
The United States presidential election of 1876 was the 23rd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1876. It was one of the most contentious and controversial presidential elections in American history, and is known for being the catalyst for the end of Reconstruction. Republican nominee Rutherford B. Hayes faced Democrat Samuel J. Tilden. After a controversial post-election process, Hayes was declared the winner.
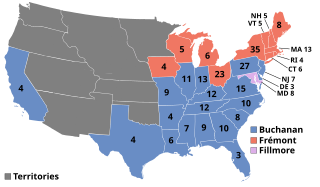
The United States presidential election of 1856 was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a three-way election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and American Party nominee Millard Fillmore.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the nineteenth quadrennial presidential election to select the President and Vice President of the United States. The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin emerged triumphant. The election of Lincoln served as the primary catalyst of the American Civil War.
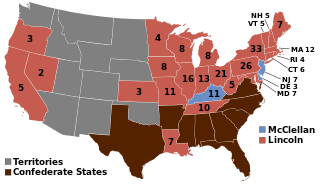
The United States presidential election of 1864, the 20th quadrennial presidential election, was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. In the midst of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 221-21 electoral votes, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.
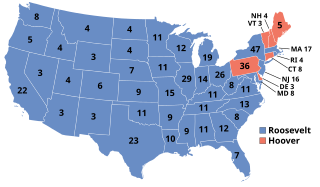
The United States presidential election of 1932 was the thirty-seventh quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. Incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the Governor of New York. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans.

The United States presidential election of 1936 was the thirty-eighth quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Governor Alf Landon of Kansas. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular and electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System.

Andrew Gregg Curtin was a U.S. lawyer and politician. He served as the Governor of Pennsylvania during the Civil War.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 2006 was held on November 7, 2006 and included the races for the Governor of Pennsylvania and Lieutenant Governor of Pennsylvania.

Edgar Cowan was an American lawyer and Republican politician from Greensburg, Pennsylvania. He represented Pennsylvania in the United States Senate during the American Civil War.

The 2010 South Carolina gubernatorial election took place on November 2, 2010. Incumbent Republican Governor Mark Sanford was term limited and unable to seek re-election. Primary elections took place on June 8, 2010 and a runoff election, as was necessary on the Republican side, was held two weeks later on June 22.

The Pennsylvania Gubernatorial election of 1998 was held on November 3, 1998. It was between incumbent Republican Tom Ridge, Democrat Ivan Itkin, Constitutionalist Peg Luksik and Libertarian Ken Krawchuk. Ridge, a popular moderate, won with 57% of the votes cast.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1994 was held on November 8, 1994. The incumbent governor, Bob Casey, Sr. (Democrat), was barred from seeking a third term by the state constitution. The Republican Party nominated Congressman Tom Ridge, while the Democrats nominated Mark Singel, Casey's lieutenant governor. Ridge went on to win the race with 45% of the vote. Singel finished with 39%, and Constitution Party candidate Peg Luksik finished third, garnering 12% of the vote.

The Pennsylvania Gubernatorial election of 1986 was held on November 4, 1986. Democrat Bob Casey narrowly defeated Republican Bill Scranton III, in a race that featured two very high-profile candidates.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1982 was held on November 2, 1982 between incumbent Republican Dick Thornburgh and Democratic U.S. Congressman Allen E. Ertel.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1978 was held on November 7, 1978 between Republican Dick Thornburgh and Democrat Pete Flaherty.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1958 was held on November 4. Democrat David Lawrence defeated Republican Art McGonigle by a smaller than anticipated margin.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1954 was held on November 2. In what is considered a crucial realigning election for the state, Democratic State Senator George Leader defeated Republican incumbent Lieutenant Governor Lloyd Wood by a surprisingly large margin.

The Pennsylvania gubernatorial election of 1950 was held on November 7. For the twenty-second time in twenty-five elections, the Republican candidate was victorious, but by a much smaller than usual margin. Superior Court Judge John S. Fine defeated Democrat Richardson Dilworth, the City Controller of Philadelphia.

The 1948 United States presidential election in New York took place on November 2, 1948. All contemporary 48 states were part of the 1948 United States presidential election. New York voters chose 47 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1956 United States presidential election in Mississippi was held on November 6, 1956. Mississippi voters chose eight representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.




























