
Lomandra, commonly known as mat rushes, is a genus of perennial, herbaceous monocots in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Lomandroideae. The genus was first described in 1805 by Jacques Labillardière.

Blandfordia punicea, commonly known as Tasmanian Christmas bell, is a species of flowering plant that is endemic to western Tasmania. It is a tufted perennial herb with linear leaves and drooping red, bell-shaped flowers that are yellow on the inside.

Utricularia dichotoma, commonly known as fairy aprons, is a variable, perennial species of terrestrial bladderwort. It is a widespread species with mauve or purple fan-shaped flowers on a slender stalk and usually grows in wet locations.

Spyridium globulosum, commonly known as basket bush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rhamnaceae and is endemic to coastal areas in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a shrub with relatively large leaves and heads of flowers covered with whitish hairs.

Gahnia trifida, the coastal saw-sedge, is a tussock-forming perennial in the family Cyperaceae, endemic to southern Australia.
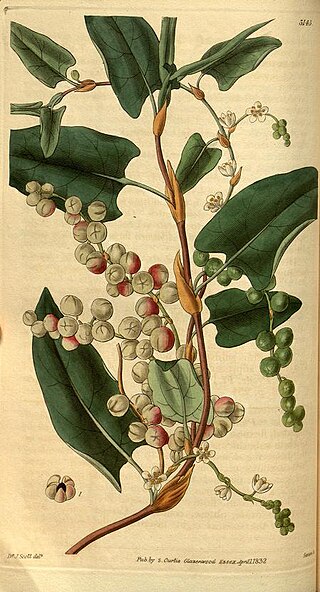
Muehlenbeckia adpressa, commonly known as climbing lignum, is a prostrate or climbing plant, native to Australia. It has thin red-brown stems up to 1 metre in length. The leaves are 1.5–6 centimetres (0.59–2.36 in) long and 1.5–3.5 centimetres (0.59–1.38 in) wide. It occurs in coastal areas of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales.

Cryptostylis subulata, commonly known as the large tongue orchid, duckbill orchid or cow orchid, is a common and widespread orchid in south eastern Australia and New Zealand. It has relatively large, leathery, dark green to yellowish-green leaves and up to twenty yellowish flowers with a reddish-brown and dark purple labellum. It is often found in damp or swampy situations but also occurs in drier places.

Stackhousia monogyna, commonly known as creamy stackhousia or creamy candles, is a flowering plant in the family Celastraceae. It is a small multi-stemmed plant with narrow leaves and terminal spikes of white, cream or yellow flowers. It is a widespread species found in all states of Australia but not the Northern Territory.

Pimelea ferruginea, commonly known as pink rice flower or coastal banjine, is a species of flowering plant in the family Thymelaeaceae and is endemic to near-coastal areas of south-western Western Australia. It is a dense, erect shrub with elliptic to narrowly elliptic leaves and head-like clusters of pale to deep pink, tube-shaped flowers.

Platysace lanceolata, commonly known as shrubby platysace, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is small, upright shrub with variable shaped leaves and white flowers.

Patersonia fragilis, commonly known as swamp iris or short purple-flag, is a species of flowering plant in the family Iridaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a tufted perennial herb with linear, cylindrical leaves and pale violet to blue-violet flowers.

Pimelea drupacea, commonly known as cherry rice-flower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Thymelaeaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is a shrub with elliptic leaves arranged in opposite pairs, and head-like clusters of white, tube-shaped flowers surrounded by two or four leaves.

Pimelea nivea is a species of flowering plant in the family Thymelaeaceae and is endemic to Tasmania. It is an erect shrub with densely hairy young stems, elliptic to round leaves arranged in opposite pairs, and compact clusters of white or cream-coloured flowers.

Hakea ruscifolia, commonly known as the candle hakea, is a shrub in the family Proteaceae. It has fragrant white flowers, arching branches and spiky foliage. It is endemic to an area in the Peel, Wheatbelt South West, Great Southern and the Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia.

Billardiera fusiformis, commonly known as Australian bluebell, is a species of flowering plant in the family Pittosporaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a sturdy, shrubby climber that has linear to narrowly elliptic leaves and blue, white or pink, nodding flowers arranged singly or in groups of up to four.

Boronia tetrandra, commonly known as yellow boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to Western Australia. It is a spreading or erect shrub with hairy stems, pinnate leaves and greenish cream to yellow or reddish brown, cup-shaped, four-petalled flowers.

Goodenia elongata, commonly known as lanky goodenia, is a species of flowering plant in the family Goodeniaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is an erect or ascending herb with lance-shaped stem leaves, and yellow flowers arranged singly or in racemes.
Pimelea clavata is a species of flowering plant in the family Thymelaeaceae and is endemic to near-coastal areas and offshore islands of southern Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with narrowly elliptic to more or less linear leaves arranged in opposite pairs, and head-like clusters of white to pale yellow, tube-shaped flowers surrounded by leaf-like involucral bracts.

Xanthosia candida is a low-lying, perennial herb in the family Apiaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has long, slender stems, irregularly toothed or lobed leaves and small white, green or creamy-yellow flowers.

Goodenia trinervis is a species of flowering plant in the family Goodeniaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a perennial herb with linear to spoon-shaped leaves at the base of the plant, yellow flowers on an ascending flower stem, and oval fruit.




















