
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver perceives the similarity between a mimic and a model and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by the selective action of a signal-receiver or dupe. Birds, for example, use sight to identify palatable insects and butterflies, whilst avoiding the noxious ones. Over time, palatable insects may evolve to resemble noxious ones, making them mimics and the noxious ones models. In the case of mutualism, sometimes both groups are referred to as "co-mimics". It is often thought that models must be more abundant than mimics, but this is not so. Mimicry may involve numerous species; many harmless species such as hoverflies are Batesian mimics of strongly defended species such as wasps, while many such well-defended species form Müllerian mimicry rings, all resembling each other. Mimicry between prey species and their predators often involves three or more species.

Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on butterflies in the rainforests of Brazil.

Müllerian mimicry is a natural phenomenon in which two or more well-defended species, often foul-tasting and sharing common predators, have come to mimic each other's honest warning signals, to their mutual benefit. The benefit to Müllerian mimics is that predators only need one unpleasant encounter with one member of a set of Müllerian mimics, and thereafter avoid all similar coloration, whether or not it belongs to the same species as the initial encounter. It is named after the German naturalist Fritz Müller, who first proposed the concept in 1878, supporting his theory with the first mathematical model of frequency-dependent selection, one of the first such models anywhere in biology.

Ant mimicry or myrmecomorphy is mimicry of ants by other organisms. Ants are abundant all over the world, and potential predators that rely on vision to identify their prey, such as birds and wasps, normally avoid them, because they are either unpalatable or aggressive. Spiders are the most common ant mimics. Additionally, some arthropods mimic ants to escape predation, while others mimic ants anatomically and behaviourally to hunt ants in aggressive mimicry. Ant mimicry has existed almost as long as ants themselves; the earliest ant mimics in the fossil record appear in the mid Cretaceous alongside the earliest ants. Indeed one of the earliest, Burmomyrma, was initially classified as an ant.

Portia labiata is a jumping spider found in Sri Lanka, India, southern China, Burma (Myanmar), Malaysia, Singapore, Java, Sumatra and the Philippines. In this medium-sized jumping spider, the front part is orange-brown and the back part is brownish. The conspicuous main eyes provide vision more acute than a cat's during the day and 10 times more acute than a dragonfly's, and this is essential in P. labiata′s navigation, hunting and mating.

Abracadabrella is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae whose spp. appear to mimics flies. The type species for the genus was described by Ludwig Koch (1879) as Marptusa elegans, transferred to Ocrisiona by Eugène Simon (1901) then placed into Abracadabrella by Marek Żabka (1991).

Cosmophasis is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae. Some species occur in Africa, while most are found in Southeast Asia, down to Australia. Although most species more or less mimic ants, there are also colorful species that follow a different strategy.

Aggressive mimicry is a form of mimicry in which predators, parasites, or parasitoids share similar signals, using a harmless model, allowing them to avoid being correctly identified by their prey or host. Zoologists have repeatedly compared this strategy to a wolf in sheep's clothing. In its broadest sense, aggressive mimicry could include various types of exploitation, as when an orchid exploits a male insect by mimicking a sexually receptive female, but will here be restricted to forms of exploitation involving feeding. An alternative term Peckhamian mimicry has been suggested, but is seldom used. For example, indigenous Australians who dress up as and imitate kangaroos when hunting would not be considered aggressive mimics, nor would a human angler, though they are undoubtedly practising self-decoration camouflage. Treated separately is molecular mimicry, which shares some similarity; for instance a virus may mimic the molecular properties of its host, allowing it access to its cells.

Animal coloration is the general appearance of an animal resulting from the reflection or emission of light from its surfaces. Some animals are brightly coloured, while others are hard to see. In some species, such as the peafowl, the male has strong patterns, conspicuous colours and is iridescent, while the female is far less visible.

Kallima paralekta, the Indian leafwing or Malayan leafwing, is a species of brush-footed butterfly of the genus Kallima. Despite its common names, it is not found in India or Malaysia, but is endemic to Java and Sumatra of Indonesia. Like other members of its genus, it is remarkable for its strong resemblance to a dead leaf when its wings are folded. It was one of the species encountered by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace in his travels in maritime Southeast Asia. It is mentioned in his famous 19th-century work The Malay Archipelago as one of the best examples of protective camouflage achieved through natural selection.

