
The walrus is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only extant species in the family Odobenidae and genus Odobenus. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus, which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus, which lives in the Pacific Ocean.

Pinnipeds, commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae, Otariidae, and Phocidae. There are 34 extant species of pinnipeds, and more than 50 extinct species have been described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic lineage. Pinnipeds belong to the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are musteloids, having diverged about 50 million years ago.

A flipper is a broad, flattened limb adapted for aquatic locomotion. It refers to the fully webbed, swimming appendages of aquatic vertebrates that are not fish.

Scrimshaw is scrollwork, engravings, and carvings done in bone or ivory. Typically it refers to the artwork created by whalers, engraved on the byproducts of whales, such as bones or cartilage. It is most commonly made out of the bones and teeth of sperm whales, the baleen of other whales, and the tusks of walruses.

Abrictosaurus is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic in what is now in parts of southern Africa such as Lesotho and South Africa. It was a bipedal herbivore or omnivore and was one of the most basal heterodontosaurids. It was approximately 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) long and weighed between 0.68 and 3 kilograms.

Appalachiosaurus is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of eastern North America. Like almost all theropods, it was a bipedal predator. Only a juvenile skeleton has been found, representing an animal approximately 6.5 metres (21 ft) long and weighing 623 kilograms (1,373 lb), which indicates an adult would have been even larger. It is the most completely known theropod from the eastern part of North America.

Enaliarctos is an extinct genus of pinnipedimorph, and may represent the ancestor to all pinnipeds. Prior to the discovery of Puijila, the five species in the genus Enaliarctos represented the oldest known pinnipedimorph fossils, having been recovered from late Oligocene and early Miocene strata of California and Oregon.

Odobenocetops is an extinct genus of small toothed whale known from Peru and Chile. Its fossils are found in Neogene-aged marine strata dating from the Tortonian to the Zanclean. It had two tusks, and, in some fossils, one tusk was longer than the other.

Gomphotaria is a genus of very large shellfish-eating dusignathine walrus found along the coast of what is now California, during the late Miocene.

Ontocetus is an extinct genus of walrus, an aquatic carnivoran of the family Odobenidae, endemic to coastal regions of the southern North Sea and the southeastern coastal regions of the U.S. during the Miocene-Pleistocene. It lived from 13.6 mya—300,000 years ago, existing for approximately 13.3 million years.

Wintonotitan is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur from late Albian -age Winton Formation of Australia. It is known from partial postcranial remains.
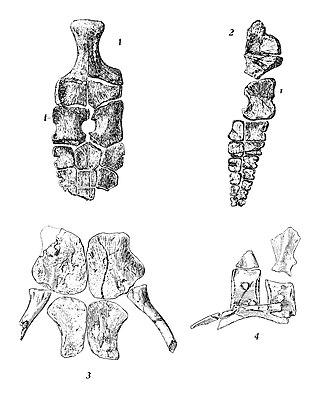
Toretocnemus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur. Its remains have been found in California, United States, in Triassic layers of the Carnian Hosselkus Limestone.

Broken Walrus I, a public sculpture by American sculptor Gary Freeman, was installed on the Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis campus, near downtown Indianapolis, Indiana, in 1975. Located north of the IUPUI Lecture Hall, the sculpture was removed around 2004 after it rusted. The work was fabricated in mild steel, painted an orange-red matte finish, and measured 36-inch (91 cm) tall by 8-foot (2.4 m) long by 24-inch (61 cm) wide.

Mesopropithecus is an extinct genus of small to medium-sized lemur, or strepsirrhine primate, from Madagascar that includes three species, M. dolichobrachion, M. globiceps, and M. pithecoides. Together with Palaeopropithecus, Archaeoindris, and Babakotia, it is part of the sloth lemur family (Palaeopropithecidae). Once thought to be an indriid because its skull is similar to that of living sifakas, a recently discovered postcranial skeleton shows Mesopropithecus had longer forelimbs than hindlimbs—a distinctive trait shared by sloth lemurs but not by indriids. However, as it had the shortest forelimbs of all sloth lemurs, it is thought that Mesopropithecus was more quadrupedal and did not use suspension as much as the other sloth lemurs.
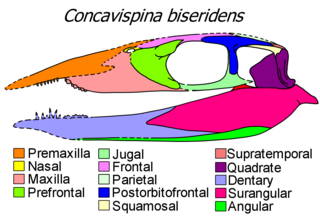
Concavispina is an extinct genus of thalattosaur reptile from the early Late Triassic Xiaowa Formation of Guangling, Guizhou, southern China. It contains a single species, Concavispina biseridens. It is known only from the holotype ZMNH M8804, a nearly complete 364 cm long skeleton. Concavispina can be differentiated from other thalattosaurs by possessing two rows of blunt teeth on the anterior part of the maxilla and a V-shaped notch on the dorsal margin of each neural spine in the dorsal (back) vertebrae. Both its generic and specific names refer to these autapomorphies, as Concavispina means "concave spine" and biseridens means "two rows of teeth". It is thought to be most closely related to Xinpusaurus, as both taxa share three derived characters: a maxilla that is curved upward at its anterior end, a humerus that is wider near the shoulder than near the elbow, and the presence of less than five cervicals.
Aenigmaspina is an extinct genus of enigmatic pseudosuchian (=crurotarsan) archosaur from the Late Triassic of the United Kingdom. Its fossils are known from the Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in South Wales, of which its type and only known species is named after, A. pantyffynnonensis. Aenigmaspina is characterised by the unusual spines on its vertebrae, which are broad and flat on top with a unique 'Y' shape. Although parts of its skeleton is relatively well known, the affinities of Aenigmaspina to other pseudosuchians are unclear, although it is possibly related to families Ornithosuchidae, Erpetosuchidae or Gracilisuchidae.
Osodobenus is an extinct genus of walrus from the Miocene to Pliocene of California. Osodobenus may have been the first tusked walrus and shows several adaptations that suggest it was a suction feeder, possibly even a benthic feeder like modern species. Three skulls are known showing pronounced sexual dimorphism, with the female lacking the same tusks as the male. Only a single species, Osodobenus eodon, is currently recognized.

Titanotaria is a genus of late, basal walrus from the Miocene of Orange County, California. Unlike much later odobenids, it lacked tusks. Titanotaria is known from an almost complete specimen which serves as the holotype for the only recognized species, Titanotaria orangensis, it is the best preserved fossil walrus currently known.




















