Night monkeys, also known as owl monkeys or douroucoulis, are nocturnal New World monkeys of the genus Aotus, the only member of the family Aotidae. The genus comprises eleven species which are found across Panama and much of South America in primary and secondary forests, tropical rainforests and cloud forests up to 2,400 metres (7,900 ft). Night monkeys have large eyes which improve their vision at night, while their ears are mostly hidden, giving them their name Aotus, meaning "earless".

The gray-bellied night monkey, also called the grey-legged douroucouli or lemurine owl monkey, is a small New World monkey of the family Aotidae. Native to tropical and subtropical forests of South America, the gray-bellied night monkey faces a significant threat from hunting, harvesting for use in pharmaceutical research and habitat destruction.

The bald uakari or bald-headed uakari is a small New World monkey characterized by a very short tail; bright, crimson face; a bald head; and long coat. The bald uakari is restricted to várzea forests and other wooded habitats near water in the western Amazon of Brazil and Peru.

The Rio Abiseo National Park is located in the San Martín department of Peru. UNESCO pronounced it as Natural and Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 1990. The park is home to many species of flora and fauna, as well as the location of over 30 pre-Columbian archaeological sites. Since 1986, the park has not been open to tourism due to the fragile nature of both the natural and archaeological environment.

The common woolly monkey, brown woolly monkey, or Humboldt's woolly monkey is a woolly monkey from Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, and Venezuela. It lives in groups of two to 70 individuals, usually splitting the group into smaller subgroups when active.

The white-eared titi monkey also known as the Bolivian titi or Bolivian gray titi, is a species of titi monkey, a type of New World monkey, from eastern Bolivia and an area of western Brazil. The species has a range that extends east from the Manique River in Beni Department, Bolivia to southern Rondônia in Brazil. The southern end of its range includes forests around the city of Santa Cruz de la Sierra.

Coimbra Filho's titi monkey or just Coimbra's titi is a species of titi, a type of New World monkey, endemic to forests in the Brazilian states of Bahia and Sergipe. It was first discovered by Shuji Kobayashi. It is considered one of the most endangered of all Neotropical primates. It is named after Adelmar F. Coimbra-Filho, founder and Former Director of the Rio de Janeiro Primate Centre, in honor of his work in the field of Brazilian primatology and biology.

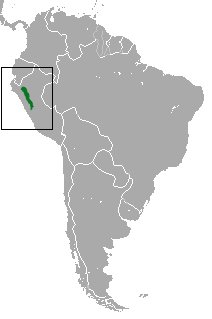
The Rio Mayo titi monkey is a species of titi monkey, a type of New World monkey, endemic to Peru. The Rio Mayo titi, was thought previously to have a small range of origin in the Alto Mayo valley, but research has proven that the range extends southward and reaches the Huayamba River, as well as Bajo Mayo. It had been classified as vulnerable but due to major habitat loss and restricted living space, it is now classified as Critically Endangered. In October 2012, it was included in The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates list. An increase in deforestation is leading to the decrease in available living space for this titi monkey, forcing it to live in sympatry with another species of Callicebus. Yet in some areas, such drastic deforestation has resulted in extremely high population density. The Rio Mayo titi is better adapted to moderately populated areas, thus overpopulation negatively impacts the species. The forests the Rio Mayo titi lives in are being destroyed for agricultural purposes, leaving little forest for the monkeys. They were only seen a few times and featured in museums until 2003 when more research was done on them. In order for this species to survive, their forests need to be protected to avoid overpopulation. Different conservation groups are working to help P. oenanthe survive. Neotropical Primate Conservation, Proyecto Mono Tocón and Amazónicos para la Amazonia are working in the more southern areas to protect the monkey. The Rio Mayo titi is a fairly inconspicuous creature, making observation and research difficult to obtain. Therefore, the traditional use of transect observation to monitor the monkey's population, is less effective. Instead, other methods of calculating the titi monkey's density in certain areas have been taken, such as research into the species-specific calls endemic to a certain area.

The gray woolly monkey or Geoffroy's woolly monkey is a subspecies of the common woolly monkey from South America. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru. L. l. cana gets its common name, gray woolly monkey, from its thick gray coat. Its hands, feet, face and the inside of the arms are dark in color. The gray woolly monkey has been considered endangered by IUCN since 2008. The subspecies is listed as endangered because it suffered a 50% decrease in population over the past 45 years due to deforestation and hunting.

The brown spider monkey or variegated spider monkey is a critically endangered species of spider monkey, a type of New World monkey, from forests in northern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela.

Azara's night monkey, also known as the southern night monkey, is a night monkey species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Peru and Paraguay. The species is monogamous, with the males providing a large amount of parental care. It is named after Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara. Although primarily nocturnal, some populations of Azara's night monkey are unique among night monkeys in being active both day and night. The species is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

Nancy Ma's night monkey is a night monkey species from South America. It is found in Brazil and Peru. The species is named after Dr. Nancy Shui-Fong Ma.

Spix's night monkey, also known as the Colombian gray night monkey, noisy night monkey and Spix's owl monkey, is a night monkey species from South America. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru.

The yellow-tailed woolly monkey is a New World monkey endemic to Peru. It is a rare primate species found only in the Peruvian Andes, in the departments of Amazonas and San Martin, as well as bordering areas of La Libertad, Huánuco, and Loreto.

The Panamanian night monkey or Chocoan night monkey is a species of night monkey formerly considered a subspecies of the gray-bellied night monkey of the family Aotidae. Its range consists of Panama and the Chocó region of Colombia. There are also unconfirmed reports of its occurrence in Costa Rica, especially on the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica. The species definitely occurs in the Atlantic lowlands of Panama close to the Costa Rica border.

The gray-handed night monkey is a species of night monkey formerly considered a subspecies of Gray-bellied night monkey of the family Aotidae. Its range consists of parts of Colombia and Venezuela. The exact classification of the gray-handed night monkey is uncertain. While some authors consider it a subspecies of the gray-bellied night monkey, A. lemurinus, other authors consider it a separate species, A. griseimembra.

The Ecuadorian capuchin, or Ecuadorian white-fronted capuchin is a species of gracile capuchin monkey of the family Cebidae. It was formerly classified as a subspecies of the white-fronted capuchin . Mittermeier and Rylands elevated it to a separate species in 2013. The primary physical distinction between C. albifrons and C. aequatorialis is their coloration. Due to low density and distribution researchers have not been able to make a confident molecular genetic assessment of the C. aequatorialis population, but assign it species status based on geographical isolation, morphological characteristics, and the phylogenetic species concept. The location range of the Ecuadorian Capuchin is from Western lowland Ecuador to North West Peru. The conservation status of the Ecuadorian Capuchin was originally near threatened but was revised in 2008 by the IUCN to critically endangered due to the population's rapid decline. Anthropogenic factors such as habitat fragmentation from rapid deforestation, creation of agricultural lands, and persecution from farmers are to blame for the species' critically endangered status.