
The Crabronidae are a large paraphyletic group of wasps, including nearly all of the species formerly comprising the now-defunct superfamily Sphecoidea. It collectively includes well over 200 genera, containing well over 9000 species. Crabronids were originally a part of the Sphecidae, but the latter name is now restricted to a separate family based on what was once the subfamily Sphecinae. Several of the subfamilies of the Crabronidae are often treated as families in their own right, as is true of the most recent phylogenies.

Pison is a cosmopolitan genus of wasps within the family Crabronidae. The genus comprises 145 described species, although many species, especially in South America remain undescribed.

Chalybion is a genus of blue mud dauber wasps in the family Sphecidae. Chalybion species nest in a wide range of natural and artificial cavities such as holes in wood, walls, plant stems, etc., where they typically provision their brood cells with paralyzed spiders. They also reuse old nests of other wasps like Trypoxylon and Sceliphron.

Ammophila sabulosa, the red-banded sand wasp, is a species of the subfamily Ammophilinae of the solitary hunting wasp family Sphecidae, also called digger wasps. Found across Eurasia, the parasitoid wasp is notable for the mass provisioning behaviour of the females, hunting caterpillars mainly on sunny days, paralysing them with a sting, and burying them in a burrow with a single egg. The species is also remarkable for the extent to which females parasitise their own species, either stealing prey from nests of other females to provision their own nests, or in brood parasitism, removing the other female's egg and laying one of her own instead.

Socca pustulosa is a Orb-weaver spider species in the family Araneidae, and it was first described by a French scientist Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1841 from Tasmania, Australia, but later on when Walckenaer examined the specimen collected from New Zealand and renamed it as a different species- Epeira verrucosa. Until 1917, Dalmas reviewed the Australian pustulosa and New Zealand verrucosa and realized they were the same species. Although S. pustulosa has been accepted for some time in the genus of Eriophora, the evidence supporting its placement within this genus were not fully convincing. Therefore, an alternative view was proposed in 2022- a new genus established to accommodate pustulosa along with 11 other spider species from Australia; the diagnostic test based on haplotype analysis and systematic morphology study by arachnologists and found the anatomical features of male pedipalp terminal apophysis differs from other orb-web species.

Tachytes is a genus of predatory, solitary wasps, containing about 300 species.

Pison spinolae, commonly known as mason wasp, is a solitary wasp of the family Crabronidae, found throughout New Zealand.
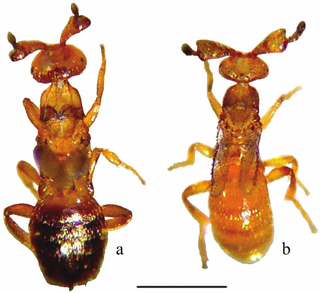
Melittobia australica is a species of chalcid wasp from the family Eulophidae which is a gregarious ecto-parasitoid of acuealate Hymenoptera.

Aha is a genus of wasp. As of 2017, it consists of two species: A. ha, and A. evansi, and is endemic to Australia. The American entomologist Arnold S. Menke named and circumscribed the genus in 1977 for his newly-described species A. ha and A. evansi.

Trypoxylini is a tribe of traditional Sphecidae in the family Crabronidae. There are at least 840 described species in Trypoxylini.
Sphecius convallis, the Pacific cicada killer, is a species of sand wasp in the family Crabronidae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Sphecius hogardii, the Caribbean cicada killer, is a species of sand wasp in the family Crabronidae. It is found in the Caribbean and North America.
Liris argentatus is a species of square-headed wasp in the family Crabronidae. It is found in the Caribbean, Central America, North America, and Oceania. Females overwinter as adults.
Pison koreense is a species of square-headed wasp in the family Crabronidae. It is found in Europe and Northern Asia, North America, and Southern Asia.
A list of the species of Hymenoptera from New Zealand; currently listing the 'stinging wasps' (Aculeata), which includes ants, bees, and social wasps.

Trichrysis cyanea is a species of cuckoo wasps, insects in the family Chrysididae.

Stictia signata is a species of sand wasp in the family Crabronidae. It is found in the Caribbean Sea, Central America, North America, and South America. It preys primarily on flies.

Maratus griseus, the white-banded house jumping spider, is a species of jumping spider in the family Salticidae. It is found in Australia and New Zealand.

Pison peletieri is a wasp of the family Crabronidae. It is endemic to Australia, and was introduced to New Zealand in 2001.
Pison marginatum is a wasp of the family Crabronidae. It is found in Australia, South East Asia and many of the islands of the Pacific Ocean.














