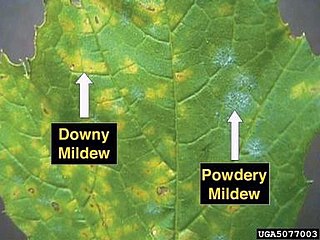
Downy mildew refers to any of several types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites of plants. Downy mildews exclusively belong to the Peronosporaceae family. In commercial agriculture, they are a particular problem for growers of crucifers, grapes and vegetables that grow on vines. The prime example is Peronospora farinosa featured in NCBI-Taxonomy and HYP3. This pathogen does not produce survival structures in the northern states of the United States, and overwinters as live mildew colonies in Gulf Coast states. It progresses northward with cucurbit production each spring. Yield loss associated with downy mildew is most likely related to soft rots that occur after plant canopies collapse and sunburn occurs on fruit. Cucurbit downy mildew only affects leaves of cucurbit plants.

Geum rivale, the water avens, is a flowering plant in the genus Geum within the family Rosaceae. Other names of the plant are nodding avens, drooping avens, cure-all, water flower and Indian chocolate. It is native to the temperate regions of Europe, Central Asia and parts of North America, where it is known as the purple avens. It grows in bogs and damp meadows, and produces nodding red flowers from May to September.

Hyaloperonospora is a genus of oomycete, obligate, plant pathogens that was originally considered to be part of Peronospora. Species in this group produce a disease called downy mildew and can infect many important crops. From the 19 downy mildew producing genera, Hyaloperonospora has been grouped with Perofascia in the brassicolous downy mildews. In the group of downy mildews, Hyaloperonospora is the third biggest genus. The most famous species in the genus is the Hyaloperonospora parasitica, or also known as Hyaloperonospora arabidopsis. This species has become a model organism from its ability to infect the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. It is used to study plant-pathogen interactions, and is currently the only Hyaloperonospora species that has an assembled genome.
Peronospora sparsa is an oomycete plant pathogen that causes downy mildew in berry producing plants; especially in the genus's Rubus and Rosa. Downy mildew plant pathogens are often host specific and cause problems in cloudberries, blackberries, boysenberries, strawberries, and arctic bramble. Since they are host specific, Peronospora sparsa will not cause downy mildew in grapes because a different plant pathogen causes downy mildew in grapes; Plasmopara viticola. Although it depends on the cultivar, symptoms do not normally start until later stages of disease and can look different on different plants. The most common symptoms include red lesions in the veins of leaves, with dry and deformed berries.
Peronospora trifoliorum, commonly known as downy mildew of alfalfa, is an oomycete plant pathogen infecting alfalfa.

Aconitum fischeri is a species of flowering plant of the genus Aconitum, in the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae. It is native to Korea and Siberia and cultivated in gardens in temperate zones for its showy flowers. Plants bloom from early to late summer. The plant contains poisonous aconite, but according to ancient Chinese medical lore, if it is carefully measured, prepared, and used, it is believed to be beneficial in the treatment of colds, coughs, and fevers. If the measuring is in the slightest degree inaccurate, however, it is pure poison. The plant is susceptible to downy mildew caused by the oomycete species Peronospora aconiti.
Peronospora conglomerata is a biotrophic plant pathogen which affects geranium species. Its conidiophores are tree-like and come from the stomata on the leaves. The conidiophores cover the underside of the affected plant's leaves in white patches. These patches may later turn purple or brown. The result of infection by Peronospora conglomerata is scrunched up, yellow leaves that are reduced in size and are prone to falling off.

Peronospora potentillae is a plant pathogen infecting strawberries. It also infects Alchemilla filicaulis.

Blackstonia perfoliata or more commonly known as the yellow-wort is a species of flowering plant in the family Gentianaceae found around the Mediterranean Basin, but extending into northwestern Europe.

Veronica polita, or grey field-speedwell, is a herbaceous flowering plant species in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It has hairy stems, is either prostrate or ascending, with dull green leaves that are one of petiolate, serrate, ovate (rounded) and usually wider than long.The flowers are small and bright blue. The plant has solitary axillary peduncles that are shorter or slightly longer than the leaves. It is native to Eurasia, possibly including the British Isles, western Asia, northern Africa, and North America, but has been introduced into suitable habitats worldwide as a weed of cultivation. It is susceptible to downy mildew disease caused by the oomycete species Peronospora agrestis.

Melampyrum pratense, the common cow-wheat, is a plant species in the family Orobanchaceae.

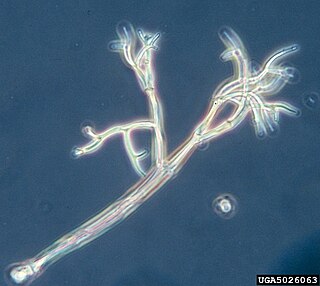
Peronospora is a genus of oomycetes that are obligate plant pathogens of many eudicots. Most species in this group produce a downy mildew disease, which can cause severe damage to many different cultivated crops, as well as wild and ornamental plants. There are 19 genera that produce downy mildew, and Peronospora has been placed alongside Pseudoperonospora in the group of downy mildews with coloured conidia. Peronospora has far more species than any other genus of the downy mildews. However, many species have been moved from this genus to be reclassified to other or new genera. Among these was the most famous Peronospora species, formerly known as Peronospora parasitica, and now known as Hyaloperonospora parasitica. Now, the Peronospora species of most importance is likely the Peronospora tabacina. Peronospora tabacina causes blue mold on tobacco plants and can severely reduce yields of this economically important crop to the point where it has been classified as a bioweapon.

Agrimonia striata is a species of perennial forb belonging to the rose family (Rosaceae). It grows to about 40 inches (1m) producing a dense cluster (raceme) of 5-parted yellow flowers on a hairy stalk above pinnately-divided leaves. It is native to the United States, Canada, and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. It is susceptible to downy mildew caused by the oomycete species Peronospora agrimoniae.

Androsace septentrionalis is a species of annual herbaceous plant in the Primrose family (Primulaceae), native to North America, Asia, and Europe.

Peronospora destructor is a plant pathogen. It causes downy mildew on leaves of cultivated and wild Allium. Allium cepa is most often affected, while Allium schoenoprasum (chives) and Allium porrum (leek) are only occasionally affected.

Lygephila viciae is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in most of Europe.

Megoura viciae is a large, green aphid in the family Aphididae native to Europe that feeds on plants in the genus Vicia. They are commonly known as vetch aphids for this reason.

Alchemilla filicaulis is a species of plants belonging to the family Rosaceae.
Peronospora aquilegiicola is a species of oomycete in the family Peronosporaceae, first described in 2019. It is a plant pathogen: it can infect susceptible plants belonging to the genus Aquilegia, causing the plant disease Aquilegia downy mildew, as well as plants belonging to the genus Semiaquilegia. Peronospora aquilegiicola is native to East Asia, however it has a widespread distribution in the United Kingdom, and has since been detected in the German states of Lower Saxony, North Rhine-Westphalia, and Bavaria.















