbent Democratic-Republican governor Simon Snyder instead chose to run for reelection. He earned a third term as the state's executive after defeating Federalist candidate Isaac Wayne, a former member of the Pennsylvania State Senate.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1808 occurred on November 8, 1808. Incumbent governor Thomas McKean, a former Democratic Republican who had faced impeachment by members of his own party during the prior term, was not a candidate. Democratic-Republican candidate Simon Snyder, former Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives defeated Federalist candidate and former U.S. Senator James Ross to become Governor of Pennsylvania. Snyder, with the aid of a supportive press, campaigned as a "New School Democrat" and attempted to ally himself with James Madison. He painted the former McKean administration as elitist and advocated for popular democracy, governmental intervention in the economy, and infrastructural support for Western Pennsylvania counties.

The 1824 United States elections elected the members of the 19th United States Congress. It marked the end of the Era of Good Feelings and the First Party System. Members of the Democratic-Republican Party continued to maintain a dominant role in federal politics, but the party became factionalized between supporters of Andrew Jackson and supporters of John Quincy Adams. The Federalist Party ceased to function as a national party, having fallen into irrelevance following a relatively strong performance in 1812.

The 1812 United States presidential election in New York took place between October 30 and December 2, 1812, as part of the 1812 United States presidential election. The state legislature chose 29 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for President and Vice President.
As most Presidents have careers in politics and some lose re-election, there have been many elections lost by presidents of the United States.