
Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the formula [(CH3)2N]3PO. This colorless liquid is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2)2 (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
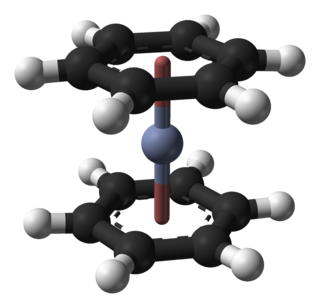
Bis(benzene)chromium is the organometallic compound with the formula Cr(η6-C6H6)2. It is sometimes called dibenzenechromium. The compound played an important role in the development of sandwich compounds in organometallic chemistry and is the prototypical complex containing two arene ligands.

Divinylbenzene (DVB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H4(CH=CH2)2 and structure H2C=CH−C6H4−HC=CH2. It is related to styrene by the addition of a second vinyl group. It is a colorless liquid manufactured by the thermal dehydrogenation of isomeric diethylbenzenes. Under synthesis conditions, o-divinylbenzene converts to naphthalene and thus is not a component of the usual mixtures of DVB.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).

Tributylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula P(CH2CH2CH2CH3)3, often abbreviated as PBu3. It is a tertiary phosphine. It is an oily liquid at room temperature, with a nauseating odor. It reacts slowly with atmospheric oxygen, and rapidly with other oxidizing agents, to give the corresponding phosphine oxide. It is usually handled using air-free techniques.

Diphenylphosphine, also known as diphenylphosphane, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PH. This foul-smelling, colorless liquid is easily oxidized in air. It is a precursor to organophosphorus ligands for use as catalysts.

Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride (THPC) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula [P(CH2OH)4]Cl. The cation P(CH2OH)4+ is four-coordinate, as is typical for phosphonium salts. THPC has applications as a precursor to fire-retardant materials, as well as a microbiocide in commercial and industrial water systems.

Dimethylphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with a formula P(C6H5)(CH3)2. The phosphorus is connected to a phenyl group and two methyl groups, making it the simplest aromatic alkylphosphine. It is colorless air sensitive liquid. It is a member of series (CH3)3-n(C6H5)2P that also includes n = 0, n = 2, and n = 3 that are often employed as ligands in metal phosphine complexes.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).
Hydrophosphination is the insertion of a carbon-carbon multiple bond into a phosphorus-hydrogen bond forming a new phosphorus-carbon bond. Like other hydrofunctionalizations, the rate and regiochemistry of the insertion reaction is influenced by the catalyst. Catalysts take many forms, but most prevalent are bases and free-radical initiators. Most hydrophosphinations involve reactions of phosphine (PH3).
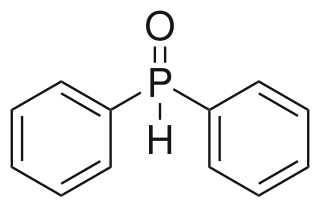
Diphenylphosphine oxide is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2P(O)H. It is a white solid that soluble in polar organic solvents.

Vinyldiphenylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCH=CH2. This colorless, air-sensitive solid is used as a precursor to ligands used in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. It is prepared by treating chlorodiphenylphosphine with vinyl Grignard reagents.
In organophosphorus chemistry, an aminophosphine is a compound with the formula R3−nP(NR2)n where R = H or an organic substituent, and n = 0, 1, 2. At one extreme, the parent H2PNH2 is lightly studied and fragile, but at the other extreme tris(dimethylamino)phosphine (P(NMe2)3) is commonly available. Intermediate members are known, such as Ph2PN(H)Ph. These compounds are typically colorless and reactive toward oxygen. They have pyramidal geometry at phosphorus.

Nontrigonal pnictogen compounds refer to tricoordinate trivalent pnictogen compounds that are not of typical trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. By virtue of their geometric constraint, these compounds exhibit distinct electronic structures and reactivities, which bestow on them potential to provide unique nonmetal platforms for bond cleavage reactions.
Gallium monoiodide is an inorganic gallium compound with the formula GaI or Ga4I4. It is a pale green solid and mixed valent gallium compound, which can contain gallium in the 0, +1, +2, and +3 oxidation states. It is used as a pathway for many gallium-based products. Unlike the gallium(I) halides first crystallographically characterized, gallium monoiodide has a more facile synthesis allowing a synthetic route to many low-valent gallium compounds.



