Adaptive Coloration in Animals is a 500-page textbook about camouflage, warning coloration and mimicry by the Cambridge zoologist Hugh Cott, first published during the Second World War in 1940; the book sold widely and made him famous.

The Colours of Animals is a zoology book written in 1890 by Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton (1856–1943). It was the first substantial textbook to argue the case for Darwinian selection applying to all aspects of animal coloration. The book also pioneered the concept of frequency-dependent selection and introduced the term "aposematism".

Concealing-Coloration in the Animal Kingdom: An Exposition of the Laws of Disguise Through Color and Pattern; Being a Summary of Abbott H. Thayer’s Discoveries is a book published ostensibly by Gerald H. Thayer in 1909, and revised in 1918, but in fact a collaboration with and completion of his father Abbott Handerson Thayer's major work.

Animal Coloration, or in full Animal Coloration: An Account of the Principal Facts and Theories Relating to the Colours and Markings of Animals, is a book by the English zoologist Frank Evers Beddard, published by Swan Sonnenschein in 1892. It formed part of the ongoing debate amongst zoologists about the relevance of Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection to the observed appearance, structure, and behaviour of animals, and vice versa.
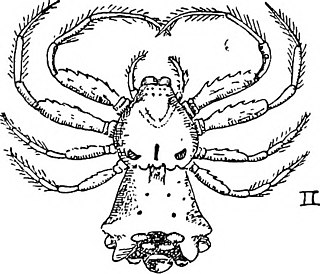
Phrynarachne is a genus of crab spiders first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1869.

Phrynarachne ceylonica, the bird dung spider, is a species of spiders of the family Thomisidae. It is found in China, Japan, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, and India. The species is known to discharge a foul smell which help it attract prey and deter predators. It both smells like and resembles bird feces, hence the name 'bird dung spider'. The bird dung spider resembles bird feces only when it curls up in response to a predatory threat. It is characteristically known for its dual-purposed ability to mimic the smell and appearance of bird feces to both lure prey and protect against predators. This species of crab spider has a flat, black-brown abdomen with bright yellow legs. The width of the female abdomen is approximately 9.3 mm and the length of the body is approximately 14.5 mm.

Animal coloration provided important early evidence for evolution by natural selection, at a time when little direct evidence was available. Three major functions of coloration were discovered in the second half of the 19th century, and subsequently used as evidence of selection: camouflage ; mimicry, both Batesian and Müllerian; and aposematism.

Mastophora hutchinsoni, also known as the American bolas spider, is a species of orb weaver in the genus Mastophora. The genus is distributed extensively throughout various subtropical geographical areas including Australia, South Africa, Oriental Asia, and the Americas and is not found in Europe. The hunting behavior of adult female M. hutchinsoni is unusual because they are bolas spiders. They mimic moth pheromones to attract male moths, and female M. hutchinsoni have evolved to alter their chemical release to target different moths. They then capture their prey with a sticky drop on the end of a silk line, resembling a bolas.

Dazzled and Deceived: Mimicry and Camouflage is a 2009 book on camouflage and mimicry, in nature and military usage, by the science writer and journalist Peter Forbes. It covers the history of these topics from the 19th century onwards, describing the discoveries of Henry Walter Bates, Alfred Russel Wallace and Fritz Müller, especially their studies of butterflies in the Amazon. The narrative also covers 20th-century military camouflage, begun by the painter Abbot Thayer who advocated disruptive coloration and countershading and continued in the First World War by the zoologist John Graham Kerr and the marine artist Norman Wilkinson, who developed dazzle camouflage. In the Second World War, the leading expert was Hugh Cott, who advised the British army on camouflage in the Western Desert.
Exechocentrus lancearius is a species of spider in the orb-weaver spider family Araneidae, found only in Madagascar. It was initially described from a partial specimen of an adult female. The first description of a complete specimen and its prey-catching behaviour was published in 2012. E. lancearius is a bolas spider. Rather than using a web, adult females catch their prey by using a line with one or two sticky drops which they swing.

















