
The San Gabriel Mountains are a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Transverse Ranges and lies between the Los Angeles Basin and the Mojave Desert, with Interstate 5 to the west and Interstate 15 to the east. The range lies in, and is surrounded by, the Angeles and San Bernardino National Forests, with the San Andreas Fault as its northern border.

Pinus flexilis, the limber pine, is a species of pine tree-the family Pinaceae that occurs in the mountains of the Western United States, Mexico, and Canada. It is also called Rocky Mountain white pine.

The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges that stretch 1,500 km (930 mi) from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific Coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from 150 to 3,300 m.

Coulter pine, or big-cone pine, is a native of the coastal mountains of Southern California in the United States and northern Baja California in Mexico. Isolated groves are found as far north as Clearlake, California on the flanks of Mt. Konocti and Black Diamond Mines Regional Preserve. It is named after Thomas Coulter, an Irish botanist and physician. The Coulter pine produces the heaviest cone of any pine tree, up to 5 kg (11 lb) and among conifers is exceeded only by the cones of Araucaria bidwillii.

The San Jacinto Mountains are a mountain range in Riverside County, located east of Los Angeles in southern California in the United States. The mountains are named for one of the first Black Friars, Saint Hyacinth, who is a popular patron in Latin America.
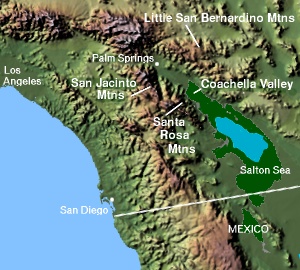
The Santa Rosa Mountains are a short mountain range in the Peninsular Ranges system, located east of the Los Angeles Basin and northeast of the San Diego metropolitan area of southern California, in the southwestern United States.

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.

The San Bernardino National Forest is a United States National Forest in Southern California encompassing 823,816 acres (3,333.87 km2) of which 677,982 acres (2,743.70 km2) are federal. The forest is made up of two main divisions, the eastern portion of the San Gabriel Mountains and the San Bernardino Mountains on the easternmost of the Transverse Ranges, and the San Jacinto and Santa Rosa Mountains on the northernmost of the Peninsular Ranges. Elevations range from 2,000 to 11,499 feet. The forest includes seven wilderness areas: San Gorgonio, Cucamonga, San Jacinto, South Fork, Santa Rosa, Cahuilla Mountain and Bighorn Mountain. Forest headquarters are located in the city of San Bernardino. There are district offices in Lytle Creek, Idyllwild, and Fawnskin.

The Sierra de la Laguna is a mountain range at the southern end of the Baja California peninsula in Mexico, and is the southernmost range of the Peninsular Ranges System.

The Sierra de la Laguna pine–oak forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion, found in the Sierra de la Laguna mountain range at the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, Mexico.

The Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument is a National Monument in southern California. It includes portions of the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto mountain ranges, the northernmost ones of the Peninsular Ranges system. The national monument covers portions of Riverside County, west of the Coachella Valley, approximately 100 miles (160 km) southeast of downtown Los Angeles.

Sierra de San Pedro Mártir National Park is a national park in the Mexican state of Baja California. The Park is part of the municipality of Ensenada, Baja California. The area was first explored by Native people then Europeans in 1701 by Eusebio Francisco Kino by Dominican orders.

Galium californicum is a species of flowering plant in the coffee family known by the common name California bedstraw.

Arctostaphylos obispoensis is a species of manzanita, known by the common names bishop manzanita and serpentine manzanita, endemic to California.

Arctostaphylos pilosula is a species of manzanita, known by the common names La Panza manzanita and Santa Margarita manzanita, that is endemic to California.

Toro Peak, in Southern California, is the highest mountain in the Santa Rosa Mountain Range. It is located 15 mi (24 km) south of Palm Springs, 12 mi (19 km) west of the Salton Sea, and 31 mi (50 km) east of Temecula, in the County of Riverside, California.

Constitution 1857 National Park is located in the pine forests of the Sierra de Juárez mountain range in the northern part of Baja California, Mexico. The park is an important preserve for many native wild animals like bighorn sheep and mule deer. The park is characterized by the large variety of coniferous plant species.

The California montane chaparral and woodlands is an ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund, spanning 7,900 square miles (20,000 km2) of mountains in the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and Coast Ranges of southern and central California. The ecoregion is part of the larger California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, and belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.

Flora of the Colorado Desert, located in Southern California. The Colorado Desert is a sub-region in the Sonoran Desert ecoregion of southwestern North America. It is also known as the Low Desert, in contrast to the higher elevation Mojave Desert or High Desert, to its north.
The Philip L. Boyd Deep Canyon Desert Research Center is one of the original seven of the total 39 sites in the University of California Natural Reserve System. It contains lands originally donated to the University by regent Philip L. Boyd in 1958. The Research Center is contained within UNESCO's Mojave and Colorado Deserts Biosphere Reserve.



















