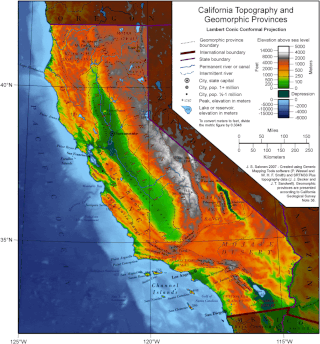
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states.

Idyllwild, Pine Cove, and Fern Valley are three adjacent unincorporated communities in the San Jacinto Mountains in Riverside County, California, United States. Idyllwild has the largest population of the three. For statistical purposes, the United States Census Bureau has defined Idyllwild–Pine Cove as a census-designated place (CDP). The CDP's population was 3,874 at the 2010 census, up from 3,504 as of the 2000 census.

The San Gabriel Mountains comprise a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Transverse Ranges and lies between the Los Angeles Basin and the Mojave Desert, with Interstate 5 to the west and Interstate 15 to the east. The range lies in, and is surrounded by, the Angeles and San Bernardino National Forests, with the San Andreas Fault as its northern border.

The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name is due to the ranges' east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.

San Jacinto Peak is a 10,834 ft (3,302 m) peak in the San Jacinto Mountains, in Riverside County, California. Lying within Mount San Jacinto State Park it is the highest both in the range and the county, and serves as the southern border of the San Gorgonio Pass. Naturalist John Muir wrote of San Jacinto Peak, "The view from San Jacinto is the most sublime spectacle to be found anywhere on this earth!"

San Gorgonio Mountain, also known locally as Mount San Gorgonio, or Old Greyback, is the highest peak in Southern California and the Transverse Ranges at 11,503 feet (3,506 m).

The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at 11,503 feet (3,506 m) at San Gorgonio Mountain – the tallest peak in Southern California. The San Bernardinos form a significant region of wilderness and are popular for hiking and skiing.
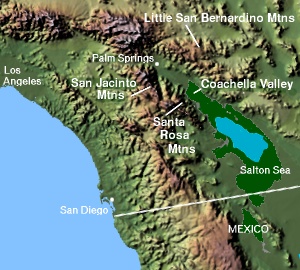
The Santa Rosa Mountains are a short mountain range in the Peninsular Ranges system, located east of the Los Angeles Basin and northeast of the San Diego metropolitan area of Southern California, in the Southwestern United States.

The San Bernardino National Forest is a United States national forest in Southern California encompassing 823,816 acres (3,333.87 km2) of which 677,982 acres (2,743.70 km2) are federal. The forest is made up of two main divisions, the eastern portion of the San Gabriel Mountains and the San Bernardino Mountains on the easternmost of the Transverse Ranges, and the San Jacinto and Santa Rosa Mountains on the northernmost of the Peninsular Ranges. Elevations range from 2,000 to 11,499 feet. The forest includes seven wilderness areas: San Gorgonio, Cucamonga, San Jacinto, South Fork, Santa Rosa, Cahuilla Mountain and Bighorn Mountain. Forest headquarters are located in the city of San Bernardino. There are district offices in Lytle Creek, Idyllwild, and Fawnskin. The Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail runs through part of the San Bernardino National Forest.

The San Gorgonio Wilderness is located in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains, in San Bernardino County and into northern Riverside County, Southern California.

The San Gorgonio Pass, or Banning Pass, is a 2,600 ft (790 m) elevation gap on the rim of the Great Basin between the San Bernardino Mountains to the north and the San Jacinto Mountains to the south. The pass was formed by the San Andreas Fault, a major transform fault between the Pacific plate and the North American plate that is slipping at a rate of 7.2 ±2.8 mm/year. The tall mountain ranges on either side of the pass result in the pass being a transitional zone from a Mediterranean climate west of the pass, to a Desert climate east of the pass. This also makes the pass area one of the windiest places in the United States, and why it is home to the San Gorgonio Pass wind farm.

The Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument is a national monument in Southern California. It includes portions of the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto mountain ranges, the northernmost ones of the Peninsular Ranges system. The national monument covers portions of Riverside County, west of the Coachella Valley, approximately 100 miles (160 km) southeast of downtown Los Angeles.

The Morongo Basin is an endorheic basin and valley region located in eastern San Bernardino County, in Southern California.

The Santa Rosa Wilderness is a 72,259-acre (292.42 km2) wilderness area in Southern California, in the Santa Rosa Mountains of Riverside and San Diego counties, California. It is in the Colorado Desert section of the Sonoran Desert, above the Coachella Valley and Lower Colorado River Valley regions in a Peninsular Range, between La Quinta to the north and Anza Borrego Desert State Park to the south. The United States Congress established the wilderness in 1984 with the passage of the California Wilderness Act, managed by both the US Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. In 2009, the Omnibus Public Land Management Act was signed into law which added more than 2,000 acres (8.1 km2). Most of the Santa Rosa Wilderness is within the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument.

Toro Peak, in Southern California, is the highest mountain in the Santa Rosa Mountain Range. It is located 15 miles (24 km) south of Palm Springs, 12 miles (19 km) west of the Salton Sea, and 31 miles (50 km) east of Temecula, in the County of Riverside, California.

Forest Falls is an unincorporated community in San Bernardino County, California, 75 miles (121 km) due east of Los Angeles. The community has a population of 1,102 and contains 712 houses. Forest Falls is best known for the waterfalls on Vivian and Falls creeks and as a point of access for recreation in the San Bernardino National Forest, particularly the San Gorgonio Wilderness Area, which lies directly north of the community.

Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the United States. The name was derived from the city of Riverside, which is the county seat.

The geography of southern California refers to the geography of southern California in the United States.

Sugarloaf Mountain is a large prominent peak in the San Bernardino Mountains in Southern California. With a peak elevation of 9,952 feet (3,033 m), it is the highest peak in the San Bernardino Mountains outside the San Gorgonio Wilderness. Wilderness permits are not required to hike the peak, but a Forest Service pass is required to park on any fire road. Sugarloaf Mountain is clearly visible in most parts of Big Bear Valley. The peak is especially prominent when entering the Big Bear area from Highway 18 from the Lucerne Valley. Located in a unique transition zone in Southern California, the climate is influenced by the deserts, the inland valley, and alpine climates. The north face of the summit is usually covered with snow during the winter months.

Sand to Snow National Monument is a U.S. National Monument located in San Bernardino County and northern Riverside County, Southern California.