
Tulbaghia is a genus of monocotyledonous herbaceous perennial bulbs native to Africa, belonging to the Amaryllis family. It is one of only two known genera in the society garlic tribe within the onion subfamily. The genus was named for Ryk Tulbagh (1699–1771), one time governor of The Cape of Good Hope.

The Restionaceae, also called restiads and restios, are a family of flowering plants native to the Southern Hemisphere; they vary from a few centimeters to 3 meters in height. Following the APG IV (2016): the family now includes the former families Anarthriaceae, Centrolepidaceae and Lyginiaceae, and as such includes 51 genera with 572 known species. Based on evidence from fossil pollens, the Restionaceae likely originated more than 65 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period, when the southern continents were still part of Gondwana.

Kniphofia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae, first described as a genus in 1794. Species are native to Africa. Common names include tritoma, red hot poker, torch lily and poker plant.

Disa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceae. It comprises about 182 species. Most of the species are indigenous to tropical and southern Africa, with a few more in the Arabian Peninsula, Madagascar, and Réunion. Disa bracteata is naturalised in Western Australia, where the local name is "African weed-orchid."
Tannodia is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1861. It is native to Africa, Madagascar, and Comoros.
- Tannodia congolensis - Zaïre
- Tannodia cordifolia - Comoros, Madagascar
- Tannodia grandiflora - Diana Region in Madagascar
- Tannodia nitida - Atsinanana in Madagascar
- Tannodia obovata - Atsinanana in Madagascar
- Tannodia pennivenia - Atsinanana in Madagascar
- Tannodia perrieri - Madagascar
- Tannodia swynnertonii - Tanzania, Mozambique, Zimbabwe
- Tannodia tenuifolia - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Zambia

Plectranthus, with some 72 species, is a genus of herbaceous perennial plants, rarely annuals or soft-wooded shrubs, sometimes succulent; sometimes with a tuberous base. Common names include spur-flower. Plectranthus species are found in Southern and Tropical Africa and Madagascar, and one in Sri Lanka.

The individual member states of the African Union (AU) coordinate foreign policy through this agency, in addition to conducting their own international relations on a state-by-state basis. The AU represents the interests of African peoples at large in intergovernmental organizations (IGO's); for instance, it is a permanent observer at the United Nations' General Assembly.
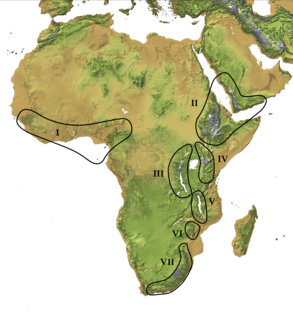
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

Mimusops is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753.

Hyparrhenia is a genus of grasses. Many species are known commonly as thatching grass.

Vahlia is a genus of herbs and subshrubs that grow in Africa and the Indian subcontinent. There are at least five species.

Microcoelia is a genus of orchids native to sub-Saharan Africa as well as to Madagascar and other islands of the Indian Ocean.
- Microcoelia aphylla(Thouars) Summerh. - from Kenya and Uganda south to KwaZulu-Natal, plus Madagascar, Mauritius and Réunion
- Microcoelia aurantiaca(Schltr.) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia bispiculataL.Jonss. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia bulbocalcarataL.Jonss. - Príncipe, Cameroon, Gabon, Uganda, Rwanda
- Microcoelia caespitosa(Rolfe) Summerh. in J.Hutchinson & J.M.Dalziel - western and central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre and Uganda
- Microcoelia corallinaSummerh. - Tanzania, Mozambique, Malawi
- Microcoelia cornuta(Ridl.) Carlsward - Madagascar, Comoros
- Microcoelia decaryanaL.Jonss. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia dolichorhiza(Schltr.) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia elliotii(Finet) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia exilisLindl. - from Kenya and Uganda south to KwaZulu-Natal, plus Madagascar
- Microcoelia gilpinae(Rchb.f. & S.Moore) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia globulosa(Hochst.) L.Jonss. - from Nigeria east to Eritrea, south to Angola and Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia hirschbergiiSummerh. - Zaïre, Zambia
- Microcoelia jonssoniiSzlach. & Olszewski - Central African Republic
- Microcoelia koehleri(Schltr.) Summerh. - from Nigeria to Tanzania, south to Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia konduensis(De Wild.) Summerh - western and central Africa
- Microcoelia leptostele(Summerh.) L.Jonss. - Central African Republic, Zaïre
- Microcoelia macrantha(H.Perrier) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia macrorhynchia(Schltr.) Summerh. in J.Hutchinson & J.M.Dalziel - central Africa
- Microcoelia megalorrhiza(Rchb.f.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi
- Microcoelia microglossaSummerh. - central Africa
- Microcoelia moreauaeL.Jonss - Kenya, Tanzania, Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia nyungwensisL.Jonss. - Rwanda
- Microcoelia obovataSummerh. - from Kenya south to KwaZulu-Natal
- Microcoelia ornithocephalaP.J.Cribb - Malawi
- Microcoelia perrieri(Finet) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia physophora(Rchb.f.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Madagascar
- Microcoelia sanfordiiL.Jonss - Cameroon
- Microcoelia smithii(Rolfe) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi
- Microcoelia stolzii(Schltr.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Cremaspora is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is the only genus in the tribe Cremasporeae. It was described by George Bentham in 1849. The genus is widespread across much of sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal to Tanzania and south to Mozambique and Zimbabwe, in addition to Madagascar, Comoros, and Cape Verde. There are, however, only two currently recognized species.

Coleochloa is a plant genus in the family Cyperaceae. It is found in sub-Saharan Africa and on the Island of Madagascar.

Karomia is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae, first described in 1932. It is native to eastern and southern Africa, Madagascar, and Vietnam.
- Karomia fragransDop - Vietnam
- Karomia gigas(Faden) Verdc. - Kenya, Tanzania
- Karomia humbertii(Moldenke) R.Fern. - Madagascar
- Karomia macrocalyx(Baker) R.Fern. - Madagascar
- Karomia madagascariensis(Moldenke) R.Fern. - Madagascar
- Karomia microphylla(Moldenke) R.Fern. - Madagascar
- Karomia mira(Moldenke) R.Fern. - Madagascar
- Karomia speciosa(Hutch. & Corbishley) R.Fern. - Mozambique, Swaziland, South Africa
- Karomia tettensis(Klotzsch) R.Fern. - Mozambique, Malawi, Zimbabwe, Zambia

Tetradenia is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae, first described in 1830. It is native to Africa, including Madagascar.
- Tetradenia bainesii(N.E.Br.) Phillipson & C.F.Steyn - Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland, KwaZulu-Natal
- Tetradenia barberae(N.E.Br.) Codd - Cape Province
- Tetradenia brevispicata(N.E.Br.) Codd - Zimbabwe, Namibia, Botswana, Transvaal
- Tetradenia clementianaPhillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia cordataPhillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia discolorPhillipson - Zambia, Zaire, Zimbabwe, Malawi, Tanzania
- Tetradenia falafaPhillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia fruticosaBenth. - Madagascar
- Tetradenia galpinii(N.E.Br.) Phillipson & C.F.Steyn - southeast Africa from Tanzania to Swaziland
- Tetradenia goudotiiBriq. - Madagascar
- Tetradenia herbacea Phillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia hildeanaPhillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia isaloensisPhillipson - Madagascar
- Tetradenia kaokoensisvan Jaarsv. & A.E.van Wyk - Namibia
- Tetradenia multiflora(Benth.) Phillipson - Ethiopia
- Tetradenia nervosaCodd - Madagascar
- Tetradenia riparia(Hochst.) Codd - southern Africa from Angola + Malawi to Swaziland
- Tetradenia tanganyikaePhillipson - Malawi, Tanzania, Zambia
- Tetradenia tuberosaT.J.Edwards - KwaZulu-Natal
- Tetradenia urticifolia(Baker) Phillipson - eastern + central Africa from Sudan + Eritrea south to Zaire and Tanzania
Aspidoglossum is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1838. It is native to Africa.
Merxmuellera is a genus of African plants in the grass family. It takes its name from Hermann Merxmueller, a German botanist and taxonomist from the 20th century with a special authority in the African flora.
The Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.














